|
Sin El Fil
Sin el-Fil ( ar, سنّ الفيل / ALA-LC: ''Sinn al-Fīl'') is a suburb east of Beirut in the Matn District of the Mount Lebanon Governorate, Lebanon. Overview Etymology The name literally means 'ivory': "tooth" (''sinn'') of "the elephant" (''al-fīl''). Being geographically closer to the ancient city of Antioch and far remote from natural elephant habitat, it is believed that the town name may have been a derogation of Saint Theophilus of Antioch. Geography With a rich red soil and moderate precipitation (but available ground water irrigation) the agricultural land of Sin el Fil in the early 20th century sprawled into a densely populated suburb. The natural landscape of the late century was dominated by stone pine. The Beirut River runs west of Sin el Fil and separates the town from the capital, Beirut. Demographics Archaeology Collections of archaeological material from this limestone "hogsback" were made from the gullies to the south of the main road on the slopes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governorates Of Lebanon
Lebanon is divided into nine governorates (''muhafazah''). Each governorate is headed by a governor (''muhafiz''): All of the governorates except for Beirut and Akkar are divided into districts, which are further subdivided into municipalities. The newest governorate is Keserwan-Jbeil, which was gazetted on 7 September 2017 but whose first governor, Pauline Deeb, was not appointed until 2020. Implementation of the next most recently created governorates, Akkar and Baalbek-Hermel, also remains ongoing since the appointment of their first governors in 2014. See also * Politics of Lebanon References External links Lebanon 1 Governorates, Lebanon Governorates A governorate is an administrative division of a state. It is headed by a governor. As English-speaking nations tend to call regions administered by governors either states or provinces, the term ''governorate'' is often used in translation from ... Subdivisions of Lebanon {{Lebanon-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
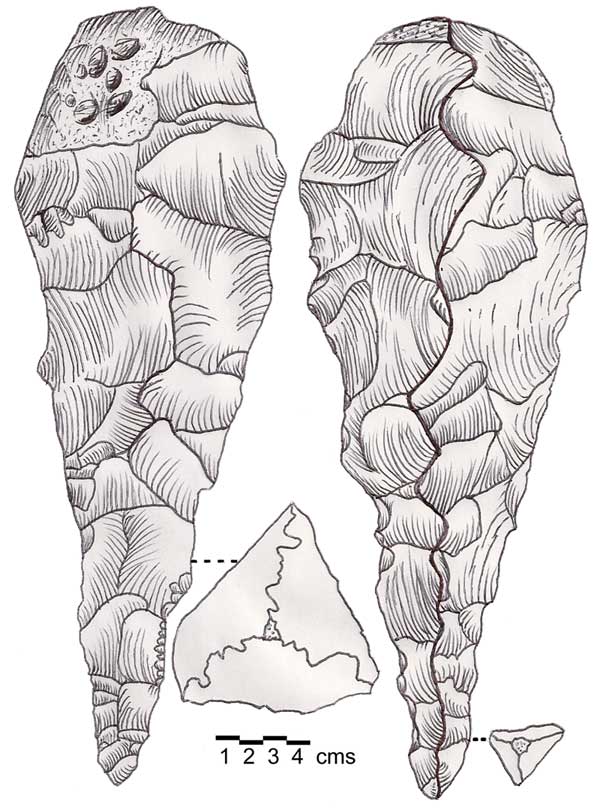
Trihedral Neolithic
Trihedral Neolithic is a name given by archaeologists to a style (or industry) of striking spheroid and trihedral flint tools from the archaeological site of Joub Jannine II in the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon.Fleisch, Henri., Les industries lithiques récentes de la Békaa, République Libanaise, Acts of the 6th C.I.S.E.A., vol. XI, no. 1. Paris, 1960. The style appears to represent a highly specialized Neolithic The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ... industry. Little comment has been made of this industry. References {{reflist Archaeological cultures of West Asia Neolithic cultures of Asia Archaeological cultures in Lebanon Lithics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acheulean
Acheulean (; also Acheulian and Mode II), from the French ''acheuléen'' after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped "hand axes" associated with ''Homo erectus'' and derived species such as ''Homo heidelbergensis''. Acheulean tools were produced during the Lower Palaeolithic era across Africa and much of West Asia, South Asia, East Asia and Europe, and are typically found with ''Homo erectus'' remains. It is thought that Acheulean technologies first developed about 1.76 million years ago, derived from the more primitive Oldowan technology associated with '' Homo habilis''. The Acheulean includes at least the early part of the Middle Paleolithic. Its end is not well defined, depending on whether Sangoan (also known as "Epi-Acheulean") is included, it may be taken to last until as late as 130,000 years ago. In Europe and Western Asia, early Neanderthals adopted Acheulean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalossian
Chalossian is an industry of flint tools from the Stone Age. Paul Bovier-Lapierre discovered it in Egypt Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter .... References Lower Paleolithic Archaeological cultures of Africa {{Egypt-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Wescombe
Peter Wescombe (4 January 1932 – 25 November 2014) was a British diplomat, amateur archaeologist, historian and founding member of the Bletchley Park Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes ( Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World War. The mansion was constructed during the years following ... Trust. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Wescombe, Peter 1932 births 2014 deaths Amateur archaeologists British diplomats Bletchley Park people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorraine Copeland
Lorraine Copeland (born Elizabeth Lorraine Adie, 1921April 2013) was a British archaeologist specialising in the Palaeolithic period of the Near East. She was a secret agent with the Special Operations Executive during World War II. Early life In 1921, Copeland was born as Elizabeth Lorraine Adie in Edinburgh, Scotland. Her father was a neurosurgeon on Harley Street in London, and she was privately educated at Wycombe Abbey girls' school in Buckinghamshire. Special Operations Executive Copeland worked for British Intelligence during the Second World War, in the Special Operations Executive. She met her American husband, Miles Copeland, Jr., during this period, when he was based in the UK undertaking counter-intelligence for the US Army Counter Intelligence Corps. They married on 25 September 1942 and soon afterwards Miles' work took them to the Near East, particularly Syria, Lebanon and Egypt, and it was whilst in this area that Copeland first developed her interest in archaeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Bergy
Reverend Father Auguste Bergy (12 May 1873 – 31 August 1955) was a French Jesuit archaeologist known for his work on prehistory in Lebanon. He is known particularly for excavations and studies at the Sands of Beirut and at Ras Beirut. In 1930 he discovered Tell Arslan The Sands of Beirut were a series of archaeological sites located on the coastline south of Beirut in Lebanon. Description The Sands were a complex of nearly 20 prehistoric sites that were destroyed due to building operations using the soft sand ..., the oldest known neolithic village settlement in the Beirut area. Selected bibliography * Bergy, Auguste., Le Paléolithique ancien stratifié à Ras Beyrouth, M.U.S.J, XVI, 169-217, 1932. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Bergy, Auguste French Jesuits French Roman Catholic missionaries French archaeologists 1873 births 1955 deaths Roman Catholic missionaries in Lebanon French expatriates in Lebanon Jesuit scientists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Bovier-Lapierre
Reverend Father Paul Bovier-Lapierre (1873–1950) was a French Jesuit archaeologist, notable for his work on prehistory in Egypt and surveys in southern Lebanon Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li .... References External links Biography (in French) - Lebanese Museum of Prehistory, Saint Joseph University Website 19th-century French Jesuits 20th-century French Jesuits French Roman Catholic missionaries French archaeologists 1873 births 1950 deaths Jesuit missionaries Jesuit scientists Roman Catholic missionaries in Egypt Roman Catholic missionaries in Lebanon French expatriates in Egypt French expatriates in Lebanon {{France-archaeologist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godefroy Zumoffen
Reverend Father Godefroy Zumoffen (1848 in France – 1928) was a French Jesuit archaeologist and geologist notable for his work on prehistory in Lebanon. He is known particularly for pioneering Lebanese archaeology, and for discovering several sites including the Antelias cave Antelias Cave was a large cave located east of Antelias, northeast of Beirut close to the wadi of Ksar Akil. It was discovered by Heidenborg in 1833. Godefroy Zumoffen made an excavation in 1893, finding an Aurignacian industry amongst large qua .... He produced the first geological map of Lebanon and authored a book about its prehistory, ''La Phénicie avant les phéniciens: l'âge de la pierre''. Notes References External links Biography (in French) - Lebanese Museum of Prehistory, Saint Joseph University Website {{DEFAULTSORT:Zumoffen, Godefroy 20th-century French Jesuits French Roman Catholic missionaries French archaeologists 1848 births 1928 deaths French geologists 19th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The society is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 nations. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. Jesuits also give retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian ministries, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of the Society of Jesus, Superior General. The headquarters of the society, its Curia, General Curia, is in Rome. The historic curia of Ignatius is now part of the attached to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)