|
Siege Of Steinvikholm (1537)
The siege of Steinvikholm was a siege of Steinvikholm Castle in Stjørdal, between the forces of the Catholic Deacon Knud Pederson Skanke and noble Tord Roed. The siege started in April after the Archbishop of Norway Olav Engelbrektsson had fled the country. Øystein Rian, "Olav Engelbrektsson", in: ''Norsk biografisk leksikon, 2. utgave, bind 2'' ''Norwegian Biographical Dictionary, 2nd Edition, Volume 2'' edited by Jon Gunnar ( Oslo : ''Kunnskapsforlaget'' Knowledge Publishers 2000 ), . The protestant forces laid siege to the castle and did a naval blockade of the fjord. The defenders fired their canons at the besiegers day and night, and refused several request to surrender to the protestant forces. But the defenders surrendered on 17 May. The reason was that the defenders heard a rumour that the noble Truid Ulfstand was on his way to Trondheim from Denmark with a force of 1500 men. The defenders stipulated for there surrender that; non of the defenders where to be puni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Wars Of Religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic Church, Catholic countries of Europe, or Christendom. Other motives during the wars involved revolt, territorial ambitions and European balance of power, great power conflicts. By the end of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), Catholic France had allied with the Protestant forces against the Catholic Habsburg monarchy. The wars were largely ended by the Peace of Westphalia (1648), which established a new political order that is now known as Westphalian sovereignty. The conflicts began with the minor Knights' Revolt (1522), followed by the larger German Peasants' War (1524–1525) in the Holy Roman Empire. Warfare intensified after the Catholic Church began the Counter-Reformation in 1545 against the growth of Protestantism. The conflicts cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huitfeldt (noble Family)
Huitfeldt is a Norwegian noble family. Name and origin Huitfeldt is originally an old Danish noble family. It came to Norway around 1581 with Anders Huitfeldt (ca. 1555–1620). In 1582 he married Margrete Pedersdatter Litle, the daughter of Peder Hansen Litle, officer in command at Akershus Fortress, and Ingeborg Nilsdatter Gyllenløve. Anders Huitfeldt became the owner of the seat farm Tronstad (''Tronstad Gård'') in Hurum in Buskerud, which for 220 years remained in the family's possession. In Denmark, the family's certainly documented paternal line goes back to Henrik Nielsen (fl. 1429) in Ventofte on Funen. During the Middle Ages, the family used the name ''Hogenskild''. Among these are the known knight Claus Hogenskild (fl. 1386) and member of the Council of the Kingdom Lord Peder Hogenskild (ca. 1400–1478). In 1526, when King Frederik I of Denmark and Norway instructed the Danish nobility to adopt permanent family names, the family took the name Huitfeldt based on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
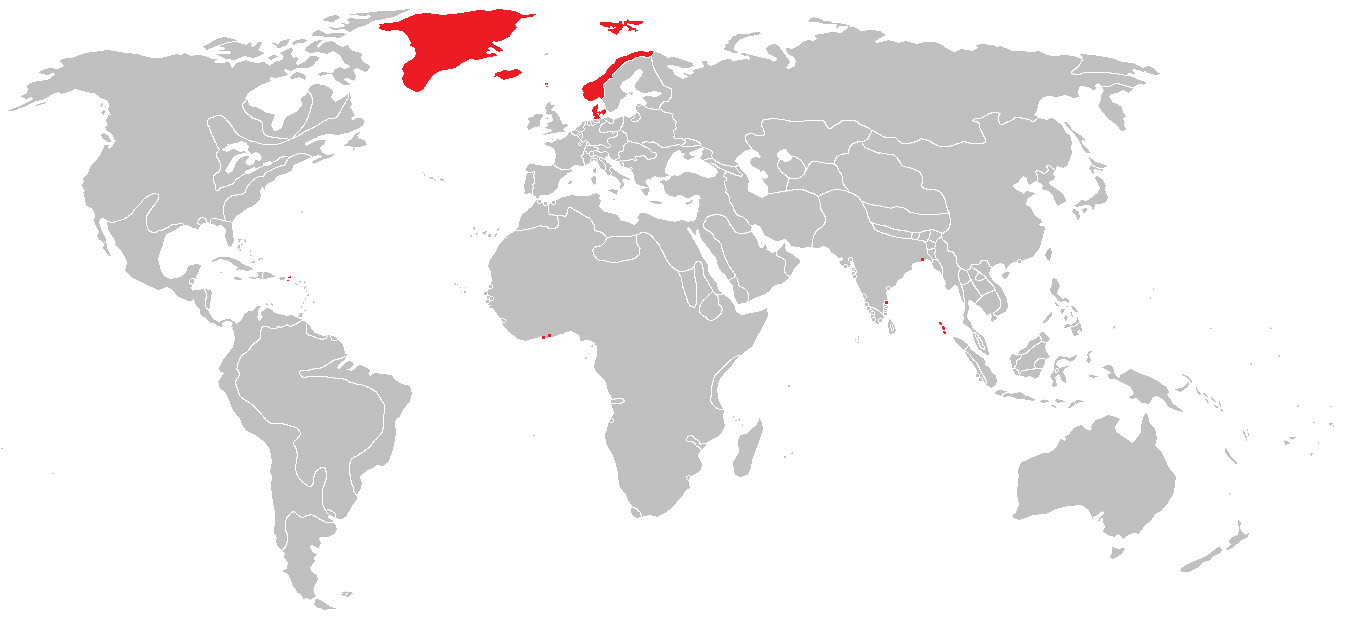
Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway (Danish and Norwegian: ) was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (including the then Norwegian overseas possessions: the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, and other possessions), the Duchy of Schleswig, and the Duchy of Holstein.Feldbæk 1998:21f, 125, 159ff, 281ff The state also claimed sovereignty over three historical peoples: Frisians, Gutes and Wends.Feldbæk 1998:21 Denmark–Norway had several colonies, namely the Danish Gold Coast, the Nicobar Islands, Serampore, Tharangambadi, and the Danish West Indies.Feldbæk 1998:23 The union was also known as the Dano-Norwegian Realm (''Det dansk-norske rige''), Twin Realms (''Tvillingerigerne'') or the Oldenburg Monarchy (''Oldenburg-monarkiet'') The state's inhabitants were mainly Danes, Norwegians and Germans, and also included Faroese, Icelanders and Inuit in the Norwegian overseas possessions, a Sami minori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving Denmark
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving Norway
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1537 In Norway
Events in the year 1537 in Norway. Overview 1537 is the year when Norway became a puppet state under the Danish Crown. Christian III did a coup d'état in Norway and made it a hereditary kingdom in a real union with Denmark that would last until 1814 when Frederick VI ceded the Kingdom of Norway to Charles XIII of Sweden. King Christian III also made by force Lutheranism state religion in Norway, and it was the state religion until 2012. 1537 is known as one of the darkest years in Norwegian history. Its also the start year for the early modern period in Norway (1537-1814), and the period known as ''The Puppet State era'' (''lydriketiden'') (1537-1660). Incumbents *Monarch: Olav Engelbrektsson as Regent (until 1 April); then Christian III Events *The Reformation in Norway: **January–February – The Commander of Bergenhus Fortress Eske Billes forces sacks farms of supporters of Archbishop Olav Engelbrektsson in Møre og Romsdal. **April 1 – The Archbishop of Norway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1537
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformation In Norway
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the ''Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X until January 1521. The Diet of Worms of May 1521 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Hamar
The siege of Hamar was a short siege that lasted for three days in late June 1537, between the forces of Catholic bishop Mogens Lauritssøn and noble Truid Ulfstand. Truid Ulfstand and his forces came down from Trondheim to arrest the bishop as a part of the Reformation in Denmark–Norway and Holstein. The bishop heard that he was going to be arrested and barricade himself and his men inside his farm at Hamar before the Protestant troops came. The Protestant troops where superior both in numbers and military tech, (most of the Protestant troops where German Landsknecht, but the Catholic troops where mostly peasant militia) and when the Protestant troops arrived they laid siege to the farm. The commander of the Protestant forces had a parley with the bishop, and gave him three days to surrender or he would burn the farm. On the third day of the siege the bishop surrendered and was taken as a prisoner to Denmark, where he died in 1542. According to the Hamar Chronicle, when the bisho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Norway
Eastern Norway ( nb, Østlandet, nn, Austlandet) is the geographical region of the south-eastern part of Norway. It consists of the counties Vestfold og Telemark, Viken, Oslo and Innlandet. Eastern Norway is by far the most populous region of Norway. It contains the country's capital, Oslo, which is Norway's most populous city. In Norwegian, the region is called ''Østlandet'' and ''Austlandet'' ("The east land") in contrast to Vestlandet ("The west land"). Geography As of 2015, the region had 2,593,085 inhabitants, 50.4% of Norway's population. The region is bounded by mountains in the north and west, the Swedish border to the east and by Viken and Skagerrak to the south. The border towards Sørlandet is less obvious. The mountains reach a height of 2469 metres in the Jotunheimen mountain range, the highest point in the Nordic countries (excluding Greenland). Other prominent mountain ranges include part of the Dovrefjell in the far north of the region, the Rondane north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Norway
Northern Norway ( nb, Nord-Norge, , nn, Nord-Noreg; se, Davvi-Norga) is a geographical Regions of Norway, region of Norway, consisting of the two northernmost counties Nordland and Troms og Finnmark, in total about 35% of the Norwegian mainland. Some of the largest towns in Northern Norway (from south to north) are Mo i Rana, Bodø, Narvik, Harstad, Tromsø and Alta, Norway, Alta. Northern Norway is often described as the land of the midnight sun and the land of the Aurora (astronomy), northern lights. Further north, halfway to the North Pole, is the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, traditionally not regarded as part of Northern Norway. The region is multi-cultural, housing not just Norwegians but also the indigenous peoples, indigenous Sami people, Norwegian Finns (known as Kven people, Kvens, distinct from the "Forest Finns" of Southern Norway) and Russians, Russian populations (mostly in Kirkenes). The Norwegian language dominates in most of the area; Sami speakers are mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trøndelag
Trøndelag (; sma, Trööndelage) is a county in the central part of Norway. It was created in 1687, then named Trondhjem County ( no, Trondhjems Amt); in 1804 the county was split into Nord-Trøndelag and Sør-Trøndelag by the King of Denmark-Norway, and the counties were reunited in 2018 after a vote of the two counties in 2016. The largest city in Trøndelag is the city of Trondheim. The administrative centre is Steinkjer, while Trondheim functions as the office of the county mayor. Both cities serve the office of the county governor; however, Steinkjer houses the main functions. Trøndelag county and the neighbouring Møre og Romsdal county together form what is known as Central Norway. A person from Trøndelag is called a ''trønder''. The dialect spoken in the area, trøndersk, is characterized by dropping out most vowel endings; see apocope. Trøndelag is one of the most fertile regions of Norway, with large agricultural output. The majority of the production ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

