|
Siege Of Namur (1577)
The siege of Namur can refer to a number of sieges of the city of Namur in Belgium: * Siege of Namur (1577) - John of Austria takes the citadel by surprise * Siege of Namur (1692) by the French (under Louis XIV and Vauban) * Siege of Namur (1695) by the Allies (Dutch, English and Brandenburgers) * by the French, during the War of the Austrian Succession * Siege of Namur (1792) by the French, during the War of the First Coalition * Siege of Namur (1914) The siege of Namur (french: Siège de Namur) was a battle between Belgian and German forces around the fortified city of Namur during the First World War. Namur was defended by a ring of modern fortresses, known as the Fortified Position of Namu ... by the Germans, during World War I See also * Fortified Position of Namur {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
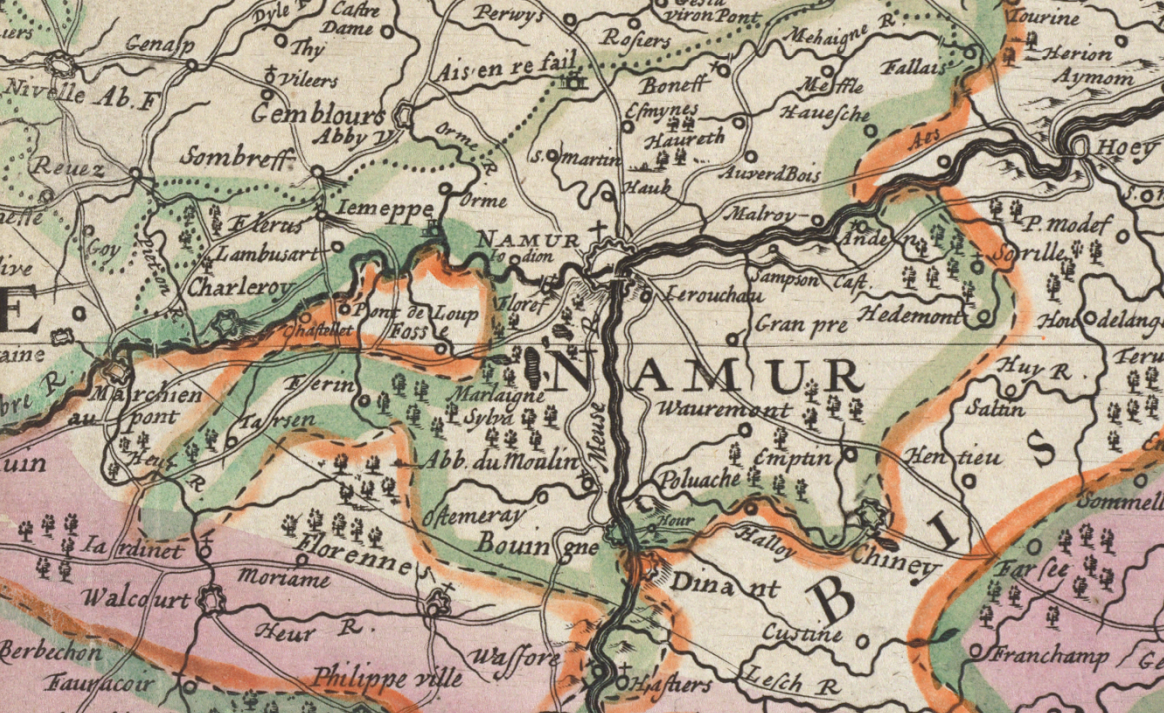
Namur (city)
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration. Namur stands at the confluence of the rivers Sambre and Meuse and straddles three different regions – Hesbaye to the north, Condroz to the south-east, and Entre-Sambre-et-Meuse to the south-west. The city of Charleroi is located to the west. The language spoken is French. The municipality consists of the following districts: Beez, Belgrade, Boninne, Bouge, Champion, Cognelée, Daussoulx, Dave, Erpent, Flawinne, Gelbressée, Jambes, Lives-sur-Meuse, Loyers, Malonne, Marche-les-Dames, Naninne, Saint-Servais, Saint-Marc, Suarlée, Temploux, Vedrin, Wépion, and Wierde. History Early history The town began as an important trading settlement in Celtic times, straddling east–west and north–south trade routes across the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Namur (1577)
The siege of Namur can refer to a number of sieges of the city of Namur in Belgium: * Siege of Namur (1577) - John of Austria takes the citadel by surprise * Siege of Namur (1692) by the French (under Louis XIV and Vauban) * Siege of Namur (1695) by the Allies (Dutch, English and Brandenburgers) * by the French, during the War of the Austrian Succession * Siege of Namur (1792) by the French, during the War of the First Coalition * Siege of Namur (1914) The siege of Namur (french: Siège de Namur) was a battle between Belgian and German forces around the fortified city of Namur during the First World War. Namur was defended by a ring of modern fortresses, known as the Fortified Position of Namu ... by the Germans, during World War I See also * Fortified Position of Namur {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Austria
John of Austria ( es, Juan, link=no, german: Johann; 24 February 1547 – 1 October 1578) was the natural son born to Holy Roman Emperor Charles V late in life when he was a widower. Charles V met his son only once, recognizing him in a secret codicil to his will. John became a military leader in the service of his half-brother, King Philip II of Spain, Charles V's legitimate heir, and is best known for his role as the admiral of the Holy Alliance fleet at the Battle of Lepanto. Life Early years Born in the Free imperial city of Regensburg, Upper Palatinate, John of Austria was the product of a brief liaison between Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (a widower since 1539) and Barbara Blomberg, a burgher's daughter and singer. In the summer of 1554, the boy was taken to the castle of Luis de Quijada in Villagarcía de Campos, Valladolid. Magdalena de Ulloa, the wife of Luis de Quijada, took charge of his education, assisted by the Latin teacher Guillén Prieto, the chaplain Garcí ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Namur (1692)
The siege of Namur, 25 May–30 June 1692, was a major engagement of the Nine Years' War, and was part of the French grand plan (devised over the winter of 1691–92) to defeat the forces of the Grand Alliance and bring a swift conclusion to the war. Namur, sitting on the confluence of the Meuse and Sambre rivers, was a considerable fortress, and was a significant political and military asset. French forces, guided by Vauban, forced the town's surrender on 5 June, but the citadel, staunchly defended by Menno van Coehoorn, managed to hold on until 30 June before capitulating, bringing an end to the 36-day siege. Concerned that King William III planned to recapture the stronghold, King Louis XIV subsequently ordered his commander-in-chief, the duc de Luxembourg, to join battle with the Allies in the field, resulting in the bloody Battle of Steenkerque on 3 August. Background As in 1691, five large armies were created for the five major fronts of the war: Flanders, the Moselle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Namur (1695)
The 1695 Siege of Namur or Second Siege of Namur took place during the Nine Years' War between 2 July and 4 September 1695. Its capture by the French in the 1692 and recapture by the Grand Alliance in 1695 are often viewed as the defining events of the war; the second siege is considered to be William III's most significant military success during the war. Background After 1693, Louis XIV assumed a largely defensive posture in Flanders. French victories at Steinkirk and Landen and the capture of Namur, Mons, Huy and Charleroi failed to force the Dutch Republic out of the war. The cost had exhausted the French economy with crop failures in 1693 and 1694 causing widespread famine in France and Northern Italy. The Dutch Republic remained intact and the Alliance held together under William through four years of war. Their losses were damaging but not critical; in 1694, they had recaptured towns like Huy and Diksmuide, and by 1695 held a numerical advantage for the first t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George's War in North America, the War of Jenkins' Ear, the First Carnatic War and the First Silesian War, First and Second Silesian Wars. Its pretext was the right of Maria Theresa to succeed her father Emperor Charles VI as ruler of the Habsburg monarchy. Kingdom of France, France, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and Electorate of Bavaria, Bavaria saw it as an opportunity to challenge Habsburg power, while Maria Theresa was backed by Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, the Dutch Republic and Electorate of Hanover, Hanover, collectively known as the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713, Pragmatic Allies. As the conflict widened, it drew in other participants, among them History of Spain (1700–1810), Spain, Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia, Electorate of Saxony, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Namur (1792)
The siege of Namur (21 November - 2 December 1792) took place during the Flanders campaign of the War of the First Coalition. The Army of the Ardennes under the Count of Valence captured the city which was then part of the Austrian Netherlands. Background After the Battle of Jemappes, the Count of Valence divided his forces and sent 35,000 men towards the Meuse. A detachment entered Liège on November 28 under the acclamations of the inhabitants; the rest was sent to undertake the siege of Namur. Due to the proximity of the Austrian army under Johann Peter Beaulieu, Valence devoted this operation to the Army of the Ardennes which would be reinforced by the Harville division. Beaulieu, avoiding battle with the Army of the Ardennes, fell back towards the Aische Forest. Three French brigades encamped around the citadel of Namur awaiting the arrival of their artillery from the Fortress of Charlemont near Givet. The strategist Antoine-Henri Jomini pointed out that by advancing mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The First Coalition
The War of the First Coalition (french: Guerre de la Première Coalition) was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797 initially against the Kingdom of France (1791-92), constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French First Republic, French Republic that succeeded it. They were only loosely allied and fought without much apparent coordination or agreement; each power had its eye on a different part of France it wanted to appropriate after a French defeat, which never occurred. Noah Shusterman – ''De Franse Revolutie (The French Revolution).'' Veen Media, Amsterdam, 2015. (Translation of: ''The French Revolution. Faith, Desire, and Politics.'' Routledge, London/New York, 2014.) Chapter 7 (p. 271–312) : The federalist revolts, the Vendée and the beginning of the Terror (summer–fall 1793). Relations between the French revolutionaries and neighbouring monarchies had deteriorated following the Declaration of Pillnitz in August 1791. Eight mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Namur (1914)
The siege of Namur (french: Siège de Namur) was a battle between Belgian and German forces around the fortified city of Namur during the First World War. Namur was defended by a ring of modern fortresses, known as the Fortified Position of Namur and guarded by the 4th Division of the Belgian Army. The purpose of the fortified Belgian cities was to delay an invasion force until troops from the states guaranteeing Belgian independence came to their aid. The French Fifth Army planned to counter-attack while the Germans were besieging Namur. The German 2nd Army arrived in force on 20 August 1914 and used the experience gained from the Battle of Liège . The Germans did not attempt a ''coup de main'' but waited until the next day and bombarded the forts using super-heavy siege artillery and four batteries on loan from Austria-Hungary. The forts were destroyed by the bombardment, some being demolished by conventional heavy artillery rather than the siege guns, due to flaws in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |