|
Sirsa Air Force Station
Sirsa Air Force Station or Sirsa AFS (ICAO: VISX) is an Indian Air Force base under Western Air Command, located at Sirsa in the state of Haryana, India. History 1971 Indo-Pak war In Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, Pakistan Air Force launched a pre-emptive raid on 12 airforce stations,Om Prakash Maurya, 2017Babu Jagjivan Ram including Sirsa station, Faridkot Stations, Halwara Air Force Station, a few railway stations, Indian armour concentrations and other targets. However, this failed to cause any significant damage except pothole damage to the runway which was quickly repaired.A.S. Ahluwalia, 2012, Airborne to Chairborne: Memoirs of a War Veteran Aviator-Lawyer of the India Air Force Dassault Mystère IV jets from Sirsa base pounded the Pakistan Army pitched against the Indian Army in the Battle of Sabuna Drain. Dassault Mystère also hit a train and destroyed 50 tanks on it between Okara and Sahiwal. Units It has No. 21 Squadron IAF of 45 Wing. Wing is an active air force c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundel Of India
A roundel is a circular disc used as a symbol. The term is used in heraldry, but also commonly used to refer to a type of national insignia used on military aircraft, generally circular in shape and usually comprising concentric rings of different colours. Other symbols also often use round shapes. Heraldry In heraldry, a ''roundel'' is a circular charge (heraldry), charge. ''Roundels'' are among the oldest charges used in coat of arms, coats of arms, dating from at least the twelfth century. Roundels in British heraldry have different names depending on their tincture (heraldry), tincture. Thus, while a roundel may be blazoned by its tincture, e.g., ''a roundel vert'' (literally "a roundel green"), it is more often described by a single word, in this case ''pomme'' (literally "apple", from the French) or, from the same origins, ''pomeis''—as in "Vert; on a cross Or five pomeis". One special example of a named roundel is the fountain (heraldry), fountain, depicted as ''a ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general. Two officers have been conferred with the rank of field marshal, a five-star rank, which is a ceremonial position of great honour. The Indian Army was formed in 1895 alongside the long established presidency armies of the East India Company, which too were absorbed into it in 1903. The princely states had their own armies, which were merged into the national army after independence. The units and regiments of the Indian Army have diverse histories and have participated in several battles and campaigns around the world, earning many battle and theatre honours before and after Independence. The primary mission of the Indian Army is to ensure national security and national unity, to defend the nation from external aggression an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Armed Forces Hospitals In India ...
As of 2020, there are 112 Military Hospitals, 12 Air Force Hospitals and 10 Naval Hospitals in India. Indian Air Force Indian Army Indian Navy See also * Command Hospital *Army Medical Corps (India) *List of Indian Navy bases *List of Indian Air Force stations References {{reflist Hospitals Hospitals Hospitals Armed Forces Hospitals A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hisar Military Station
Hisar Military Station, established in 15 November 1982 at Hisar in Haryana state of India, is the base headquarters of the ''33rd Armoured Division'' of Mathura-headquartered ''I Corps'' strike battle formation of Jaipur-headquartered '' South Western Command'' of Indian Army. History It was raised on 15 November 1982 by Major General L. B. Sondhi. It was converted into a fully Armoured Division in December 1993. Facilities Married Accommodation Hisar Military station has 2366 married Dwelling Units (DU) of 152,200.000 Sqm carpet area for Officers, JCO’s & other ranks. Construction started in 2006 and work was completed in four packages (Pkg-II, III, IV & V) in April, 2009 at the cost o Rs. 250 crores at 2009 price. The scope of work comprises building work of RCC Frame structure construction (G+2 Storied), underground/overhead RCC reservoirs, Internal & External electrification, Internal & External Water supply, Road/Path/Culvers, Plumbing work, Sewage works etc. Whol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurugram Air Force Station
Gurugram Air Force Station, of the Indian Air Force's Western Air Command, is located at sector-33 of Gurugram city in Haryana state of India. It is located 28 km south of New Delhi.S Sridhara, 2016, Vertebrate Pests In Agriculture, Page 340 History On 8 October 1932, the Indian Air Force was established in British India as an auxiliary air force of Royal Air Force, and adopted the Royal Air Force uniforms, badges, brevets and insignia. In 1948, first airstrip was built in Haryana when Ambala Air Force Station was established following the independence of India. After the independence of India in 1947, an air force logistics base was established at Faridabad. The Western Air Command, of which Gurugram Air Force Logistics Station is a key component within the National Capital Region, has been the major operational command involved in most of the war fought by India, including the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947, Sino-Indian War in 1962, the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, Indo-Paki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambala Air Force Station
Ambala () is a city and a municipal corporation in Ambala district in the state of Haryana, India, located on the border with the Indian state of Punjab and in proximity to both states capital Chandigarh. Politically, Ambala has two sub-areas: Ambala Cantonment (also known as Ambala Cantt) and Ambala City, eight kilometres apart, therefore it is also known as "Twin City". It has a large Indian Army and Indian Air Force presence within its cantonment area. It is located 200 km (124 mi) to the north of New Delhi, India's capital, and has been identified as a counter-magnet city for the National Capital Region to develop as an alternative center of growth to Delhi. Ambala separates the Ganges river network from the Indus river network and is surrounded by two rivers – Ghaggar and Tangri – to the north and to the south. Due to its geographical location, the Ambala district plays an important role in local tourism, being located south of Chandigarh, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airports Authority Of India
The Airports Authority of India, or AAI, is a public sector enterprise under the ownership of the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India. It is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining, and managing civil aviation infrastructure in India. It provides Communication Navigation Surveillance/Air Traffic Management (CNS/ATM) services over Indian airspace and adjoining oceanic areas. AAI is currently managing a total of 137 airports, including 34 international airports, 10 Customs Airports, 81 domestic airports, and 23 Civil enclaves at defense airfields. AAI also has ground installations at all airports and 25 other locations to ensure the safety of aircraft operations. AAI covers all major air routes over Indian landmass via 29 Radar installations at 11 locations along with 700 VOR/DVOR installations co-located with Distance Measuring Equipment (DME). 52 runways are provided with Instrument landing system (ILS) installations with Night Landing Facilities at most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bharat Rakshak
Bharat Rakshak ("Defenders of India") is a website devoted to discussing the Military of India. It was started and is run by military enthusiasts. History Bharat Rakshak was started in April 1997 by bringing together the individual websites of Indian Defence enthusiasts. The website was officially launched on 1 July 1997 by Seetal Patel and Rupak Chattopadhyay. While the concept of Open Source intelligence, as defined by the United States intelligence community, is still evolving in India, Bharat Rakshak has been cited as a website that could be held in the same category as its western counterparts. The forum has many members with experience in Indian Armed Forces and defence technology firms. The site gained some notoriety in December 2007, when it was cited for leaking the Official War Histories written by the Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD) that had remained classified for sometime. Features *An active discussion forum, which has been referred to in the press as a think-tank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
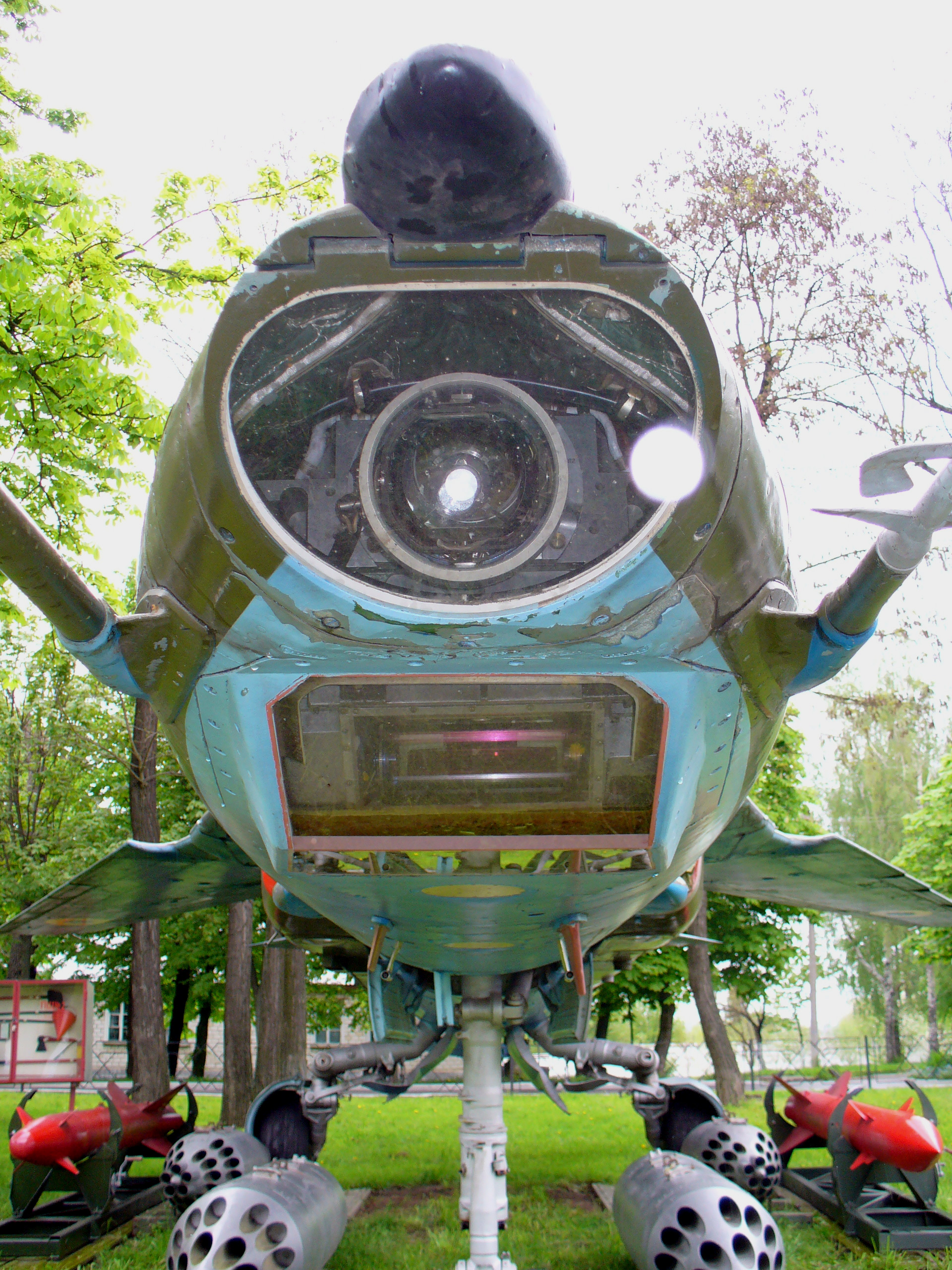
MiG-27
The Mikoyan MiG-27 (russian: Микоян МиГ-27; NATO reporting name: Flogger-D/J) is a variable-sweep ground-attack aircraft, originally built by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau in the Soviet Union and later licence-produced in India by Hindustan Aeronautics as the ''Bahadur'' ("Valiant"). It is based on the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 fighter aircraft, but optimised for air-to-ground attack. Unlike the MiG-23, the MiG-27 did not have widespread use outside Russia, as most countries opted for the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23BN and Sukhoi Su-22 instead. It remains in service only with the Kazakh Air Forces in the ground attack role. All Russian, Indian, Sri Lankan and Ukrainian MiG-27s have been retired. Design and development The MiG-27 shares the basic airframe of the MiG-23, but with a revised nose – nicknamed "''Utkonos''" ("Platypus") or "'' Krokodil Gena''" in Russian service, first introduced on the MiG-23B. Dissatisfaction with the MiG-23BN led to the further deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
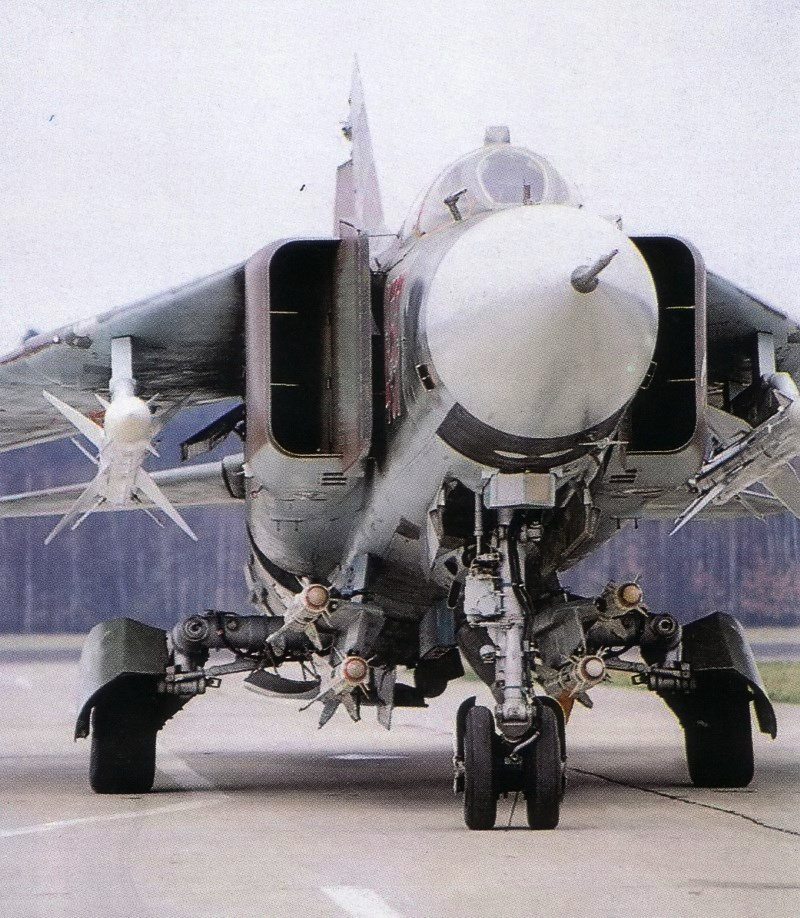
MiG-23
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-23; NATO reporting name: Flogger) is a variable-geometry fighter aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau in the Soviet Union. It is a third-generation jet fighter, alongside similar Soviet aircraft such as the Su-17 "Fitter". It was the first Soviet fighter to field a look-down/shoot-down radar, the RP-23 Sapfir, and one of the first to be armed with beyond-visual-range missiles. Production started in 1969 and reached large numbers with over 5,000 aircraft built, making it the most produced variable-sweep wing aircraft in history. Today the MiG-23 remains in limited service with some export customers. The basic design was also used as the basis for the Mikoyan MiG-27, a dedicated ground-attack variant. Among many minor changes, the MiG-27 replaced the MiG-23's nose-mounted radar system with an optical panel holding a laser designator and a TV camera. Development The MiG-23's predece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Su-30MKI
The Sukhoi Su-30MKI (NATO reporting name: Flanker-H) is a twinjet multirole air superiority fighter developed by Russia's Sukhoi and built under licence by India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF). A variant of the Sukhoi Su-30, it is a heavy, all-weather, long-range fighter. Development of the variant started after India signed a deal with Russia in 2000 to manufacture 140 Su-30 fighter jets. The first Russian-made Su-30MKI variant was accepted into the Indian Air Force in 2002, while the first Su-30MKI assembled in India entered service with the IAF in 2004. The IAF has nearly 260 Su-30MKIs in inventory as of January 2020. The Su-30MKI is expected to form the backbone of the Indian Air Force's fighter fleet to 2020 and beyond.Pandit, Rajat"Russia conducts first test of fifth generation Sukhoi." ''The Times of India'', 30 January 2010. The aircraft is tailor-made for Indian specifications and integrates Indian systems and avionics as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
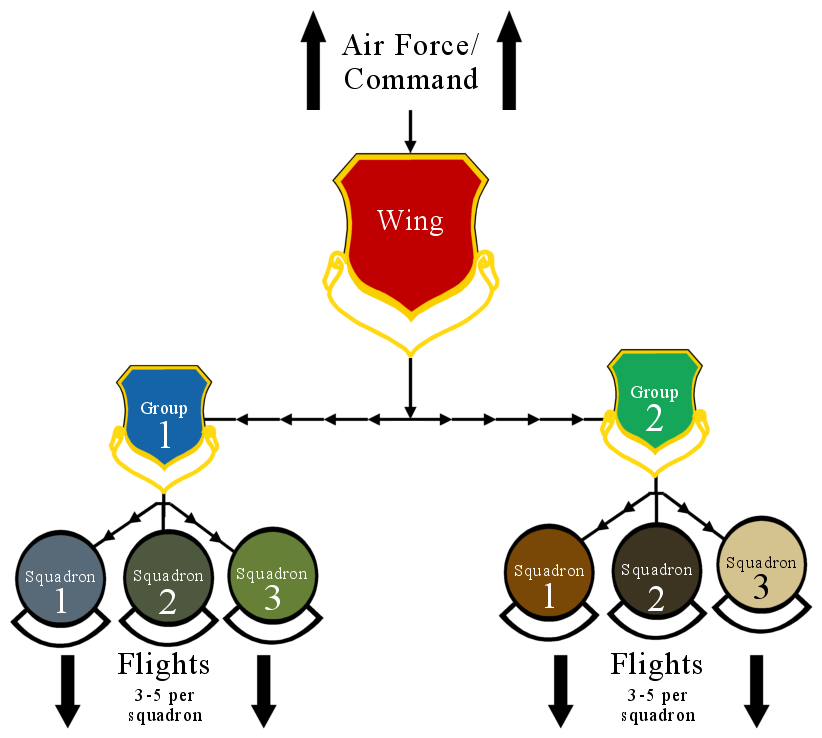
Wing (military Aviation Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squadro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |