|
Simeon Of Beth Arsham
Simeon of Beth Arsham ( syr, ܫܡܥܘܢ ܕܒܝܬ ܐܪܫܡ, Shemʿun di-Beth Arsham) was a Syrian bishop who spread his teachings at the beginning of the sixth century. He was the bishop of Beth Arsham (''House of Arsames''), which was located near Seleucia- Ctesiphon. Life Simeon was known as an eloquent and passionate disputant, and devoted to his Orthodox faith. He used to argue with Nestorians, Manicheans, Eutychians and the doctrines of Marcion of Sinope and Bardaisan in which he earned the title 'The Persian Disputant'. He spent most of his life in Mesopotamia and Persia preaching Christianity, where many pagan Arabs, dignitaries of Persian Zoroastrianism and Magians were baptized by him. Three baptized Magi were denounced by the king Kavadh I and their former colleagues, they were found dead ten days after their baptism. According to John of Ephesus, Simeon was threatened with death and had to grow his hair and beard to go unnoticed. An alliance broke out between the Nest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syrian
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indigenous elements and the foreign cultures that have come to inhabit the region of Syria over the course of thousands of years. The mother tongue of most Syrians is Levantine Arabic, which came to replace the former mother tongue, Aramaic, following the Muslim conquest of the Levant in the 7th century. The conquest led to the establishment of the Caliphate under successive Arab dynasties, who, during the period of the later Abbasid Caliphate, promoted the use of the Arabic language. A minority of Syrians have retained Aramaic which is still spoken in its Eastern and Western dialects. In 2018, the Syrian Arab Republic had an estimated population of 19.5 million, which includes, aside from the aforementioned majority, ethnic minorities such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth Column
A fifth column is any group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. According to Harris Mylonas and Scott Radnitz, "fifth columns" are “domestic actors who work to undermine the national interest, in cooperation with external rivals of the state." The activities of a fifth column can be overt or clandestine. Forces gathered in secret can mobilize openly to assist an external attack. This term is also extended to organised actions by military personnel. Clandestine fifth column activities can involve acts of sabotage, disinformation, espionage, and/or terrorism executed within defense lines by secret sympathizers with an external force. Origin The term "fifth column" originated in Spain (originally ''quinta columna'') during the early phase of the Spanish Civil War. It gained popularity in the Republican faction (Spanish Civil War), Loyalist faction media in early October 1936 and immediately started to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
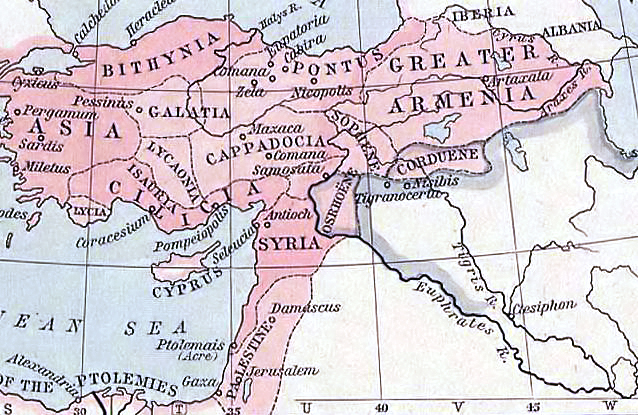
Nisibis
Nusaybin (; '; ar, نُصَيْبِيْن, translit=Nuṣaybīn; syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, translit=Nṣībīn), historically known as Nisibis () or Nesbin, is a city in Mardin Province, Turkey. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009 and is predominantly Kurdish. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius ( grc, Μυγδόνιος). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac-speaking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the Persian Gulf. Geography The Tigris is 1,750 km (1,090 mi) long, rising in the Taurus Mountains of eastern Turkey about 25 km (16 mi) southeast of the city of Elazığ and about 30 km (20 mi) from the headwaters of the Euphrates. The river then flows for 400 km (250 mi) through Southeastern Turkey before becoming part of the Syria-Turkey border. This stretch of 44 km (27 mi) is the only part of the river that is located in Syria. Some of its affluences are Garzan, Anbarçayi, Batman, and the Great and the Little Zab. Close to its confluence with the Euphrates, the Tigris splits into several channels. First, the artificial Shatt al-Hayy branches off, to join the Euphrates near Nasiriya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beth Arsham
{{disambiguation, surname ...
Beth may refer to: Letter and number *Bet (letter), or beth, the second letter of the Semitic abjads (writing systems) *Hebrew word for "house", often used in the name of synagogues and schools (e.g. Beth Israel) Name *Beth (given name) lists people with the given name Beth *Beth (singer), Elisabeth Rodergas Cols (born 1981) *Evert Willem Beth (1908–1964), Dutch philosopher and logician Other uses * "Beth" (song), by the band Kiss *List of storms named Beth See also * Bayt (other)Bayt/Beit/Beth/Bet (other), meaning 'house' in various Semitic languages; part of many place-names *Bet (other) *Elizabeth (other) Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to: People * Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name) * Elizabeth (biblical figure) Elizabeth (also spelled Elisabeth; Hebrew: אֱלִישֶׁבַע / אֱלִישָׁבַ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marzban
Marzbān, or Marzpān (Middle Persian transliteration: mrzwpn, derived from ''marz'' "border, boundary" and the suffix ''-pān'' "guardian"; Modern Persian: ''Marzbān'') were a class of margraves, warden of the marches, and by extension military commanders, in charge of border provinces of the Parthian Empire (247 BC–224 AD) and mostly Sasanian Empire (224–651 AD) of Iran. Etymology The Persian word ''marz'' is derived from Avestan ''marəza'' "frontier, border"; ''pān/pāvan'' is cognate with Avestan and Old Persian ''pat'' "protector". The word was borrowed from New Persian into Arabic as ''marzubān'' (plural ''marāziba''). "Al-Marzubani" () has been used as a '' nisba'' (family title) for some Iranian families whose ancestor was a marzbān. The prominent Islamic scholar Abu Hanifa, whose formal name is given in Islamic sources as Nu'man ibn Thabit ibn Zuta ''ibn Marzubān'' (), was descended from the marzbāns of Kabul, where his father came from. The Bavand (651� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbayistan
Arbāyistān ( xpr, 𐭀𐭓𐭁𐭉𐭎𐭈𐭍 �rbstn; Middle Persian: ''Arwāstān''; Armenian: ''Arvastan'') or Beth Arabaye ( Syriac: ''Bēṯ ʿArbāyē'') was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity. Due to its situation and its road systems, the province was a source of income from commercial traffic, as well as a constant area of contention during the Roman–Persian Wars. The province reached across Upper Mesopotamia toward the Khabur and north to the lower districts of Armenia; it bordered Adiabene in the east, Armenia in the north and Asoristan in the south. On the west, it bordered the Roman provinces of Osroene and Mesopotamia. The principal city of the Arbayistan province was Nisibis and it also included the fortress of Sisauranon. Name ''Arbāyistān'' (Old Persian: ''Arabāya-stāna)'' is mentioned in Shapur I's inscription on Ka'ba-ye Zartosht. According to historian Geo Widengren, the name refers to the Arab inhabitants of Upper Mesopotamia. The terms ''Arb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisibis (East Syrian Ecclesiastical Province)
The Metropolitanate of Nisibis was an East Syriac metropolitan province of the Church of the East, between the fifth and seventeenth centuries. The ecclesiastical province of Nisibis (Syriac: Nisibin, , often abbreviated to Soba, ) had a number of suffragan dioceses at different periods in its history, including Arzun, Beth Rahimaï, Beth Qardu (later renamed Tamanon), Beth Zabdaï, Qube d’Arzun, Balad, Shigar (Sinjar), Armenia, Beth Tabyathe and the Kartawaye, Harran and Callinicus (Raqqa), Maiperqat (with Amid and Mardin), Reshaïna, Qarta and Adarma, Qaimar and Hesna d'Kifa. Aoustan d'Arzun and Beth Moksaye were also suffragan dioceses in the fifth century. Background In 363 the Roman emperor Jovian was obliged to cede Nisibis and five neighbouring districts to Persia to extricate the defeated army of his predecessor Julian from Persian territory. The Nisibis region, after nearly fifty years of rule by Constantine and his Christian successors, may well have contained m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siirt
Siirt ( ar, سِعِرْد, Siʿird; hy, Սղերդ, S'gherd; syr, ܣܥܪܬ, Siirt; ku, Sêrt) is a city in southeastern Turkey and the seat of Siirt Province. The population of the city according to the 2009 census was 129,188. History Previously known as ''Saird'', in pre-Islamic times Siirt was a diocese of the Eastern Orthodox Church (''Sirte'', Σίρτη in Byzantine Greek). In the medieval times, Arzen was the main city and it competed with Hasankeyf over the control the region, Siirt was only to become a center of the region in the 14th century. But it was still dependent from Hasankeyf until the 17th century. An illuminated manuscript known as the Syriac Bible of Paris might have originated from the Bishop of Siirt's library, Siirt's Christians would have worshipped in Syriac, a liturgical language descended from Aramaic still in use by the Syriac Rite,Chaldean Rite, other Eastern Christians in India, and the Nestorians along the Silk Road as far as China. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arzun
Arzen (in Syriac ''Arzŏn'' or ''Arzŭn'', Armenian ''Arzn'', ''Ałzn'', Arabic ''Arzan'') was an ancient and medieval city, located on the border zone between Upper Mesopotamia and the Armenian Highlands. The site of the ancient Armenian capital of Tigranocerta, according to modern scholars, in Late Antiquity it was the capital of the district of Arzanene, a Syriac bishopric and a Sasanian Persian border fortress in the Roman–Persian Wars of the period. After the Muslim conquests, it briefly became the seat of an autonomous dynasty of emirs in the 9th century, before being devastated in the wars between the Byzantine Empire and the Hamdanids in the 10th century. By the 12th century, it had been abandoned and ruined. Today, few traces of the town survive. Antiquity The origin of the name ''Arzĕn'' (reflecting the Armenian pronunciation) is unknown, but non-Armenian. Its site, on the banks of the river Garzan Su (ancient ''Nicephorius'') in southeastern Turkey, was visited and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophysite
Monophysitism ( or ) or monophysism () is a Christological term derived from the Greek (, "alone, solitary") and (, a word that has many meanings but in this context means "nature"). It is defined as "a doctrine that in the person of the incarnated Word (that is, in Jesus Christ) there was only one nature—the divine". Background The First Council of Nicaea (325) declared that Christ was divine ( homoousios, consubstantial, of one being or essence, with the Father) and human (was incarnate and became man). In the fifth century a heated controversy arose between the sees and theological schools of Antioch and Alexandria about how divinity and humanity existed in Christ, the former stressing the humanity, the latter the divinity of Christ. Cyril of Alexandria succeeded in having Nestorius, a prominent exponent of the Antiochian school, condemned at the Council of Ephesus in 431, and insisted on the formula "one ''physis'' of the incarnate Word", claiming that any formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babai (Nestorian Patriarch)
Babai, also Babaeus, was Catholicos of Seleucia-Ctesiphon and Patriarch of the Church of the East from 497 to 503. Under his leadership, the Church in Sasanian Empire (Persia) became increasingly aligned with the Nestorian movement, declared heretical in the Roman Empire."Nestorian" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved January 28, 2010. Babai was also known as patriarch of Seleucia-Ctesiphon. When he became patriarch, he was married. With the permission of , Babai was allowed to call a |