|
Sindhuli Fort 02
Sindhuli District ( ne, सिन्धुली जिल्ला), a part of the Bagmati Province, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal, a landlocked country of South Asia. The district, with Sindhulimadhi Kamalamai as its district headquarters and covers an area of . In 2001, it had a population of 279,821, in 2011 the population was 296,192.Household and population by districts, Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) Nepal 
Etymology i) Before being annexed as an integral part of Nepal, it was under the governance ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Nepal
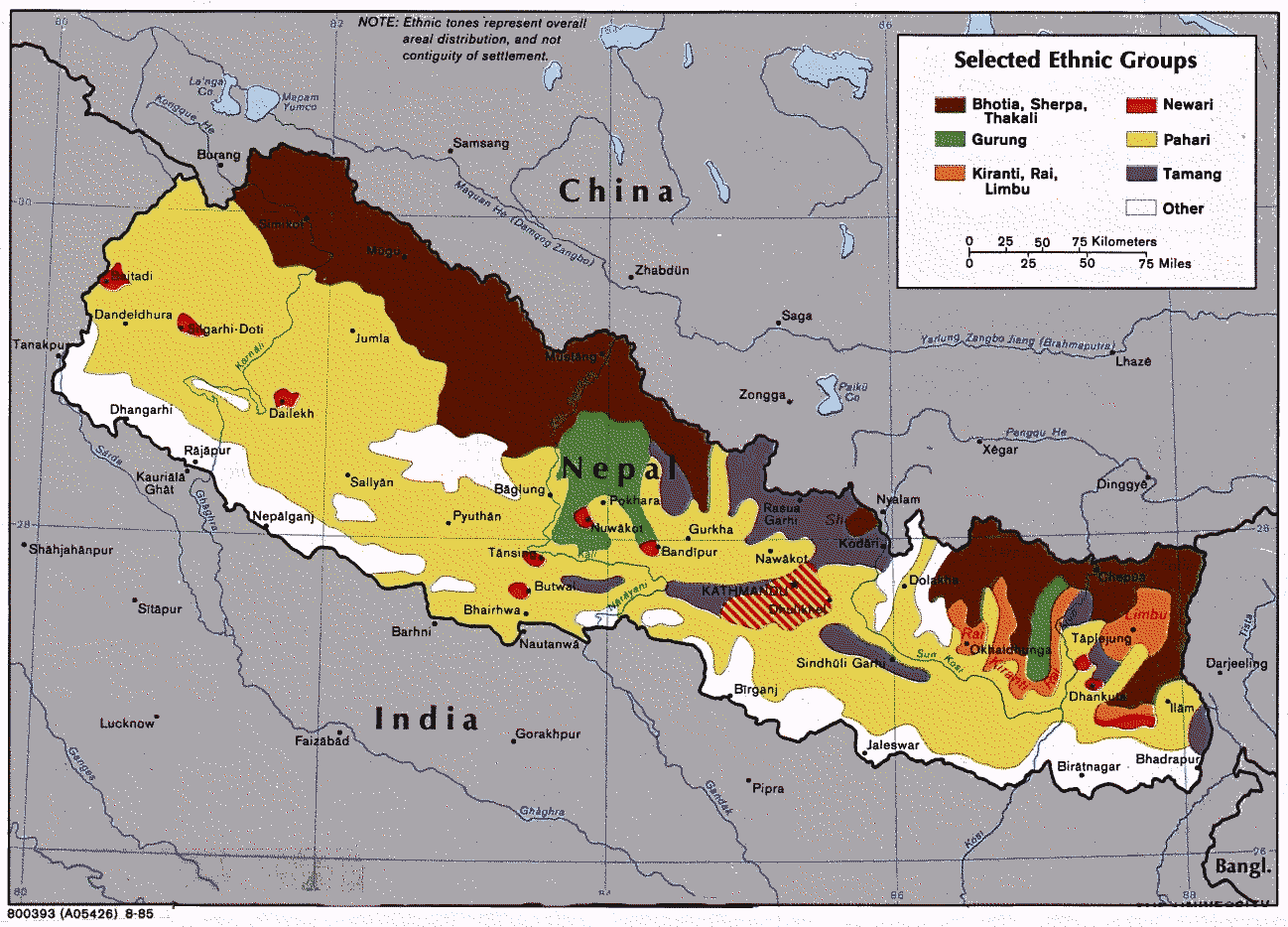
Districts in Nepal are second level of administrative divisions after provinces. Districts are subdivided in municipalities and rural municipalities. There are seven provinces and 77 districts in Nepal. After the state's reconstruction of administrative divisions, Nawalparasi District and Rukum District were divided into Parasi District (officially Nawalparasi (West of Bardaghat Susta) District) and Nawalpur District (officially Nawalparasi (East of Bardaghat Susta) District), and Eastern Rukum District and Western Rukum District respectively. District official include: * Chief District Officer, an official under Ministry of Home Affairs is appointed by the government as the highest administrative officer in a district. The C.D.O is responsible for proper inspection of all the departments in a district such as health, education, security and all other government offices. * District Coordination Committee acts as an executive to the District Assembly. The DCC coordinates with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Language
A person's second language, or L2, is a language that is not the native language (first language or L1) of the speaker, but is learned later. A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a foreign language. A speaker's dominant language, which is the language a speaker uses most or is most comfortable with, is not necessarily the speaker's first language. For example, the Canadian census defines first language for its purposes as "the first language learned in childhood and still spoken", recognizing that for some, the earliest language may be lost, a process known as language attrition. This can happen when young children start school or move to a new language environment. Second-language acquisition The distinction between acquiring and learning was made by Stephen Krashen (1982) as part of his Monitor Theory. According to Krashen, the ''acquisition'' of a language is a natural process; whereas ''learning'' a language is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantawa Language
The Bantawa Language (also referred to as An Yüng, Bantaba, Bantawa Dum, Bantawa Yong, Bantawa Yüng, Bontawa, Kirawa Yüng), is a Kirati languages spoken in the eastern Himalayan hills of eastern Nepal by Kirati Bantawa ethnic groups. They use a syllabic alphabet system known as Kirat Rai script . Among the Khambu or Rai people of Eastern Nepal, Sikkim, Darjeeling and Kalimpong in India. Bantawa is the largest language spoken. According to the 2001 National Census, at least 1.63% of the Nepal's total population speaks Bantawa. About 370,000 speak Bantawa Language mostly in eastern hilly regions of Nepal (2001). Although Bantawa is among the more widely used variety of the Bantawa language, it falls in the below-100,000 category of endangered languages. It is experiencing language shift to Nepali, especially in the northern region. Bantawa is spoken in subject-object-verb order, and has no noun classes or genders. Dialects Most of the Bantawa clan are now settled in Bhojpu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunwar Language
Sunuwar, Sunuwar, or Kõinch (; ; other spellings are Koinch and Koincha), is a Kiranti language spoken in Nepal and India by the Sunuwar people. It was first comprehensively attested by the Himalayan Languages Project. It is also known as Kõits Lo ( ; ), Kiranti-Kõits ( ; ), Mukhiya ( ; ). The Sunwar language is one of the smaller members of the Tibeto-Burman language family. About 40,000 speakers are residing in eastern Nepal. Names The language is commonly known as ''Koic,'' for many ethnic Sunwar and Sunwar speakers also refer to the language as “''Sunuwar, Kõinch'' '', Koinch'' or ''Koincha'' (कोँइच); ''Kõits Lo'' (कोँइच लो), ''Kiranti-Kõits'' (किराँती-कोँइच) or ''Mukhiya'' (मुखिया).” Moreover, most Sunwar speakers have the surname (सुनुवार), ''Sunuvār'' in Latin script. Many affiliated Sunwar with Sunar; they share the initial syllable, ''sun'', “gold,” in Nepali, similar to the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majhi Language
Majhi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in parts of Nepal and formerly in some small pockets of neighboring India.:1 The language is associated with the Majhi people, an ethnic group in those regions who dwell historically near the Saptakoshi River and its tributaries and elsewhere in central and eastern Nepal. The Majhi people generally subsist off of work associated with rivers, including fishing and ferrying.:2 Majhi is written using the Devanagari writing system. Ethnologue classifies Mahji as a 6b threatened language. There are roughly 24,400 L1 speakers of Majhi in Nepal and roughly 46,120 L1 and L2 speakers of the language around the globe. Most of the Majhi speakers in Nepal are bilingual with the more predominant Nepali language,:2 and the latter language is replacing Majhi in use. Majhi's lack of official status, use in education, in media, in print, etc. places the survival of the language in a precarious position.:2 The last speaker in India, Thak Bahadur Majhi of Jor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maithili Language
Maithili () is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in parts of Languages of India, India and Languages of Nepal, Nepal. It is native to the Mithila region, which encompasses parts of the Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand as well as Nepal's eastern Terai. It is one of the 22 Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, officially recognised languages of India and the second most spoken Languages of Nepal, Nepalese language in Nepal. The language is predominantly written in Devanagari, but there were two other historically important scripts: Tirhuta script, Tirhuta, which has retained some use until the present, and Kaithi script, Kaithi. Official status In 2003, Maithili was included in the 8th Schedule, Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution as a recognised language of India, Indian language, which allows it to be used in education, government, and other official contexts in India. Maithili language is included as an optional paper in the Union Public Service Commission, UP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar Language
Newar (), or Newari and known officially in Nepal as Nepal Bhasa, is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Newar people, the indigenous inhabitants of Nepal Mandala, which consists of the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding regions in Nepal. "Nepal Bhasa" literally means "Nepalese language", however the language is not the same as Nepali (Devanāgarī: नेपाली), the country's current official language of the central government. The two languages belong to different language families (Sino-Tibetan and Indo-European, respectively), but centuries of contact have resulted in a significant body of shared vocabulary. Newar was Nepal's administrative language from the 14th to the late 18th century. From the early 20th century until democratisation, Newar suffered from official suppression. From 1952 to 1991, the percentage of Newar speakers in the Kathmandu Valley dropped from 75% to 44% and today Newar culture and language are under threat. The language has been listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danwar Language
Danwar (also rendered ''Danuwar'', ''Denwar'', ''Dhanvar'', ''Dhanwar'') is a language spoken in parts of Nepal by an Indo-Aryan ethnic group of fifty thousand. It is close to Bote-Darai but otherwise unclassified within the Indo-Aryan languages. A variety called Danwar Rai, It is not related to the Rai RAI – Radiotelevisione italiana (; commercially styled as Rai since 2000; known until 1954 as Radio Audizioni Italiane) is the national public broadcasting company of Italy, owned by the Ministry of Economy and Finance. RAI operates many ter ... of the Tibeto-Burman family. References Languages of Nepal Indo-Aryan languages {{IndoAryan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magar Language
Magar Dhut ( ne, मगर ढुट, ) is a Sino-Tibetan Language spoken mainly in Nepal, Southern Bhutan, and in Darjeeling and Sikkim, India, by the Magar people. It is divided into two groups (Eastern and Western) and further dialect divisions give distinct tribal identity. In Nepal 788,530 people speak the language. While the government of Nepal developed Magar language curricula, as provisioned by the constitution, the teaching materials have never successfully reached Magar schools, where most school instruction is in the Nepali language. It is not unusual for groups with their own language to feel that the "mother-tongue" is an essential part of identity. The Dhut Magar language is sometimes lumped with the Magar Kham language spoken further west in Bheri, Dhaulagiri, and Rapti zones. Although the two languages share many common words, they have major structural differences and are not mutually intelligible. Geographical distribution Western Magar Western Magar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamang (Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāng'') is a term used to collectively refer to a dialect cluster spoken mainly in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% to 63%. For comparison, lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese, is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepali Language
Nepali (; , ) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Himalayas region of South Asia. It is the official, and most widely spoken, language of Nepal, where it also serves as a '' lingua franca''. Nepali has official status in the Indian state of Sikkim and in the Gorkhaland Territorial Administration of West Bengal. It is spoken by about a quarter of Bhutan's population. Nepali also has a significant number of speakers in the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Uttarakhand. In Myanmar it is spoken by the Burmese Gurkhas. The Nepali diaspora in the Middle East, Brunei, Australia and worldwide also use the language. Nepali is spoken by approximately 16 million native speakers and another 9 million as a second language. Nepali is commonly classified within the Eastern Pahari group of the Northern zone of Indo-Aryan. The language originated from the Sinja Valley, Karnali Province then the capital city of the Khasa K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |