|
Silver Diammine Fluoride
Silver diammine fluoride (SDF), also known as silver diamine fluoride in most of the dental literature, (although this is a chemical misnomer) is a topical medication used to treat and prevent dental caries (tooth decay) and relieve dentinal hypersensitivity. It is a colorless (most products) or blue-tinted (Advantage Arrest), odourless liquid composed of silver, ammonium and fluoride ions at a pH of 10.4 (most products) or 13 (Riva Star). Ammonia compounds reduce the oxidative potential of SDF, increase its stability and helps to maintain a constant concentration over a period of time, rendering it safe for use in the mouth. Silver and fluoride ions possess antimicrobial properties and are used in the remineralization of enamel and dentin on teeth for preventing and arresting dental caries. SDF is also known as diammine silver fluoride, silver fluoride, and silver ammonium fluoride. It is frequently spelled "silver diamine fluoride" (with one ''m''); however, this is a misnom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topical Medication
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a tooth. The word ''topical'' derives from Greek τοπικός ''topikos'', "of a place". Justification Topical drug delivery is a route of administering drugs via the skin to provide topical therapeutic effects. As skin is one of the largest and most superficial organs in the human body, pharmacists utilise it to deliver various drugs. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
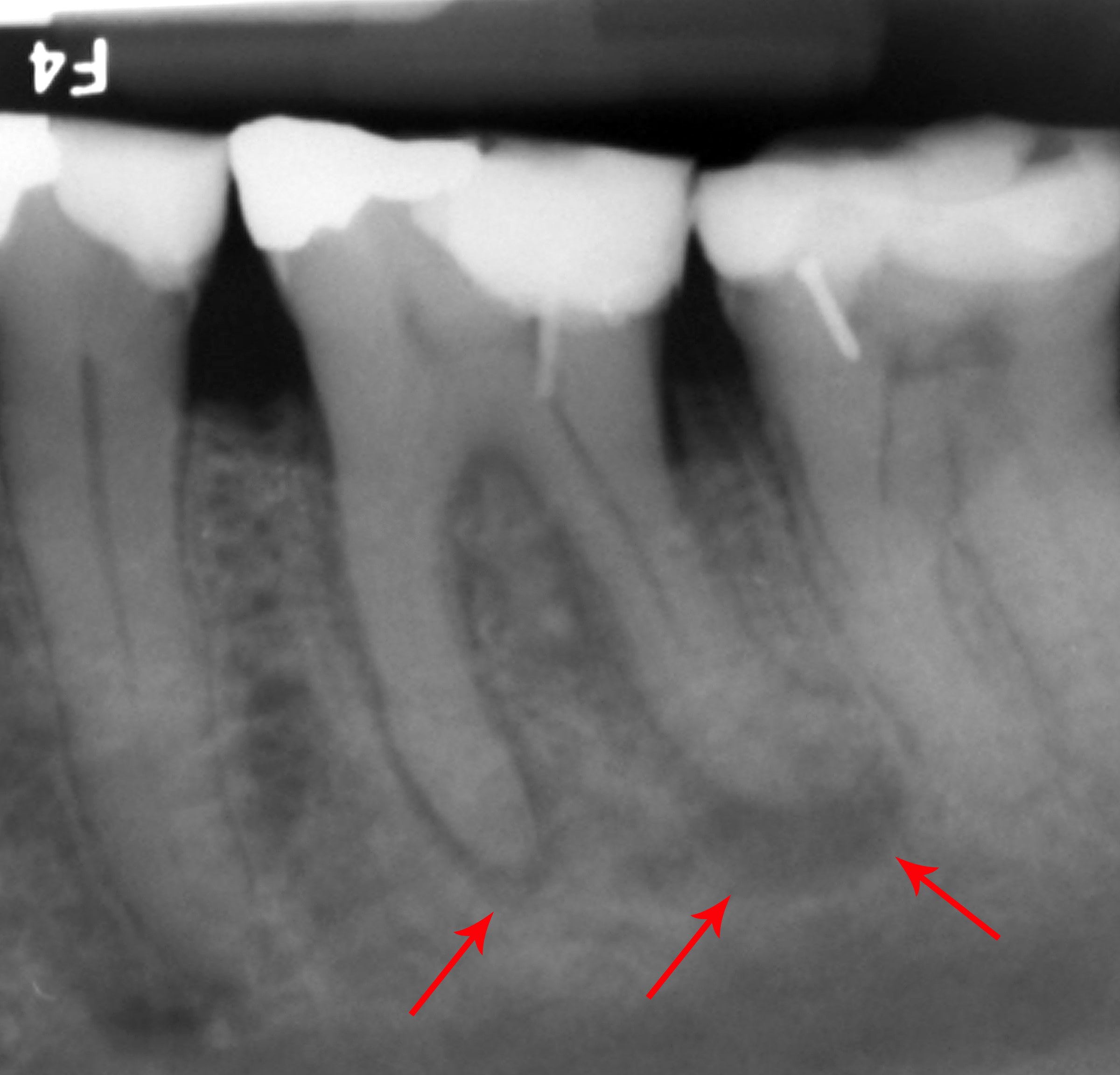
Early Childhood Caries
Early childhood caries (ECC), formerly known as nursing bottle caries, baby bottle tooth decay, night bottle mouth and night bottle caries, is a disease that affects teeth in children aged between birth and 71 months.American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, American Academy of Pediatrics. Policy on early childhood caries (ECC): classifications, consequences, and preventive strategies. Pediatr Dent nternet 2016;38(6):52–54. Available from: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/aapd/pd/2016/00000038/00000006/art00024Fejerskov O, Edwina A, Kidd M. Dental Caries: The Disease and its Clinical Management. 2nd ed. Oxford; Ames, Iowa: Blackwell Munksgaard;2008. ECC is characterized by the presence of 1 or more decayed (noncavitated or cavitated lesions), missing (due to caries), or filled tooth surfaces in any primary tooth. ECC has been shown to be a very common, transmissible bacterial infection, usually passed from the primary caregiver to the child.Elsevier. Early childhood caries: res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
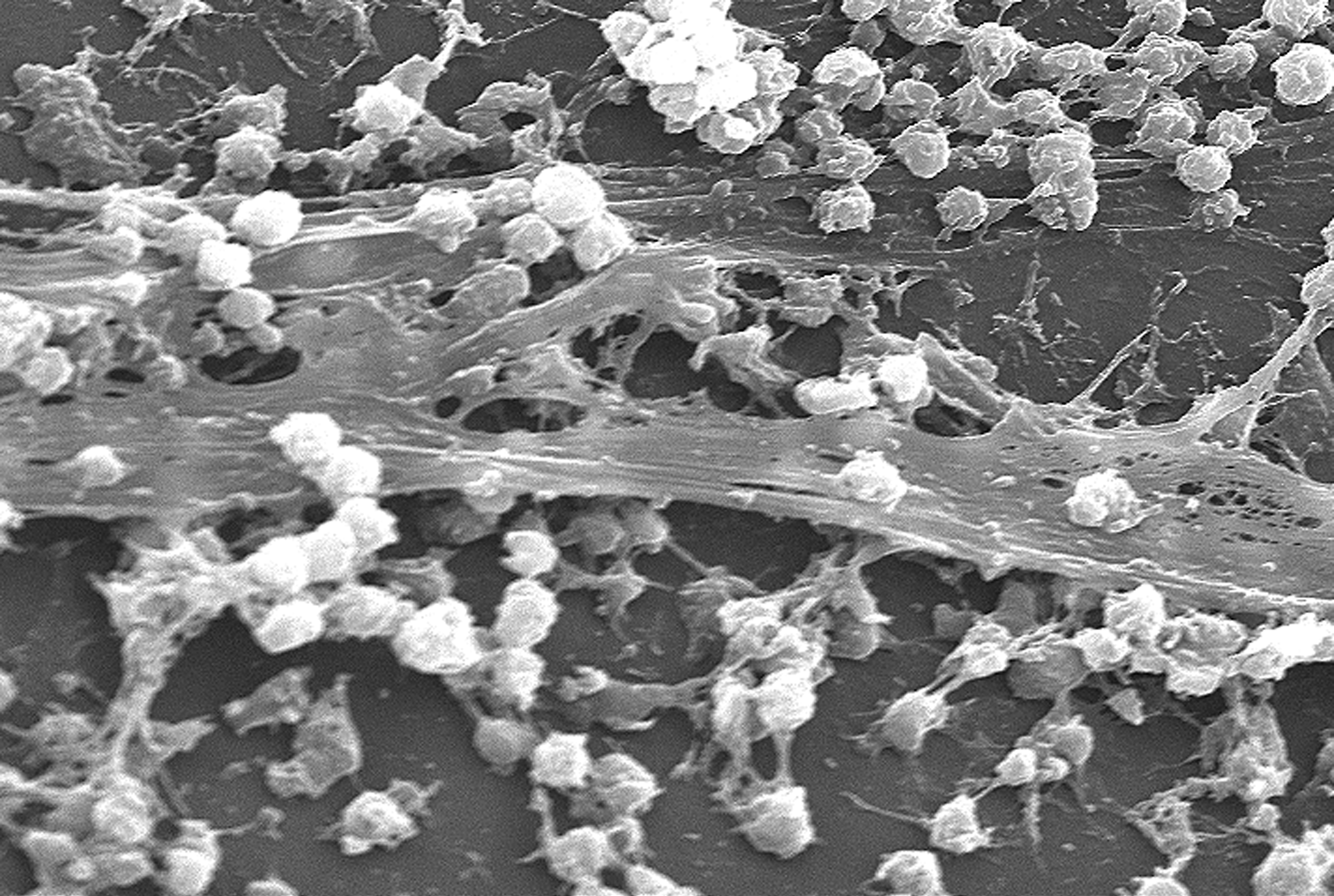
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulpitis
Pulpitis is inflammation of dental pulp tissue. The pulp contains the blood vessels, the nerves, and connective tissue inside a tooth and provides the tooth’s blood and nutrients. Pulpitis is mainly caused by bacterial infection which itself is a secondary development of caries (tooth decay). It manifests itself in the form of a toothache. Signs and symptoms Increased sensitivity to stimuli, specifically hot and cold, is a common symptom of pulpitis. A prolonged throbbing pain may be associated with the disease. However, pulpitis can also occur without any pain. Reversible pulpitis is characterised by intermittent, brief discomfort initiated by a hot, cold or sweet stimulus. The pain evoked is of short duration and there is no lingering or spontaneous pain. The pain ceases within a short period after removal of the stimulus. With a reversible pulpitis, sleep is usually not affected and no analgesics are necessary. Usually, no atypical change is evident on the radiograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is inflammation of the mouth and lips. It refers to any inflammatory process affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips, with or without oral ulceration. In its widest meaning, stomatitis can have a multitude of different causes and appearances. Common causes include infections, nutritional deficiencies, allergic reactions, radiotherapy, and many others. When inflammation of the gums and the mouth generally presents itself, sometimes the term ''gingivostomatitis'' is used, though this is also sometimes used as a synonym for herpetic gingivostomatitis. The term is derived from the Greek ''stoma'' (), meaning "mouth", and the suffix ''-itis'' (), meaning "inflammation". Causes Nutritional deficiency Malnutrition (improper dietary intake) or malabsorption (poor absorption of nutrients into the body) can lead to nutritional deficiency states, several of which can lead to stomatitis. For example, deficiencies of iron, vitamin B2 (riboflavin), vitamin B3 (niacin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG) is a common, non-contagious infection of the gums with sudden onset. The main features are painful, bleeding gums, and ulceration of inter-dental papillae (the sections of gum between adjacent teeth). This disease, along with necrotizing (ulcerative) periodontitis (NP or NUP) is classified as a necrotizing periodontal disease, one of the seven general types of gum disease caused by inflammation of the gums (periodontitis). The often severe gum pain that characterizes ANUG distinguishes it from the more common chronic periodontitis which is rarely painful. If ANUG is improperly treated or neglected, it may become chronic and/or recurrent. The causative organisms are mostly anaerobic bacteria, particularly Fusobacteriota and spirochete species. Predisposing factors include poor oral hygiene, smoking, poor nutrition, psychological stress, and a weakened immune system. When the attachments of the teeth to the bone are involved, the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp (tooth)
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour. Anatomy The pulp is the neurovascular bundle central to each tooth, permanent or primary. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 164. Because of the continuous deposition of the dentine, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor than on the roof or sidewalls. Radicular pulp canals extend down from the cervical region of the crown to the root apex. They are not always straight but vary in shape, size, and number. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
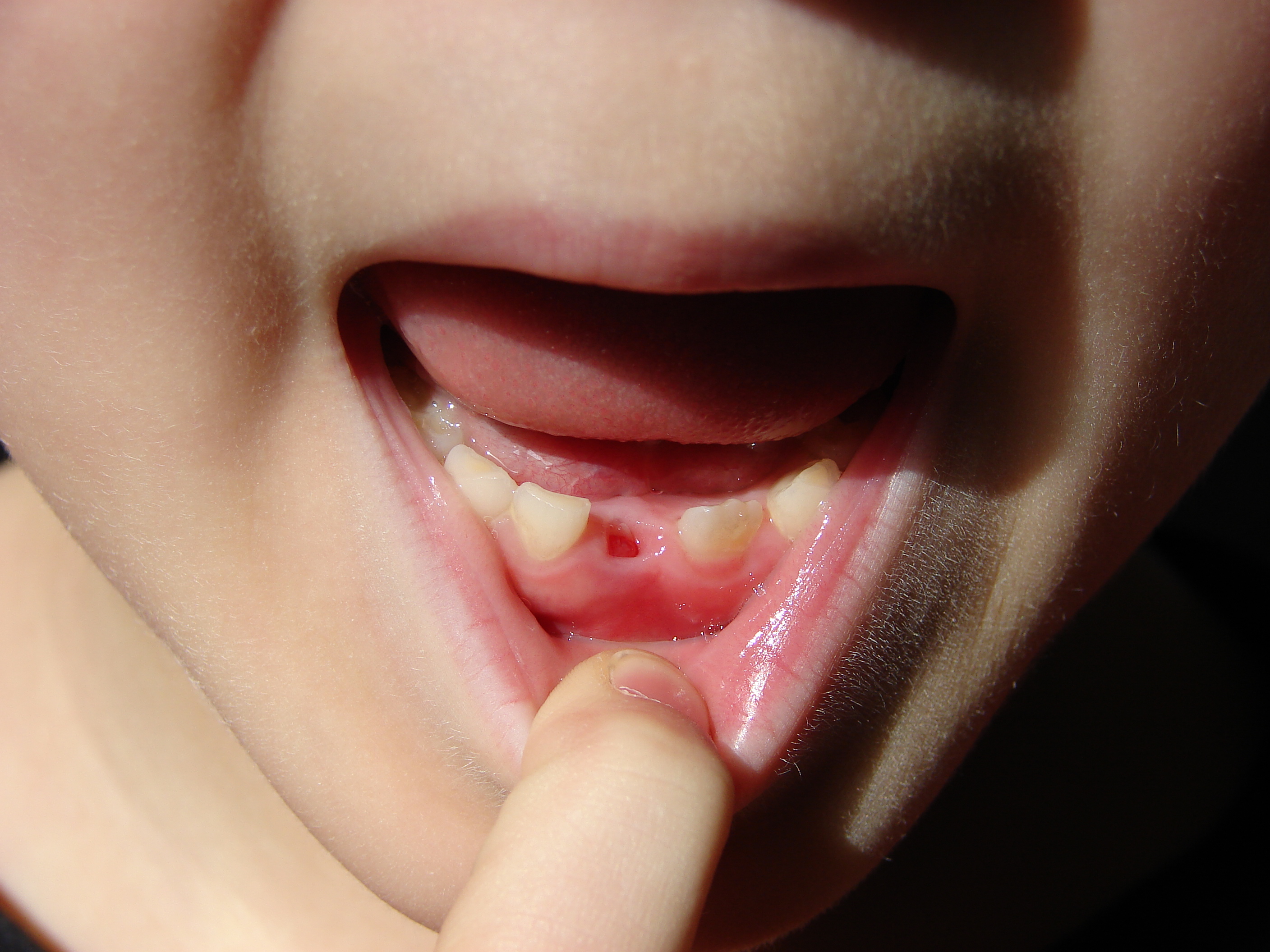
Dental Extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth (wisdom teeth that are stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed (cleaning, antibiotics and operculectomy). In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened. Procedure Extractions could be categorized into non-surgical (simple) and surgical, depending on the type of tooth to be removed and other fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deciduous Teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 255 are the first set of teeth in the growth and development of humans and other diphyodonts, which include most mammals but not elephants, kangaroos, or manatees which are polyphyodonts. Deciduous teeth develop during the embryonic stage of development and erupt (break through the gums and become visible in the mouth) during infancy. They are usually lost and replaced by permanent teeth, but in the absence of their permanent replacements, they can remain functional for many years into adulthood. Development Formation Primary teeth start to form during the embryonic phase of human life. The development of primary teeth starts at the sixth week of tooth development as the dental lamina. This process starts at the midline and then spreads back into the posterior region. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerosol-generating Procedure
An aerosol-generating procedure (AGP) is a medical or health-care procedure that a public health agency such as the World Health Organization or the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has designated as creating an increased risk of transmission of an aerosol borne contagious disease, such as COVID-19. The implication is that the risk of transmission of the contagious disease from a patient having an AGP performed on them is higher than for a patient who is not having an AGP performed upon them. This then informs decisions on infection control, such as what personal protective equipment (PPE) is required by a healthcare worker performing the medical procedure. Medical procedures that have been designated as AGPs include positive-pressure mechanical ventilation including BiPAP and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), high-frequency ventilation, tracheal intubation, airway suction, tracheostomy, chest physiotherapy, nebuliser treatment, sputum indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Fear
Dental fear, or dentophobia, is a normal emotional reaction to one or more specific threatening stimuli in the dental situation. However, dental anxiety is indicative of a state of apprehension that something dreadful is going to happen in relation to dental treatment, and it is usually coupled with a sense of losing control. Similarly, dental phobia denotes a severe type of dental anxiety, and is characterised by marked and persistent anxiety in relation to either clearly discernible situations or objects (e.g. drilling, local anaesthetic injections) or to the dental setting in general. The term ‘dental fear and anxiety’ (DFA) is often used to refer to strong negative feelings associated with dental treatment among children, adolescents and adults, whether or not the criteria for a diagnosis of dental phobia are met. Dental phobia can include fear of dental procedures, dental environment or setting, fear of dental instruments or fear of the dentist as a person. People with dent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |