|
Sinulog Festival
The Sinulog Festival (also known as Sinug and Sulog) is an annual Filipino cultural and religious festival held on the third Sunday of January in Cebu, with the center of the activities being in Cebu City; and is the core of Santo Niño Christian celebrations in the country. The festival is widely regarded as one of the largest cultural and religious celebrations in the Philippines, with the 2025 event attracting over four million attendees. Aside from the religious aspect of the festival, Sinulog is also famous for its street parties, usually happening the night before and on the night of the main festival. The event is sometimes referred to as the "Grandest Festival in the Philippines" by participants and locals. Other places in the Philippines also celebrate their own version of the festival in honor of the Santo Niño, both within the province of Cebu, such as Carmen, and outside, including Tondo, Kabankalan, General Santos, Maasin, Cagayan de Oro, Butuan, Pagadian, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebu City
Cebu City, officially the City of Cebu, is a Cities of the Philippines#Legal classification, highly urbanized city in the Central Visayas region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 964,169 people, making it the sixth-most populated city in the nation and the most populous in the Visayas and the Central Visayas Region. It serves as the capital of Cebu wherein it is geographically situated and grouped under the province by the Philippine Statistics Authority, but is one of three cities (together with Lapu-Lapu City, Lapu-Lapu and Mandaue) that are administratively independent of the provincial government and also the largest city within that province. It also serves as the regional center of Central Visayas, and its Metro Cebu, metropolitan area exerts influence on commerce, trade, industry, education, culture, tourism, and healthcare beyond the region, over Central and Eastern Visayas and partly over Mindanao. It is the Philippines' main do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butuan
Butuan (pronounced ), officially the City of Butuan (; Butuanon: ''Dakbayan hong Butuan''; ), is a highly urbanized city and the regional center of Caraga, Philippines. It is the '' de facto'' capital of the province of Agusan del Norte where it is geographically situated but has an administratively independent government. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 372,910 people making it the most populous city in Caraga Region. It served as the former capital of the Rajahnate of Butuan before 1001 until about 1521. The city used to be known during that time as the best in gold and boat manufacturing in the entire Philippine archipelago, having traded with places as far as Champa, Ming, Srivijaya, Majapahit, and the Bengali coasts. It is located at the northeastern part of the Agusan Valley, Mindanao, sprawling across the Agusan River. It is bounded to the north, west and south by Agusan del Norte, to the east by Agusan del Sur and to the northwest by Butu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajah Humabon
Rajah Humabon (also ''Hamabao'' or ''Hamabar'' in other editions of the " First Voyage Around the World") later baptized as Don Carlos Valderrama, was one of the recorded chiefs in historic polity of Cebu who encountered Ferdinand Magellan in the 16th century. Humabon ruled at the time of the arrival of Portuguese-born Spanish explorer Ferdinand Magellan in the Philippines in 1521. Humabon, his wife, and his subjects were the first known Christian converts in the Philippines. However, since there were no Catholic priests in Cebu from 1521 to 1565, this Christianity was not practised until the return of the Spaniards to Cebu. There is no official record of Humabon's existence before the Spanish contact. The existing information was written by Magellan's Italian voyage chronicler, Antonio Pigafetta on Humabon and the indigenous Philippine peoples that existed prior to Spanish colonization. Rajah Humabon is cited as the reason for why Magellan fought in the Battle of Mactan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskritisation
Sanskritisation (or Sanskritization) is a term in sociology which refers to the process by which castes or tribes placed lower in the caste hierarchy seek upward mobility by emulating the rituals and practices of the dominant castes or upper castes. It is a process similar to "passing" in sociological terms. This term was made popular by Indian sociologist M. N. Srinivas in the 1950s. Sanskritisation has in particular been observed among mid-ranked members of caste-based social hierarchies. In a broader sense, also called Brahmanisation, it is a historical process in which local Indian religious traditions become syncretised, or aligned to and absorbed within the Brahmanical religion, resulting in the pan-Indian religion of Hinduism. Definition Srinivas defined ''Sanskritisation'' as a process by which In a broader sense, Sanskritisation is In this process, local traditions (little traditions) become integrated into the great tradition of Brahmanical religion, disse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater India
Greater India, also known as the Indian cultural sphere, or the Indic world, is an area composed of several countries and regions in South Asia, East Asia and Southeast Asia that were historically influenced by Indian culture, which itself formed from the various distinct indigenous cultures of South Asia. It is an umbrella term encompassing the Indian subcontinent and surrounding countries, which are culturally linked through a diverse cultural cline. These countries have been transformed to varying degrees by the acceptance and introduction of cultural and institutional elements from each other. The term Greater India as a reference to the Indian cultural sphere was popularised by a network of Bengali scholars in the 1920s, but became obsolete in the 1970s. Since around 500 BCE, Asia's expanding land and maritime trade had resulted in prolonged socio-economic and cultural stimulation and diffusion of Buddhist and Hindu beliefs into the region's cosmology, in particular in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Colonial Era In The Philippines
Spanish might refer to: * Items from or related to Spain: **Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain **Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas **Spanish cuisine ** Spanish history **Spanish culture **Languages of Spain, the various languages in Spain Other places * Spanish, Ontario, Canada * Spanish River (other), the name of several rivers * Spanish Town, Jamaica Other uses * John J. Spanish (1922–2019), American politician * "Spanish" (song), a single by Craig David, 2003 See also * * * Español (other) * Spain (other) * España (other) * Espanola (other) * Hispania, the Roman and Greek name for the Iberian Peninsula * Hispanic, the people, nations, and cultures that have a historical link to Spain * Hispanic (other) * Hispanism * Spain (other) * National and regional identity in Spain * Culture of Spain The culture of Spain is influenced by its Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel López De Legazpi
Miguel López de Legazpi (12 June 1502 – 20 August 1572), also known as ''Adelantado, El Adelantado'' and ''El Viejo'' (The Elder), was a Spanish conquistador who financed and led an expedition to conquer the Philippines, Philippine islands in the mid-16th century. He was joined by Guido de Lavezares, relative Martin de Goiti, friar Andrés de Urdaneta, and his grandsons Juan de Salcedo, Juan and Felipe de Salcedo, in the expedition. Legazpi established the first Spanish settlement in the East Indies after his expedition crossed the Pacific Ocean, arriving in Cebu in 1565. He became the first Governor-General of the Philippines, governor-general of the Spanish East Indies, which was administered from New Spain for the Spanish Empire, Spanish crown. It also encompassed other Pacific islands, namely Guam, the Mariana Islands, Palau, and the Caroline Islands, Carolinas. After obtaining peace with various indigenous tribes and kingdoms, he made Cebu City the capital of the Span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
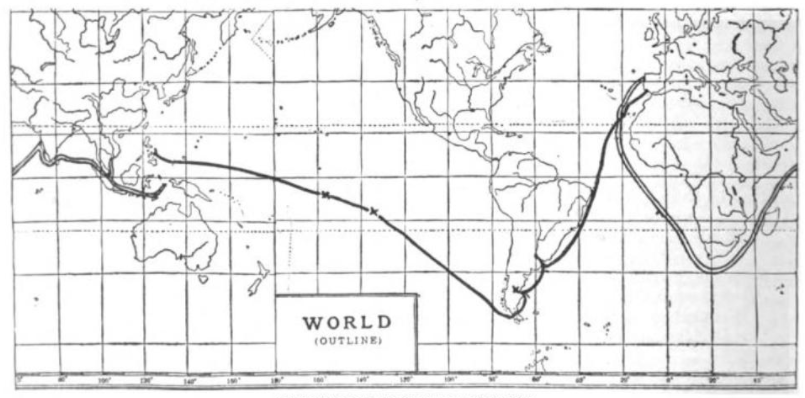
Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies. During this expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fleet to pass from the Atlantic into the Pacific Ocean and perform the first European navigation to Asia via the Pacific. Magellan was killed in battle in the Philippines and his crew, commanded by the Spanish Juan Sebastián Elcano, completed the return trip to Spain in 1522 achieving the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. Born around 1480 into a family of minor Portuguese nobility, Magellan became a skilled sailor and naval officer in service of the Portuguese Crown in Asia. King Manuel I refused to support Magellan's plan to reach the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, by sailing westwards around the American continent. Magellan then proposed the same plan to King Charles I of Spain, who approved it. In Seville, he married, fathere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animism
Animism (from meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and in some cases words—as being animated, having agency and free will. Animism is used in anthropology of religion as a term for the belief system of many Indigenous peoples in contrast to the relatively more recent development of organized religions. Animism is a metaphysical belief which focuses on the supernatural universe: specifically, on the concept of the immaterial soul. Although each culture has its own mythologies and rituals, animism is said to describe the most common, foundational thread of indigenous peoples' "spiritual" or "supernatural" perspectives. The animistic perspective is so widely held and inherent to most indigenous peoples that they often do not even have a word in their languages that corresponds to "animism" (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Jesus
The Christ Child—also known as Baby Jesus, Infant Jesus, Child Jesus, Divine Child, Divine Infant and the Holy Child—refers to Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ during his early years. The term refers to a period of life of Jesus, Jesus' life, described in the canonical Gospels, encompassing his nativity of Jesus, nativity in Bethlehem, the visit of the Magi, and his Presentation of Jesus, presentation at the Temple in Jerusalem. It also includes his childhood, culminating in the event where his parents Finding in the Temple, find him in the Temple at age 12, after which the Gospels Unknown years of Jesus, remain silent about his life until the start of his ministry of Jesus, ministry. Liturgical feasts Liturgical feasts relating to Christ's infancy and childhood include: * Christmas, The Feast of the Nativity of Jesus Christ (25 December) * The Feast of the Circumcision of Christ#Byzantine Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches, Feast of the Circumcision of Christ (1 Janu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents (upwelling and downwelling) playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean. Ocean currents flow for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth's regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebuano Language
Cebuano ( )Cebuano on Merriam-Webster.com is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken in the southern Philippines by Cebuano people and other Ethnic groups in the Philippines, ethnic groups as a secondary language. It is natively, though informally, called by the generic name Bisayâ (), or Binisayâ () (both terms are translated into English as ''Visayan'', though this should not be confused with other Bisayan languages) and sometimes referred to in English sources as Cebuan ( ). It is spoken by the Visayans, Visayan ethnolinguistic groups native to the islands of Cebu, Bohol, Siquijor, the eastern half of Negros Island, Negros, the western half of Leyte, the northern coastal areas of Northern Mindanao and the eastern part of Zamboanga del Norte due to Captaincy General of the Philippines, Spanish settlements during the 18th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |