|
Silent Speech
Imagined speech (also called silent speech, covert speech, inner speech, or, in the original Latin terminology used by clinicians, endophasia) is thinking in the form of sound – “hearing” one’s own voice silently to oneself, without the intentional movement of any extremities such as the lips, tongue, or hands.Brigham, K.; Vijaya Kumar, B.V.K.,Imagined Speech Classification with EEG Signals for Silent Communication: A Preliminary Investigation into Synthetic Telepathy, June 2010 Logically, imagined speech has been possible since the emergence of language, however, the phenomenon is most associated with its investigation through signal processingBrigham, K.; Vijaya Kumar, B.V.K.,Subject Identification from Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals During Imagined Speech, September 2010. and detection within electroencephalograph (EEG) dataA. Porbadnigk; M. Wester; Schultz, T.,EEG-Based Speech Recognition: Impact of Temporal Effects", 2009. as well as data obtained using alternativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
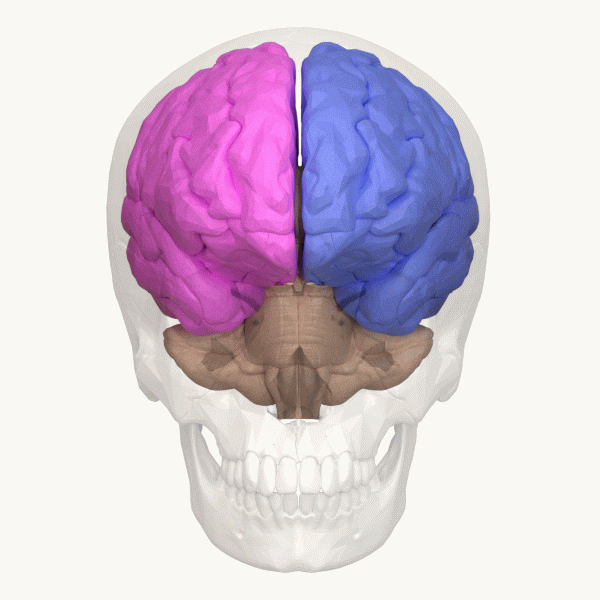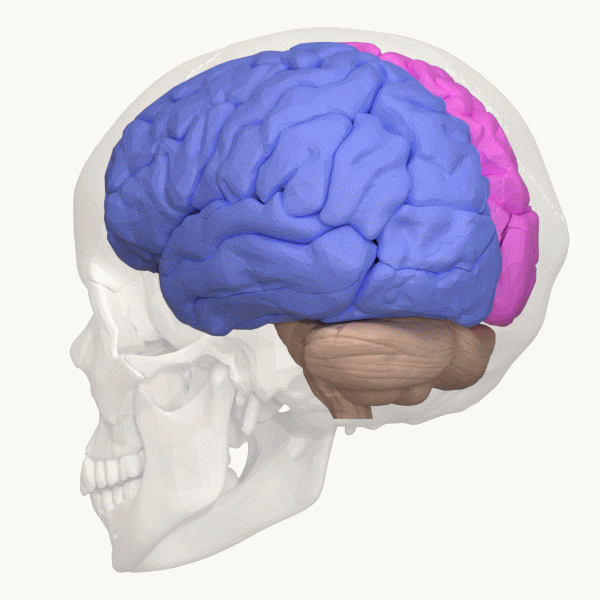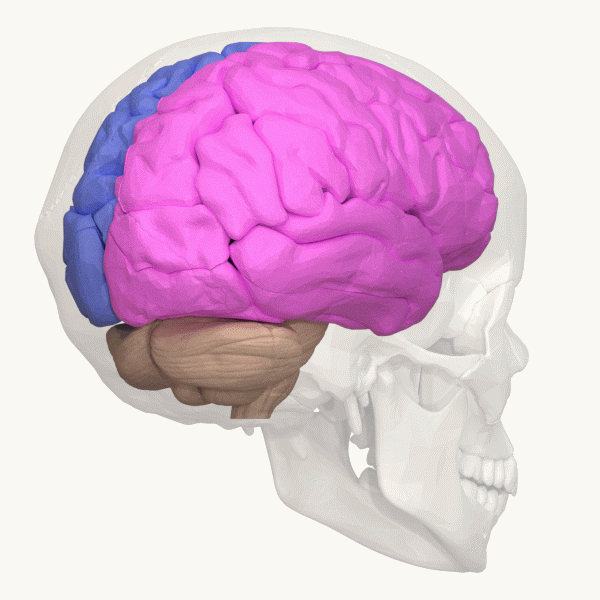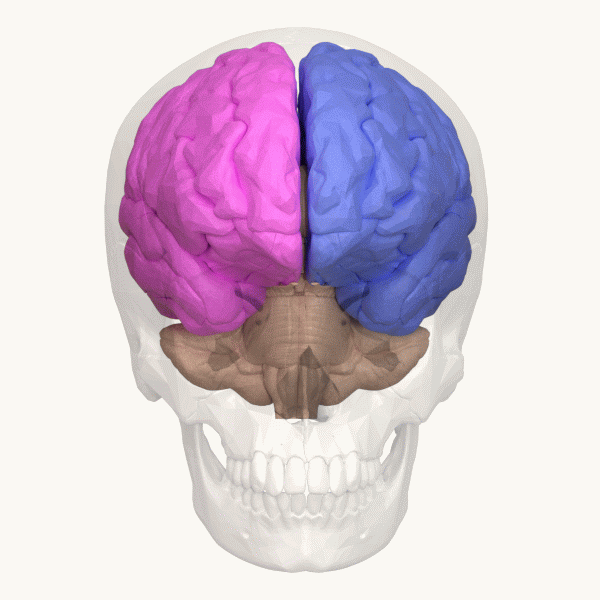
Lateralization Of Brain Function
The lateralization of brain function is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. Although the macrostructure of the two hemispheres appears to be almost identical, different composition of neuronal networks allows for specialized function that is different in each hemisphere. Lateralization of brain structures is based on general trends expressed in healthy patients; however, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization. Each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger anthropological history. The best examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback (NFB), also called neurotherapy, is a type of biofeedback that presents real-time feedback from brain activity in order to reinforce healthy brain function through operant conditioning. Typically, electrical activity from the brain is collected via sensors placed on the scalp using electroencephalography (EEG), with feedback presented using video displays or sound. The effectiveness of neurofeedback is disputed. While studies and reviews have often found neurofeedback treatment to be beneficial for the patient, it has yet to be shown these effects are directly caused by the neurofeedback technique applied. Placebo-controlled trials have often found the control group to show the same level of improvement as the group receiving actual neurofeedback treatment, which suggests these improvements may be caused by secondary effects instead. Despite this controversy and never having gaining prominence in the medical mainstream, it has been practiced for over four decades. NFB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Oscillations
Neural oscillations, or brainwaves, are rhythmic or repetitive patterns of neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in an electroencephalogram. Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mind Machine
A mind machine (aka ''brain machine'' or ''light and sound machine'') uses pulsing rhythmic sound, flashing light, or a combination of these to alter the frequency of the user's brainwaves. Mind machines can induce deep states of relaxation, concentration, and in some cases altered states of consciousness, which have been compared to those obtained from meditation and shamanic exploration. Photic mind machines work with flickering lights embedded in sunglasses or a lamp that sits above or facing the user's head. The user then "watches" with their eyes closed. The process applied by some of these machines is said to induce brainwave synchronisation or entrainment. History The influence of rhythmic sounds and drums to enter altered states of consciousness is used in different indigenous tribes (see Shamanic music), as well as optical stimulation produced by the flickering light of camp fires or pressing lightly on the eyeballs. This "stroboscopic photo-stimulation produces 'photi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetoencephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electrical currents occurring naturally in the brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Arrays of SQUIDs (superconducting quantum interference devices) are currently the most common magnetometer, while the SERF (spin exchange relaxation-free) magnetometer is being investigated for future machines. Applications of MEG include basic research into perceptual and cognitive brain processes, localizing regions affected by pathology before surgical removal, determining the function of various parts of the brain, and neurofeedback. This can be applied in a clinical setting to find locations of abnormalities as well as in an experimental setting to simply measure brain activity. History MEG signals were first measured by University of Illinois physicist David Cohen in 1968, before the availability of the SQUID, using a copper induction coil as the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Field Potentials
Local field potentials (LFP) are transient electrical signals generated in nervous and other tissues by the summed and synchronous electrical activity of the individual cells (e.g. neurons) in that tissue. LFP are "extracellular" signals, meaning that they are generated by transient imbalances in ion concentrations in the spaces outside the cells, that result from cellular electrical activity. LFP are 'local' because they are recorded by an electrode placed nearby the generating cells. As a result of the Inverse-square law, such electrodes can only 'see' potentials in spatially limited radius. They are 'potentials' because they are generated by the voltage that results from charge separation in the extracellular space. They are 'field' because those extracellular charge separations essentially create a local electric field. LFP are typically recorded with a high-impedance microelectrode placed in the midst of the population of cells generating it. They can be recorded, for exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Activity
Neural oscillations, or brainwaves, are rhythmic or repetitive patterns of neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in an electroencephalogram. Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoencephalography
Hemoencephalography (HEG) is a neurofeedback technique in the field of neurotherapy. Neurofeedback, a specific form of biofeedback, is based on the idea that human beings can consciously alter their brain function through training sessions in which they attempt to change the signal generated by their brain and measured via a neurological feedback mechanism. On completion of the process, participants increase cerebral blood flow to a specified region of the brain, consequently increasing brain activity and performance on tasks involving the specific region of the brain.Tinius, T. (2004). New Developments in Blood Flow Hemoencephalography. Hawthorne Press. Overview Both approaches to hemoencephalography, near infrared and passive infrared, are indirect measures of neural activity based on neurovascular coupling. Neurovascular coupling is the mechanism by which cerebral blood flow is matched to metabolic activity. When a region of the cortex is used in a specific cognitive task, neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotiv Systems
Emotiv Systems is an Australian electronics innovation company developing technologies to evolve human computer interaction incorporating non-conscious cues into the human-computer dialog to emulate human to human interaction. Developing brain–computer interfaces (BCIs) based on electroencephalography (EEG) technology, Emotiv Systems produced the EPOC near headset, a peripheral targeting the gaming market for Windows, OS X and Linux platforms. The EPOC has 16 electrodes and was originally designed to work as a BCI input device. The company was founded in 2003 by technology entrepreneurs Tan Le, Nam Do, Allan Snyder, and Neil Weste. However, doing a search of business entity name on Emotiv Systems at the business entity registry of the California Secretary of State reveals Emotiv Systems has ceased to exist, and, therefore, it should not be mixed up or confused with the currently active U.S. bioinformatics company Emotiv founded by Tan Le in 2011 in which Nam Do, Allan Snyder, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evoked Potential
An evoked potential or evoked response is an electrical potential in a specific pattern recorded from a specific part of the nervous system, especially the brain, of a human or other animals following presentation of a Stimulus (physiology), stimulus such as a light flash or a pure tone. Different types of potentials result from stimuli of different Stimulus modality, modalities and types. Evoked potential is distinct from spontaneous potentials as detected by electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), or other electrophysiology, electrophysiologic recording method. Such potentials are useful for electrodiagnostic medicine, electrodiagnosis and monitoring (medicine), monitoring that include detections of disease and drug-related sensory dysfunction and intraoperative monitoring of sensory pathway integrity. Evoked potential amplitudes tend to be low, ranging from less than a microvolt to several microvolts, compared to tens of microvolts for EEG, millivolts for EMG, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Consumer Brain-computer Interface Devices
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and to what degree. Where characteristics are different, the differences may then be evaluated to determine which thing is best suited for a particular purpose. The description of similarities and differences found between the two things is also called a comparison. Comparison can take many distinct forms, varying by field: To compare things, they must have characteristics that are similar enough in relevant ways to merit comparison. If two things are too different to compare in a useful way, an attempt to compare them is colloquially referred to in English as "comparing apples and oranges." Comparison is widely used in society, in science and in the arts. General usage Comparison is a natural activity, which even animals engage in when deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |