|
Silent Sinus Syndrome
Silent sinus syndrome is a spontaneous, asymptomatic collapse of an air sinus (usually the maxillary sinus and orbital floor) associated with negative sinus pressures. It can cause painless facial asymmetry, diplopia and enophthalmos. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms, and can be confirmed using a CT scan. Treatment is surgical involving making an outlet for mucous drainage from the obstructed sinus, and, in some cases, paired with reconstruction of the orbital floor. It is slightly more common in middle age. Signs and symptoms Silent sinus syndrome can cause facial asymmetry (usually without pain), and vision problems (such as diplopia and enophthalmos). It may also cause headaches, and a feeling of fullness in the nose. Mechanism Silent sinus syndrome most often affects the maxillary sinus, usually with a collapse of the orbital floor. It may also affect the frontal sinus or the ethmoid sinus. When the maxillary sinus is involved, the inferior oblique muscle may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ENT Surgery
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + ''rhino-'' + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enophthalmos
Enophthalmos is a posterior displacement of the eyeball within the orbit. It is due to either enlargement of the bony orbit and/or reduction of the orbital content, this in relation to each other. It should not be confused with its opposite, exophthalmos, which is the anterior displacement of the eye. It may be a congenital anomaly, or be acquired as a result of trauma (such as in a blowout fracture of the orbit), Horner's syndrome (apparent enophthalmos due to ptosis), Marfan syndrome, Duane's syndrome, silent sinus syndrome or phthisis bulbi Phthisis bulbi is a shrunken, non-functional eye. It may result from severe eye disease, inflammation or injury, or it may represent a complication of eye surgery. Treatment options include insertion of a prosthesis, which may be preceded by e .... References Further reading * External links Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit {{med-sign-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncinate Process Of Ethmoid Bone
In the ethmoid bone, a sickle shaped projection, the uncinate process, projects posteroinferiorly from the ethmoid labyrinth. Between the posterior edge of this process and the anterior surface of the ethmoid bulla, there is a two-dimensional space, resembling a crescent shape. This space continues laterally as a three-dimensional slit-like space - the ethmoidal infundibulum. This is bounded by the uncinate process, medially, the orbital lamina of ethmoid bone (lamina papyracea), laterally, and the ethmoidal bulla, posterosuperiorly. This concept is easier to understand if one imagine the infundibulum as a prism so that its medial face is the hiatus semilunaris. The "lateral face" of this infundibulum contains the ostium of the maxillary sinus, which, therefore, opens into the infundibulum. Variations The uncinate process can be attached to either the lateral nasal wall, on the lamina papyracea (50%), the anterior cranial fossa, on the ethmoidal roof (25%), or the middle concha (2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this. Manometric u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Oblique Muscle
The inferior oblique muscle or obliquus oculi inferior is a thin, narrow muscle placed near the anterior margin of the floor of the orbit. The inferior oblique is one of the extraocular muscles, and is attached to the maxillary bone (origin) and the posterior, inferior, lateral surface of the eye (insertion). The inferior oblique is innervated by the inferior branch of the oculomotor nerve. Structure The inferior oblique arises from the orbital surface of the maxilla, lateral to the lacrimal groove. Unlike the other extraocular muscles (recti and superior oblique), the inferior oblique muscle does ''not'' originate from the common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn). Passing lateralward, backward, and upward, between the inferior rectus and the floor of the orbit, and just underneath the lateral rectus muscle, the inferior oblique inserts onto the scleral surface between the inferior rectus and lateral rectus. In humans, the muscle is about 35 mm long. Innervation The i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoid Sinus
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The cells are variable in both size and number in the lateral mass of each of the ethmoid bones and cannot be palpated during an extraoral examination. They are divided into anterior and posterior groups. The ethmoid air cells are numerous thin-walled cavities situated in the ethmoidal labyrinth and completed by the frontal, maxilla, lacrimal, sphenoidal, and palatine bones. They lie between the upper parts of the nasal cavities and the orbits, and are separated from these cavities by thin bony lamellae. Groups of sinuses The groups of the ethmoidal air cells drain into the nasal meatuses.Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Anniko, Springer, 2010, page 188 * The posterior group the ''posterior ethmoidal sinus'' drains into the superior meatus above the middle nasal concha; sometimes one or more opens into the sphenoidal sinus. * The anterior group the ''anterior ethmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
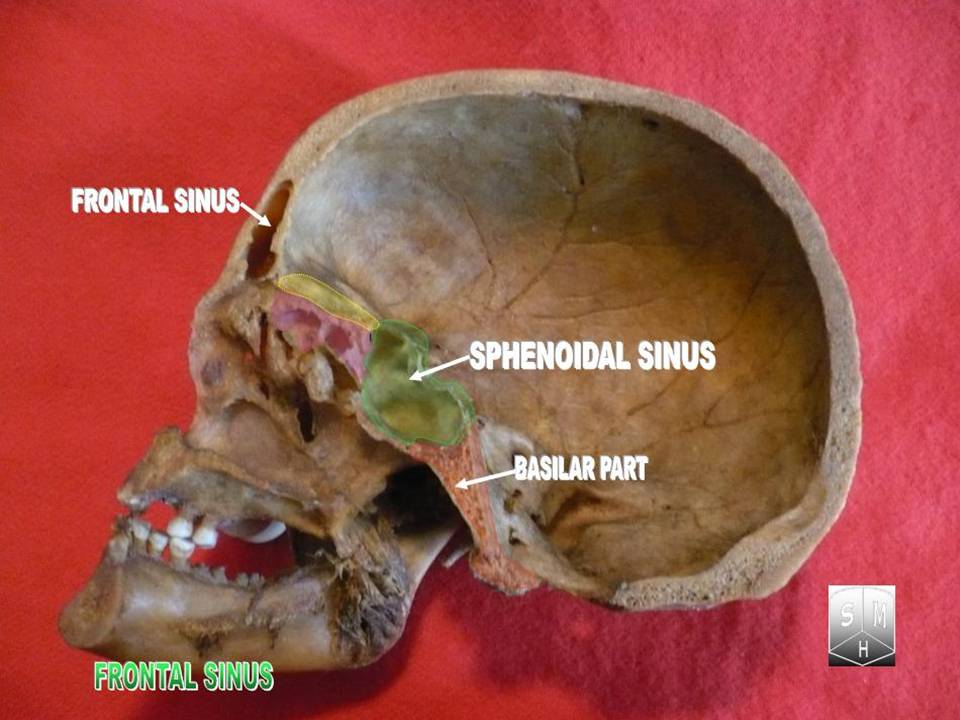
Frontal Sinus
The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. Each opens into the anterior part of the corresponding middle nasal meatus of the nose through the frontonasal duct which traverses the anterior part of the labyrinth of the ethmoid. These structures then open into the semilunar hiatus in the middle meatus. Structure Each frontal sinus is situated between the external and internal plates of the frontal bone.Frontal sinuses are rarely symmetrical. Their average measurements are as follows: height 28 mm, breadth 24 mm, depth 20 mm, creating a space of 6-7 ml. Blood supply The mucous membrane of the frontal sinuses receives arterial supply via the supraorbital artery, and anterior ethmoidal artery. Innervation The mucous membrane in this sinus is innervated by the supraorbital nerve, which contains the postganglionic parasympathetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery
The ''Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal that publishes original research in oral and maxillofacial surgery, oral pathology, and other related topics. It is published monthly by Elsevier on behalf of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. The current editor-in-chief is James R. Hupp and associate editor is Thomas Dodson. Another journal is ''Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery'' published by Springer Springer or springers may refer to: Publishers * Springer Science+Business Media, aka Springer International Publishing, a worldwide publishing group founded in 1842 in Germany formerly known as Springer-Verlag. ** Springer Nature, a multinationa ..., started at 1997. References External links * Dentistry journals Surgery journals Monthly journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 1943 {{dentistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nose
A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes through the pharynx, shared with the digestive system, and then into the rest of the respiratory system. In humans, the nose is located centrally on the face and serves as an alternative respiratory passage especially during suckling for infants. The protruding nose that completely separate from the mouth part is a characteristic found only in therian mammals. It has been theorized that this unique mammalian nose evolved from the anterior part of the upper jaw of the reptilian-like ancestors ( synapsids). Air treatment Acting as the first interface between the external environment and an animal's delicate internal lungs, a nose conditions incoming air, both as a function of thermal regulation and filtration during respiration, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced horizontally or vertically in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often voluntary. However, when occurring involuntarily, it results in impaired function of the extraocular muscles, where both eyes are still functional, but they cannot turn to target the desired object. Problems with these muscles may be due to mechanical problems, disorders of the neuromuscular junction, disorders of the cranial nerves ( III, IV, and VI) that innervate the muscles, and occasionally disorders involving the supranuclear oculomotor pathways or ingestion of toxins. Diplopia can be one of the first signs of a systemic disease, particularly to a muscular or neurological process, and it may disrupt a person's balance, movement, or reading abilities. Causes Diplopia has a diverse range of ophthalmologic, infectious, autoimmune, neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Asymmetry
Facial symmetry is one specific measure of bodily symmetry. Along with traits such as averageness and youthfulness it influences judgments of aesthetic traits of physical attractiveness and beauty. For instance, in mate selection, people have been shown to have a preference for symmetry. Facial bilateral symmetry is typically defined as fluctuating asymmetry of the face comparing random differences in facial features of the two sides of the face. The human face also has systematic, directional asymmetry: on average, the face (mouth, nose and eyes) sits systematically to the left with respect to the axis through the ears, the so-called ''aurofacial asymmetry''. Directional asymmetry Directional asymmetry is a systematic asymmetry of some parts of the face across the population. A theory of directional asymmetries in the human body is the axial twist hypothesis. As predicted by this theory, the eyes, nose and mouth are, on average, located slightly to the left of the axis through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)