|
Silver Subfluoride
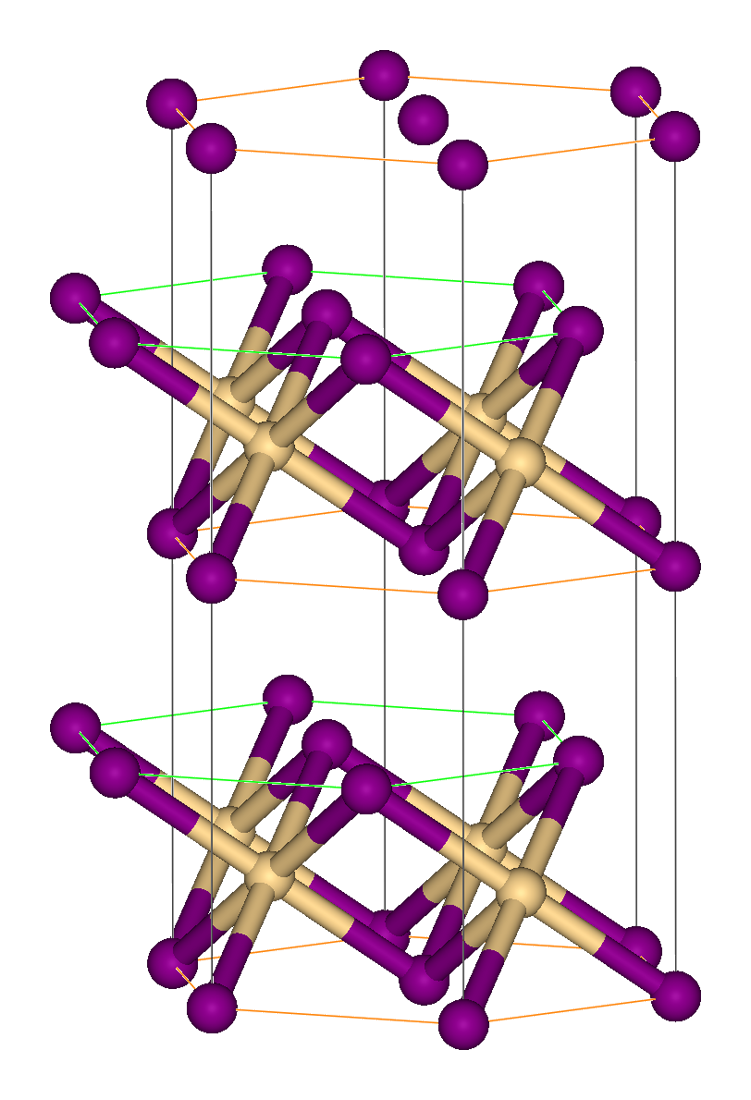
Silver subfluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Ag2F. This is an unusual example of a compound where the oxidation state of silver is fractional. The compound is produced by the reaction of silver and silver(I) fluoride:Lee Poyer, Maurice Fielder, Hugh Harrison, Burl E. Bryant "Disilver Fluoride: (Silver “Subfluoride”)" Inorganic Syntheses, 1957, Volume 5, 92–94. :Ag + AgF → Ag2F It forms small crystals with a bronze reflex and is a good conductor of electricity. On contact with water almost instant hydrolysis occurs with the precipitation of silver (Ag) powder. Crystal structure Ag2F adopts the anti-CdI2 crystal structure, i.e. the same structure as cadmium iodide Cadmium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compoun ..., CdI2, but with "Ag½+ " centres i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decomposition
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is essential for recycling the finite matter that occupies physical space in the biosphere. Bodies of living organisms begin to decompose shortly after death. Animals, such as worms, also help decompose the organic materials. Organisms that do this are known as decomposers or detritivores. Although no two organisms decompose in the same way, they all undergo the same sequential stages of decomposition. The science which studies decomposition is generally referred to as ''taphonomy'' from the Greek word ''taphos'', meaning tomb. Decomposition can also be a gradual process for organisms that have extended periods of dormancy. One can differentiate abiotic decomposition from biotic decomposition (biodegradation). The former means "the degradation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver(I) Fluoride
Silver(I) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula AgF. It is one of the three main fluorides of silver, the others being silver subfluoride and silver(II) fluoride. AgF has relatively few niche applications; it has been employed as a fluorination and desilylation reagent in organic synthesis and in aqueous solution as a topical caries treatment in dentistry. The hydrates of AgF present as colourless, while pure anhydrous samples are yellow. Preparation High-purity silver(I) fluoride can be produced by the heating of silver carbonate to under a hydrogen fluoride environment, in a platinum tube: :Ag2CO3 + 2 HF -> 2 AgF + H2O + CO2 Laboratory routes to the compound typically avoid the use of gaseous hydrogen fluoride. One method is the thermal decomposition of silver tetrafluoroborate: :AgBF4 -> AgF + BF3 In an alternative route, silver(I) oxide is dissolved in concentrated aqueous hydrofluoric acid, and the silver fluoride is precipitated out of the resulti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver(II) Fluoride
Silver(II) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula AgF2. It is a rare example of a silver(II) compound. Silver usually exists in its +1 oxidation state. It is used as a fluorinating agent. Preparation AgF2 can be synthesized by fluorinating Ag2O with elemental fluorine. Also, at 200 °C (473 K) elemental fluorine will react with AgF or AgCl to produce AgF2. As a strong fluorinating agent, AgF2 should be stored in Teflon or a passivated metal container. It is light sensitive. AgF2 can be purchased from various suppliers, the demand being less than 100 kg/year. While laboratory experiments find use for AgF2, it is too expensive for large scale industry use. In 1993, AgF2 cost between 1000-1400 US dollars per kg. Composition and structure AgF2 is a white crystalline powder, but it is usually black/brown due to impurities. The F/Ag ratio for most samples is < 2, typically approaching 1.75 due to contamination with [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver(III) Fluoride
Silver(III) fluoride, AgF3, is an unstable, bright-red, diamagnetic compound containing silver in the unusual +3 oxidation state. Its crystal structure is very similar to that of gold(III) fluoride: it is a polymer consisting of rectangular AgF4 units linked into chains by fluoro bridges. Preparation AgF3 can be prepared by treating a solution containing tetrafluoroargentate(III) ions in anhydrous hydrogen fluoride with boron trifluoride; the potassium tetrafluoroargentate(III) was prepared by heating a stoichiometric mix of potassium and silver nitrate in a sealed container filled with pressurised fluorine gas at 400C for 24 hours, twice. When dissolved in anhydrous HF, it decomposes spontaneously to Ag3F8 overnight at room temperature. The high-valence silver compounds described in the thesis are notable for their variety of colours: KAgF4 is bright orange, AgF3 bright red, AgFAsF6 is deep blue, Ag3F8 deep red-brown, and Pd(AgF4)2 is lime-green. Earlier preparations were m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation State
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge. The oxidation state of an atom does not represent the "real" formal charge on that atom, or any other actual atomic property. This is particularly true of high oxidation states, where the ionization energy required to produce a multiply positive ion is far greater than the energies available in chemical reactions. Additionally, the oxidation states of atoms in a given compound may vary depending on the choice of electronegativity scale used in their calculation. Thus, the oxidation state of an atom in a compound is purely a formalism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver(I) Fluoride
Silver(I) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula AgF. It is one of the three main fluorides of silver, the others being silver subfluoride and silver(II) fluoride. AgF has relatively few niche applications; it has been employed as a fluorination and desilylation reagent in organic synthesis and in aqueous solution as a topical caries treatment in dentistry. The hydrates of AgF present as colourless, while pure anhydrous samples are yellow. Preparation High-purity silver(I) fluoride can be produced by the heating of silver carbonate to under a hydrogen fluoride environment, in a platinum tube: :Ag2CO3 + 2 HF -> 2 AgF + H2O + CO2 Laboratory routes to the compound typically avoid the use of gaseous hydrogen fluoride. One method is the thermal decomposition of silver tetrafluoroborate: :AgBF4 -> AgF + BF3 In an alternative route, silver(I) oxide is dissolved in concentrated aqueous hydrofluoric acid, and the silver fluoride is precipitated out of the resulti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of Three-dimensional space (mathematics), three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive Translation (geometry), translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of the principal axes, or edges, of the unit cell and the angles between them are the lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Iodide
Cadmium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects. Preparation Cadmium iodide is prepared by the addition of cadmium metal, or its oxide, hydroxide or carbonate to hydroiodic acid. Also, the compound can be made by heating cadmium with iodine. Crystal structure In cadmium iodide the iodide anions form a hexagonal close packed arrangement while the cadmium cations fill all of the octahedral sites in alternate layers. The resultant structure consists of a layered lattice. This same basic structure is found in many other salts and minerals. Cadmium iodide is mostly ionically bonded but with partial covalent character. Cadmium iodide's crystal structure is the prototype on which the crystal structures many other compounds can be consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |