|
Siege Of Aspis
The siege of Aspis or Clupea was fought in 255BC between Carthage and the Roman Republic. It was the first fighting on African land during the First Punic War. Background After defeating the Carthaginian navy sent to stop them from reaching Africa at the battle of Cape Ecnomus, the Romans landed close to Aspis, to the south of Carthage. Battle The Romans moved to besiege Aspis by building a trench and palisade to defend their ships. Carthage was not yet prepared to fight on land and the city fell after the garrison made a short resistance.Siege of Aspis, 256 B.C. Rickard, J (10 May 2007), Siege of Aspis, 256 BC. Retrieved on December 13, 2008. By taking Clupea, the Romans controlled the area of land opposite to Carthage and secured their rear in order to scour the enemy before them. The Romans forced Aspis to surrender, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated. The war began in 264 BC with the Romans gaining a foothold on Sicily at Messana (modern Messina). The Romans then pressed Syracuse, the only significant independent power on the island, into allying with them and laid siege to Carthage's main base at Akragas. A large Carthaginian army attempted to lift the siege in 262 BC but was heavily defeated at the Battle of Akragas. The Romans then built a navy to challenge the Carthaginians', and using novel tactics inflicted severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelibia
Kelibia (Kélibia) ( ar, قليبية, link=no '), often referred to as Klibia or Gallipia by European writers, is a coastal town on the Cap Bon peninsula, Nabeul Governorate in the far north-eastern part of Tunisia. Its sand beaches are considered some of the finest in the Mediterranean. History Known in Roman times as Clypia or Clupea, ( grc, Κλυπέα) the town was founded by the Carthaginians as the fortified town of Aspis ( grc, Ἀσπίς) in the 5th century BC. The Siege of Aspis in 255BC was the first African battle of the First Punic War. Clupea was also the seat of an ancient Christian bishopric. At the Council of Carthage (411), which brought together Catholic and Donatist bishops, Clypia was represented by Bishop Leodicius and the Donatist Geminius. Aurilius was one of the bishops whom the Arian Vandal king Huneric summoned to Carthage in 484 and then exiled. Two other bishops of Clypia took part in the Council of Carthage (525) (Bishop Crescentius) and Counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
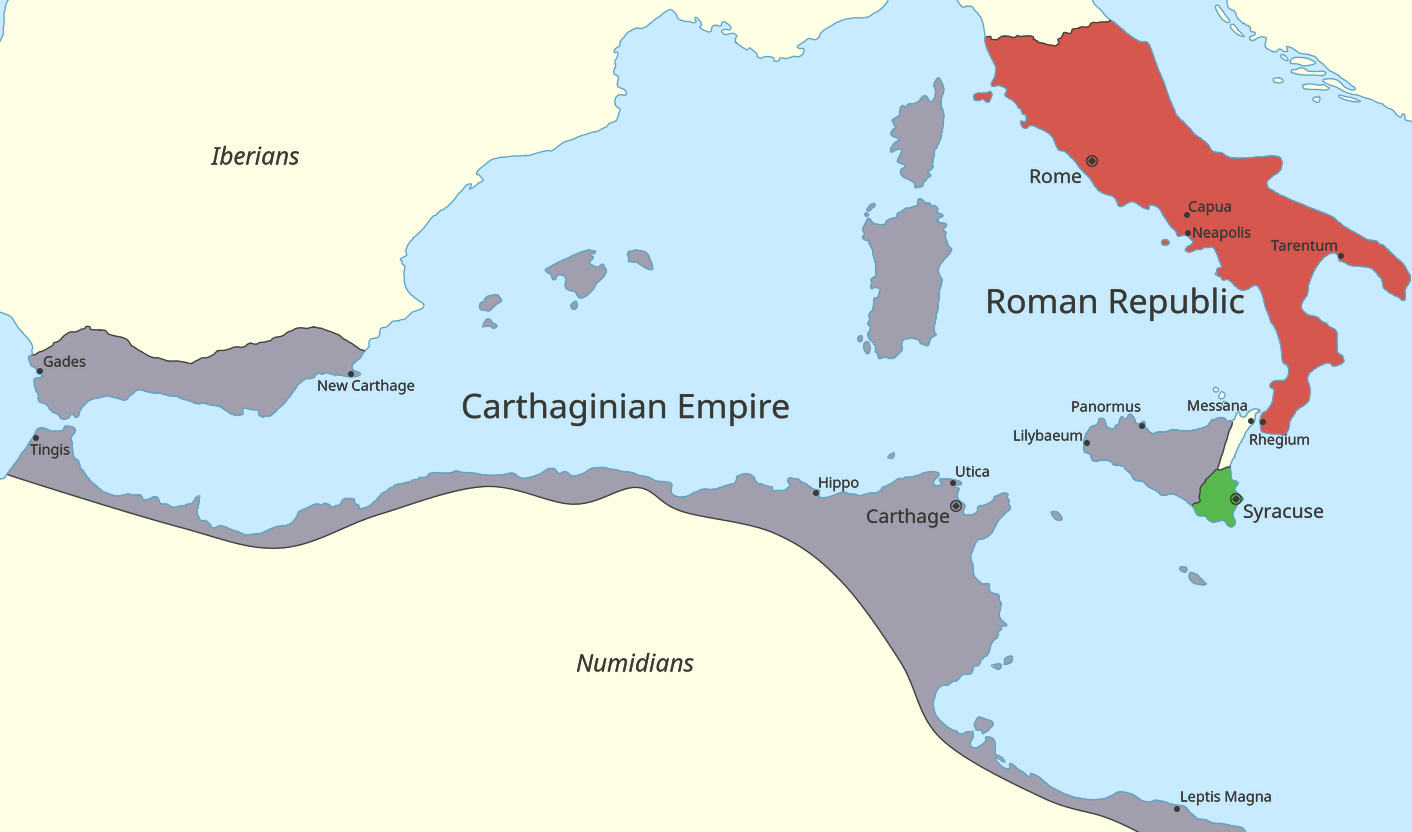
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage (state)
Carthage () was a settlement in modern Tunisia that later became a city-state and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians in the ninth century BC, Carthage reached its height in the fourth century BC as one of the largest metropolises in the worldGeorge Modelski, ''World Cities: –3000 to 2000'', Washington DC: FAROS 2000, 2003. . Figures in main tables are preferentially cited. Part of former estimates can be read at Evolutionary World Politics Homepage Archived 2008-12-28 at the Wayback Machine and the centre of the Carthaginian Empire, a major power in the ancient world that dominated the western Mediterranean. Following the Punic Wars, Carthage was destroyed by the Romans in 146 BC, who later rebuilt the city lavishly. Carthage was settled around 814 BC by colonists from Tyre, a leading Phoenician city-state located in present-day Lebanon. In the seventh century BC, following Phoenicia's conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Carthage became independent, gradually e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Atilius Regulus
Marcus Atilius Regulus () was a Roman statesman and general who was a consul of the Roman Republic in 267 BC and 256 BC. Much of his career was spent fighting the Carthaginians during the first Punic War. In 256 BC, he and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus defeated the Carthaginians at the massive naval battle off Cape Ecnomus; afterwards he led the Roman expedition to Africa but was defeated at the Bagradas River in spring of 255 BC. He was captured and then probably died of natural causes. Life Regulus was first consul in 267 BC. He campaigned with his co-consul (Lucius Julius Libo) against the Sallentini, captured Brundisium, and thence celebrated a double triumph. During the first Punic War, he then was elected suffect consul in 256 BC, in place of Quintus Caedicius, who had died in office. With his colleague, Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus, he fought and defeated a large Carthaginian fleet off the coast of Sicily – the Battle of Cape Ecnomus – and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa Province
Africa Proconsularis was a Roman province on the northern African coast that was established in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the coast of western Libya along the Gulf of Sirte. The territory was originally inhabited by Berber people, known in Latin as ''Mauri'' indigenous to all of North Africa west of Egypt; in the 9th century BC, Phoenicians built settlements along the Mediterranean Sea to facilitate shipping, of which Carthage rose to dominance in the 8th century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic. It was one of the wealthiest provinces in the western part of the Roman Empire, second only to Italy. Apart from the city of Carthage, other large settlements in the province were Hadrumetum (modern Sousse, Tunisia), capital of Byzacena, and Hippo Regius (modern Annaba, Algeria). History Rome's first province in northern Africa was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cape Ecnomus
The Battle of Cape Ecnomus or Eknomos ( grc, Ἔκνομος) was a naval battle, fought off southern Sicily, in 256 BC, between the fleets of Carthage and the Roman Republic, during the First Punic War (264–241 BC). It was the largest battle of the war and one of the largest naval battles in history. The Carthaginian fleet was commanded by Hanno and Hamilcar; the Roman fleet jointly by the consuls for the year, Marcus Atilius Regulus and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus. It resulted in a clear victory for the Romans. The Roman fleet of 330 warships plus an unknown number of transports had sailed from Ostia, the port of Rome, and had embarked approximately 26,000 picked legionaries shortly before the battle. They planned to cross to Africa and invade the Carthaginian homeland, in what is now Tunisia. The Carthaginians were aware of the Romans' intentions and mustered all available warships, 350, off the south coast of Sicily to intercept them. With a combined total of about 680 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palisade
A palisade, sometimes called a stakewall or a paling, is typically a fence or defensive wall made from iron or wooden stakes, or tree trunks, and used as a defensive structure or enclosure. Palisades can form a stockade. Etymology ''Palisade'' derives from ''pale'', from the Latin word ', meaning stake, specifically when used side by side to create a wood defensive wall. Typical construction Typical construction consisted of small or mid-sized tree trunks aligned vertically, with as little free space in between as possible. The trunks were sharpened or pointed at the top, and were driven into the ground and sometimes reinforced with additional construction. The height of a palisade ranged from around a metre to as high as 3–4 m. As a defensive structure, palisades were often used in conjunction with earthworks. Palisades were an excellent option for small forts or other hastily constructed fortifications. Since they were made of wood, they could often be quickly and easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in the west, to Egypt's Suez Canal. Varying sources limit it to the countries of Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia, a region that was known by the French during colonial times as "''Afrique du Nord''" and is known by Arabs as the Maghreb ("West", ''The western part of Arab World''). The United Nations definition includes Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, and the Western Sahara, the territory disputed between Morocco and the Sahrawi Republic. The African Union definition includes the Western Sahara and Mauritania but not Sudan. When used in the term Middle East and North Africa (MENA), it often refers only to the countries of the Maghreb. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and plazas de s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Adys
The battle of Adys (or Adis) took place in late 255 BC during the First Punic War between a Carthaginian army jointly commanded by Bostar, Hamilcar and Hasdrubal and a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus. Earlier in the year, the new Roman navy had established naval superiority and used this advantage to invade the Carthaginian homeland, which roughly aligned with modern Tunisia in North Africa. After landing on the Cape Bon Peninsula and conducting a successful campaign, the fleet returned to Sicily, leaving Regulus with 15,500 men to hold the lodgement in Africa over the winter. Instead of holding his position, Regulus advanced towards the Carthaginian capital, Carthage. The Carthaginian army established itself on a rocky hill near Adys (modern Uthina) where Regulus was besieging the town. Regulus had his forces execute a night march to launch twin dawn assaults on the Carthaginians' fortified hilltop camp. One part of this force was repulsed and pursued down the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
255 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 255 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Nobilior and Paullus (or, less frequently, year 499 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 255 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Republic * The Battle of Adis (or Adys) is fought near the city of that name, 40 miles (64 kilometres) southeast of Carthage, between Carthaginian forces and a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus. The Romans inflict a crushing defeat upon the Carthaginians, and the latter then sue for peace. The ensuing negotiations between the parties lead to Regulus demanding Carthage agree to an unconditional surrender, cede Sicily, Corsica and Sardinia to Rome, renounce the use of their navy, pay an indemnity, and sign a vassal-like treaty. These terms are so harsh that the people of Cartha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The First Punic War
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wherea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)