|
Simon Smith Kuznets
Simon Smith Kuznets (; rus, Семён Абра́мович Кузне́ц, p=sʲɪˈmʲɵn ɐˈbraməvʲɪtɕ kʊzʲˈnʲɛts; April 30, 1901 – July 8, 1985) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1971 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences "for his empirically founded interpretation of economic growth which has led to new and deepened insight into the economic and social structure and process of development." Kuznets made a decisive contribution to the transformation of economics into an empirical science and to the formation of quantitative economic history. Biography Early life Simon Kuznets was born in Pinsk in 1901, in the Russian Empire, or what is today Belarus, to Lithuanian-Jewish parents. He completed his schooling, first at the Rivne, then, Kharkiv Realschule of present-day Ukraine. In 1918, Kuznets entered the Kharkiv Institute of Commerce where he studied economic sciences, statistics, history and mathematics under the guidance of prof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institutional Economics
Institutional economics focuses on understanding the role of the Sociocultural evolution, evolutionary process and the role of institutions in shaping Economy, economic Human behavior, behavior. Its original focus lay in Thorstein Veblen's instinct-oriented dichotomy between technology on the one side and the "ceremonial" sphere of society on the other. Its name and core elements trace back to a 1919 ''American Economic Review'' article by Walton H. Hamilton. Institutional economics emphasizes a broader study of institutions and views markets as a result of the complex interaction of these various institutions (e.g. individuals, firms, states, social norms). The earlier tradition continues today as a leading Heterodox economics, heterodox approach to economics.Warren J. Samuels ([1987] 2008). "institutional economics," ''The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics''Abstract. "Traditional" institutionalism rejects the ''reduction'' of institutions to simply tastes, technology, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley Engerman
Stanley Lewis Engerman (born March 14, 1936) is an economist and economic historian at the University of Rochester. He received his Ph.D. in economics in 1962 from Johns Hopkins University. Engerman is known for his quantitative historical work along with Nobel Prize–winning economist Robert Fogel. His first major book, co-authored with Robert Fogel in 1974, was '' Time on the Cross: The Economics of American Negro Slavery.'' This significant work, winner of the Bancroft Prize in American history, challenged readers to think critically about the economics of slavery. Engerman has also published over 100 articles and has authored, co-authored or edited 16 book-length studies. Engerman served as president of the Social Science History Association as well as president of the Economic History Association. He is professor of Economics and Professor of History at the University of Rochester, where he teaches classes in economic history and the economics of sports and entertainment. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.Kharkiv "never had eastern-western conflicts" ''Euronews'' (23 October 2014) Located in the northeast of the country, it is the largest city of the historic Sloboda Ukraine, Slobozhanshchyna region. Kharkiv is the administrative centre of Kharkiv Oblast and of the surrounding Kharkiv Raion. The latest population is Kharkiv was founded in 1654 as Kharkiv fortress, and after these humble beginnings, it grew to be a major centre of industry, trade and Ukrainian culture in the Russian Empire. At the beginning of the 20th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivne
Rivne (; uk, Рівне ),) also known as Rovno (Russian: Ровно; Polish: Równe; Yiddish: ראָוונע), is a city in western Ukraine. The city is the administrative center of Rivne Oblast (province), as well as the surrounding Rivne Raion (district created in the USSR) within the oblast.On bringing the name of Rovno city and Rovno Oblast in accordance to rules of Ukrainian spelling . . 11 June 1991 Administratively, Rivne is incorporated as a cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Jews
Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks () are Jews with roots in the territory of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania (covering present-day Lithuania, Belarus, Latvia, the northeastern Suwałki and Białystok regions of Poland, as well as adjacent areas of modern-day Russia and Ukraine). The term is sometimes used to cover all Haredi Jews who follow a " Lithuanian" ( Ashkenazi, non- Hasidic) style of life and learning, whatever their ethnic background. The area where Lithuanian Jews lived is referred to in Yiddish as , hence the Hebrew term (). No other famous Jew is more closely linked to a specifically Lithuanian city than Vilna Gaon (in Yiddish, "the genius of Vilna"). Rabbi Elijah ben Solomon Zalman (1720–1797) to give his rarely used full name, helped make Vilna (modern-day Vilnius) a world center for Talmudic learning. Chaim Grade (1910–1982) was born in Vilna, the city about which he would write. The inter-war Republic of Lithuania was home to a large and influential Jewish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Econometric History
Cliometrics (, also ), sometimes called new economic history or econometric history, is the systematic application of economic theory, econometric techniques, and other formal or mathematical methods to the study of history (especially social and economic history). It is a quantitative approach to economic history (as opposed to qualitative or ethnographic). Edward L. Glaeser"Remembering the Father of Transportation Economics" ''The New York Times'' (Economix), October 27, 2009. There has been a revival in 'new economic history' since the late 1990s. History The new economic history originated in 1958 with ''The Economics of Slavery in the Antebellum South'' by American economists Alfred H. Conrad and John R. Meyer. The book would cause a firestorm of controversy with its claim, based on statistical data, that slavery would not have ended in the absence of the U.S. Civil War, as the practice was economically efficient and highly profitable for slaveowners. The term ''cliometrics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical Science
In philosophy, empiricism is an epistemological theory that holds that knowledge or justification comes only or primarily from sensory experience. It is one of several views within epistemology, along with rationalism and skepticism. Empiricism emphasizes the central role of empirical evidence in the formation of ideas, rather than innate ideas or traditions. However, empiricists may argue that traditions (or customs) arise due to relations of previous sensory experiences. Historically, empiricism was associated with the "blank slate" concept (''tabula rasa''), according to which the human mind is "blank" at birth and develops its thoughts only through experience. Empiricism in the philosophy of science emphasizes evidence, especially as discovered in experiments. It is a fundamental part of the scientific method that all hypotheses and theories must be tested against observations of the natural world rather than resting solely on ''a priori'' reasoning, intuition, or reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally related groups or sets of roles, with different functions, meanings, or purposes. Examples of social structure include family, religion, law, economy, and class. It contrasts with "social system", which refers to the parent structure in which these various structures are embedded. Thus, social structures significantly influence larger systems, such as economic systems, legal systems, political systems, cultural systems, etc. Social structure can also be said to be the framework upon which a society is established. It determines the norms and patterns of relations between the various institutions of the society. Since the 1920s, the term has been in general use in social science, especially as a variable whose sub-components needed to be disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Memorial Prize In Economic Sciences
The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel ( sv, Sveriges riksbanks pris i ekonomisk vetenskap till Alfred Nobels minne), is an economics award administered by the Nobel Foundation. Although not one of the five Nobel Prizes which were established by Alfred Nobel's will in 1895, it is commonly referred to as the Nobel Prize in Economics. The winners of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences are chosen in a similar way, are announced along with the Nobel Prize recipients, and the prize is presented at the Nobel Prize Award Ceremony. The award was established in 1968 by an endowment "in perpetuity" from Sweden's central bank, Sveriges Riksbank, to commemorate the bank's 300th anniversary. It is administered and referred to along with the Nobel Prizes by the Nobel Foundation. Laureates in the Memorial Prize in Economics are selected by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Growth
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate of increase in the real gross domestic product, or real GDP. Growth is usually calculated in real terms – i.e., inflation-adjusted terms – to eliminate the distorting effect of inflation on the prices of goods produced. Measurement of economic growth uses national income accounting. Since economic growth is measured as the annual percent change of gross domestic product (GDP), it has all the advantages and drawbacks of that measure. The economic growth-rates of countries are commonly compared using the ratio of the GDP to population (per-capita income). The "rate of economic growth" refers to the geometric annual rate of growth in GDP between the first and the last year over a period of time. This growth rate represents the trend in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
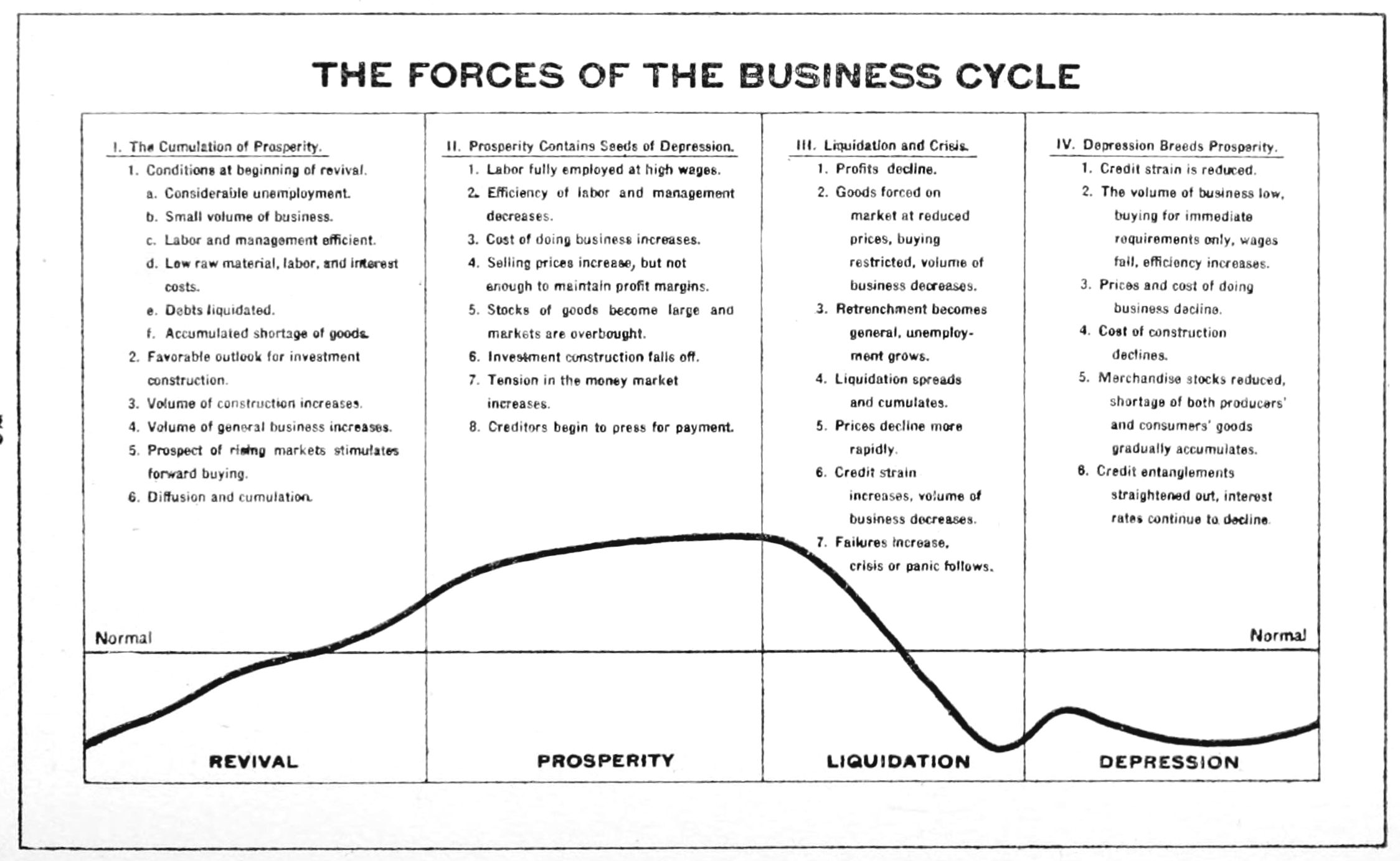
Business Cycle
Business cycles are intervals of Economic expansion, expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in [Harvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics''], such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Income
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national income (NNI), and adjusted national income (NNI adjusted for natural resource depletion – also called as NNI at factor cost). All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and services produced within the economy and by various sectors. The boundary is usually defined by geography or citizenship, and it is also defined as the total income of the nation and also restrict the goods and services that are counted. For instance, some measures count only goods & services that are exchanged for money, excluding bartered goods, while other measures may attempt to include bartered goods by ''imputing'' monetary values to them. National accounts Arriving at a figure for the total production of goods and services in a large region like a country entails a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |