|
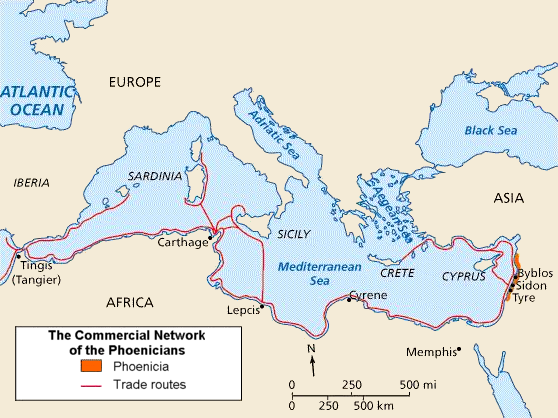
Siege Of Tunis (Mercenary War)
During the Siege of Tunis in October 238 BC a rebel army under Mathos was besieged by a Carthaginian force under Hamilcar Barca and Hannibal. The Carthaginian army, which had served on Sicily during the First Punic War, mutinied in late 241 BC in the wake of Carthage's defeat, starting the Mercenary War. After three years of increasingly bitter war, the Carthaginians defeated the rebel field army at the Battle of the Saw, capturing its leaders. The Carthaginians then moved to besiege the rebels' strongest remaining stronghold at Tunis. The Carthaginian commander, Hamilcar, split his forces to blockade the rebels from both north and south. At the northern camp, commanded by his subordinate Hannibal, he had the ten captured rebel leaders tortured to death and their bodies crucified before returning to his own base to the south of Tunis. Mathos organised a night attack against Hannibal's camp, which took the ill-disciplined Carthaginian defenders by surprise. It scattered their ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercenary War
The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian control. It lasted from 241 to late 238 or early 237 BC and ended with Carthage suppressing both the mutiny and the revolt. The war began in 241 BC as a dispute over the payment of wages owed to 20,000 foreign soldiers who had fought for Carthage in Sicily during the First Punic War. When a compromise seemed to have been reached, the army erupted into full-scale mutiny under the leadership of Spendius and Matho. 70,000 Africans from Carthage's oppressed dependent territories flocked to join them, bringing supplies and finance. War-weary Carthage fared poorly in the initial engagements of the war, especially under the generalship of Hanno. Hamilcar Barca, a veteran of the campaigns in Sicily (and father of Hannibal Barca), was given jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conquered or otherwise threatened to conquer. In case of alliances, lesser parties may pay tribute to more powerful parties as a sign of allegiance and often in order to finance projects that would benefit both parties. To be called "tribute" a recognition by the payer of political submission to the payee is normally required; the large sums, essentially protection money, paid by the later Roman and Byzantine Empires to barbarian peoples to prevent them attacking imperial territory, would not usually be termed "tribute" as the Empire accepted no inferior political position. Payments ''by'' a superior political entity to an inferior one, made for various purposes, are described by terms including " subsidy". The ancient Persian Achaemenid Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigel Bagnall
Field Marshal Sir Nigel Thomas Bagnall, (10 February 1927 – 8 April 2002) was Chief of the General Staff (CGS), the professional head of the British Army, from 1985 to 1988. Early in his military career he saw action during the Palestine Emergency, the Malayan Emergency, the Cyprus Emergency and the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation, and later in his career he provided advice to the British Government on the future role of Britain's nuclear weapons. Army career Born the son of Lieutenant Colonel Harry Stephen Bagnall and Marjory May Bagnall and educated at Wellington College,Debrett's People of Today 1994 Bagnall undertook National Service for a year before being commissioned into the Green Howards on 5 January 1946. Shortly afterwards, however, on 13 February 1946 he transferred to the Parachute Regiment and was deployed to Palestine where the British Mandate was about to end. Promoted to lieutenant on 24 September 1949, he served in Malaya, where as a platoon commander, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Utica
The Battle of Utica took place early in 240 BC between a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian army commanded by Hanno II the Great, Hanno and a force of rebellious mutiny, mutineers possibly led by Spendius. It was the first major engagement of the Mercenary War between Carthage and the combined forces of mutinous ex-Carthaginian troops and rebellious African cities which broke out in the wake of the First Punic War. Both sides were routed during the course of the battle, which ended with the rebels occupying the field but was strategically inconclusive. The rebel army, some 10,000 strong, was blockade, blockading the city of Utica, Tunisia, Utica when the Carthaginian army of 8,000–10,000 men and 100 War elephant, elephants stormed their camp and routed them. Satisfied with their victory, the Carthaginians failed to pursue and dispersed to loot, forage and celebrate. The rebels regrouped, returned, attacked the Carthaginians who were occupying their old camp and routed them in tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Elephants
A war elephant was an elephant that was trained and guided by humans for combat. The war elephant's main use was to charge the enemy, break their ranks and instill terror and fear. Elephantry is a term for specific military units using elephant-mounted troops. Description War elephants played a critical role in several key battles in antiquity, especially in Ancient India. While seeing limited and periodic use in Ancient China, they became a permanent fixture in armies of historical kingdoms in Southeast Asia. During classical antiquity they were also used in ancient Persia and in the Mediterranean world within armies of Macedon, Hellenistic Greek states, the Roman Republic and later Empire, and Carthage in North Africa. In some regions they maintained a firm presence on the battlefield throughout the Middle Ages. However, their use declined with the spread of firearms and other gunpowder weaponry in early modern warfare. After this, war elephants became restricted to non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bizerte
Bizerte or Bizerta ( ar, بنزرت, translit=Binzart , it, Biserta, french: link=no, Bizérte) the classical Hippo, is a city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia. It is the northernmost city in Africa, located 65 km (40mil) north of the capital Tunis. It is also known as the last town to remain under French control after the rest of the country won its independence from France. The city had 142,966 inhabitants in 2014. Names Hippo is the latinization of a PunicPerseus Digital Library Perseus.tufts.edu name ( xpu, 𐤏𐤐𐤅𐤍, ), probably related to the word ''ûbôn'', meaning "harbor". To distinguish it from Hippo Regius (the modern |
Hippo Diarrhytus
Bizerte or Bizerta ( ar, بنزرت, translit=Binzart , it, Biserta, french: link=no, Bizérte) the classical Hippo, is a city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia. It is the northernmost city in Africa, located 65 km (40mil) north of the capital Tunis. It is also known as the last town to remain under French control after the rest of the country won its independence from France. The city had 142,966 inhabitants in 2014. Names Hippo is the latinization of a PunicPerseus Digital Library Perseus.tufts.edu name ( xpu, 𐤏𐤐𐤅𐤍, ), probably related to the word ''ûbôn'', meaning "harbor". To distinguish it from (the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utica, Tunisia
Utica () was an ancient Phoenician and Carthaginian city located near the outflow of the Medjerda River into the Mediterranean, between Carthage in the south and Hippo Diarrhytus (present-day Bizerte) in the north. It is traditionally considered to be the first colony to have been founded by the Phoenicians in North Africa. After Carthage's loss to Rome in the Punic Wars, Utica was an important Roman colony for seven centuries. Today, Utica no longer exists, and its remains are located in Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia – not on the coast where it once lay, but further inland because deforestation and agriculture upriver led to massive erosion and the Medjerda River silted over its original mouth."Utica (Utique) Tunisia" ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercenary War Manoeuvres
A mercenary, sometimes Pseudonym, also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rather than for political interests. Beginning in the 20th century, mercenaries have increasingly come to be seen as less entitled to protections by rules of war than non-mercenaries. The Geneva Conventions declare that mercenaries are not recognized as legitimate combatants and do not have to be granted the same legal protections as captured service personnel of the military, armed forces. In practice, whether or not a person is a mercenary may be a matter of degree, as financial and political interests may overlap. Modern mercenary organizations are generally referred to as Private military company, private military companies or PMCs. Laws of war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail. Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed constitution or the separation of powers in government, his in-depth discussion of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", which influenced Montesquieu's ''The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's ''Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909–2008), who published studies related to him for 50 years, including a long commentary of his ''Histories'' and a biography. Early life Polybius was born around 200 BC in Megalopolis, Greece, Megalopolis, Arcadia (region), Arcadia, when it was an active member of the Achaean League. The town was revived, along with other Achaean states, a century before he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg , caption = The Berber ethnic flag , population = 36 million , region1 = Morocco , pop1 = 14 million to 18 million , region2 = Algeria , pop2 = 9 million to ~13 million , region3 = Mauritania , pop3 = 2.9 million , region4 = Niger , pop4 = 2.6 million, Niger: 11% of 23.6 million , region5 = France , pop5 = 2 million , region6 = Mali , pop6 = 850,000 , region7 = Libya , pop7 = 600,000 , region8 = Belgium , pop8 = 500,000 (including descendants) , region9 = Netherlands , pop9 = 467,455 (including descendants) , region10 = Burkina Faso , pop10 = 406,271, Burkina Faso: 1.9% of 21.4 million , region11 = Egypt , pop11 = 23,000 or 1,826,580 , region12 = Tunisia , pop12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In Ancient Rome
Slavery in ancient Rome played an important role in society and the economy. Besides manual labour, slaves performed many domestic services and might be employed at highly skilled jobs and professions. Accountants and physicians were often slaves. Slaves of Greek origin in particular might be highly educated. Unskilled slaves, or those sentenced to slavery as punishment, worked on farms, in mines, and at mills. Slaves were considered property under Roman law and had no legal personhood. Most slaves would never be freed. Unlike Roman citizens, they could be subjected to corporal punishment, sexual exploitation (prostitutes were often slaves), torture and summary execution. Over time, however, slaves gained increased legal protection, including the right to file complaints against their masters. One major source of slaves had been Roman military expansion during the Republic. The use of former enemy soldiers as slaves led perhaps inevitably to a series of ''en masse'' armed rebel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)