|
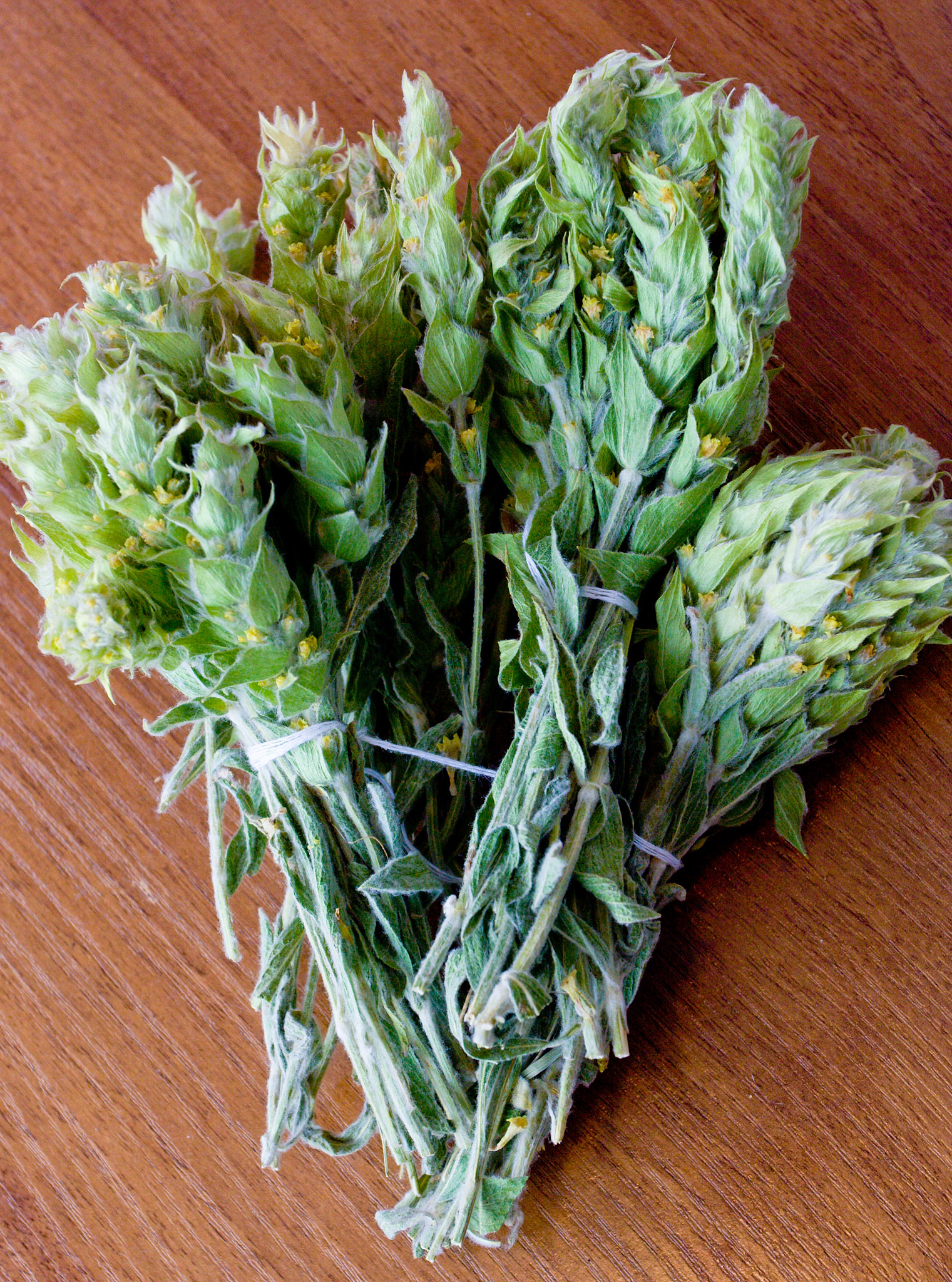
Sideritis Elica
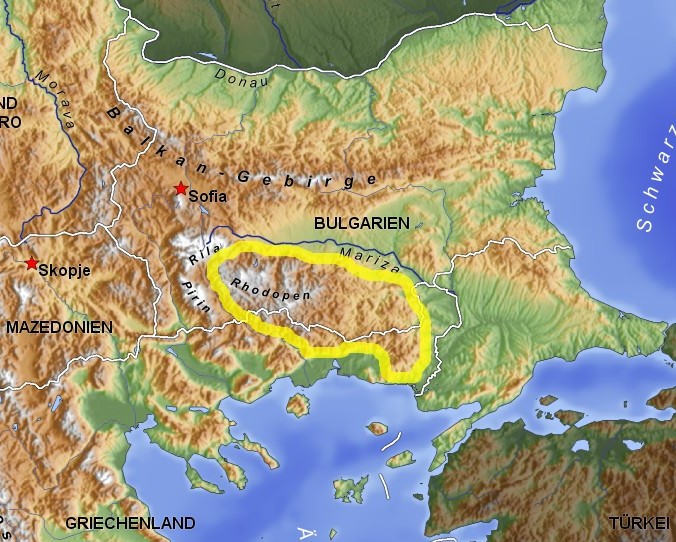
''Sideritis elica'' is a plant species in the genus '' Sideritis'', endemic to Bulgaria. The species was discovered and described by Associate Prof. Ina Aneva and Senior Assistant Prof. Georgi Bonchev of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, as well as by Prof. Petar Zhelev of the University of Forestry in Sofia. The molecular analysis supports the morphological data about the divergence between the more widespread '' Sideritis scardica'' and ''Sideritis elica''. The studied populations of the two taxa were found to be genetically distant. The species is only known from the northern foothills of the central Rhodope Mountains The Rhodopes (; , ; , ''Rodopi''; ) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak ..., where it grows in the Chervenata Stena Reserve near Asenovgrad and Bachkovo Monastery. References {{Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sideritis
''Sideritis'', also known as ironwort, mountain tea, Greek tea and shepherd's tea, is a genus of flowering plants known for their use as herbal medicine, commonly as a herbal tea. They are abundant in Mediterranean regions, the Balkans, the Iberian Peninsula and Macaronesia, but can also be found in Central Europe and temperate Asia. History and etymology In Greek, "sideritis" ( Gr: σιδηρίτις) can be literally translated as "he who is made of iron". The plant was known to ancient Greeks, specifically Pedanius Dioscorides and Theophrastus. Although Dioscorides describes three species, only one (probably ''S. scordioides'') is thought to belong to ''Sideritis''. In ancient times "sideritis" was a generic reference for plants capable of healing wounds caused by iron weapons during battles. However, others hold that the name stems from the shape of the sepal, which resembles the tip of a spear. Taxonomy In 2002, molecular phylogenetic research found ''Sideritis'' and five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey to the south, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, and Romania to the north. It covers a territory of and is the tenth largest within the European Union and the List of European countries by area, sixteenth-largest country in Europe by area. Sofia is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city; other major cities include Burgas, Plovdiv, and Varna, Bulgaria, Varna. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Karanovo culture (6,500 BC). In the 6th to 3rd century BC, the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Ancient Macedonians, Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Academy Of Sciences
The Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (abbreviated BAS; , ''Bŭlgarska akademiya na naukite'', abbreviated БАН) is the National Academy of Bulgaria, established in 1869. The Academy, with headquarters in Sofia, is autonomous and consists of a Society of Academicians, Correspondent Members and Foreign Members. It publishes and circulates different scientific works, encyclopaedias, dictionaries and journals, and runs its own publishing house. The activities are distributed in three main branches: ''Natural, mathematical and engineering sciences''; ''Biological, medical and agrarian sciences'' and ''Social sciences, humanities and art''. They are structured in 42 independent scientific institutes, and a dozen of laboratories and other sections. Julian Revalski has been the president of the BAS since 2016. As of 2022, its budget was 119,860 million leva (€61.28 million). History As Bulgaria was part of the Ottoman Empire, Bulgarian émigrés founded the ''Bulgarian Literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Forestry, Sofia
The University of Forestry (, often abbreviated as LTU), based in Sofia, is a state university with six faculties with a total of 30 departments. It is located in Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria and is close to the Technical University and the University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy. The University of Forestry has two Research Forests: the first one located near the village of Yundola in coniferous forest, and the other in the village of Barzia in deciduous forest. It also has a Training and Experimental Field Station in Vrazhdebna suburb of Sofia. For more than 90 years now, the University of Forestry has been the only university in Bulgaria providing education in forestry, forest management, landscape architecture and wood processing. In the 1990s, the range of scientific fields was expanded to include ecology, agronomy, veterinary medicine and business management. In mid 1990s, the university adopted the three-level degree system of bachelor, master and doctor degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofia
Sofia is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain, in the western part of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar (river), Iskar river and has many mineral springs, such as the Sofia Central Mineral Baths. It has a humid continental climate. Known as Serdica in Classical antiquity, antiquity, Sofia has been an area of human habitation since at least 7000 BC. The recorded history of the city begins with the attestation of the conquest of Serdica by the Roman Republic in 29 BC from the Celtic settlement of Southeast Europe, Celtic tribe Serdi. During the decline of the Roman Empire, the city was raided by Huns, Visigoths, Pannonian Avars, Avars, and Slavs. In 809, Serdica was incorporated into the First Bulgarian Empire by Khan (title), Khan Krum and became known as Sredets. In 1018, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines ended Bulgarian rule until 1194, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian National Radio
Bulgarian National Radio (, ''Bǎlgarsko nacionalno radio''; abbreviated to БНР, BNR) is Bulgaria's national radio broadcasting organisation. It operates two national channels and nine regional channels, as well as an international service ( Radio Bulgaria) which broadcasts in 11 languages. History Until World War II Listening to radio broadcasts from other countries having become popular in Bulgaria by the late 1920s, a group of engineers and intellectuals founded ''Rodno Radio'' ("Native, or Homeland, Radio") on 30 March 1930 with the aim of providing Sofia with its own radio station. Broadcasting began in June of the same year. ''Rodno Radio'' was renamed ''Radio Sofija'' in 1934. On 25 January 1935, Boris III of Bulgaria signed a Decree nationalising ''Rodno Radio'' and making all broadcasting in Bulgaria a state-organised activity. In early 1936, a new and more powerful medium-wave transmitter sited near Sofia was joined by additional transmitting stations at Stara Zagor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sideritis Scardica
''Sideritis scardica'' is a species of flowering plant in the family ''Lamiaceae''. It is commonly called Greek mountain tea, is a flowering plant species of ''Sideritis'', native to Albania, Bulgaria, Greece in particular in the area of the Mount Olympus, Kosovo, North Macedonia North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n .... It was first described in 1844. References {{Taxonbar, from= Q15367189 scardica Taxa named by August Grisebach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; , ; , ''Rodopi''; ) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. Name and mythology The name of the Rhodope Mountains is of Thracian origin. Rhod-ope (Род-oпа) is interpreted as the first name of a river, meaning "rusty/reddish river", wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asenovgrad
Asenovgrad ( ) is a town in central southern Bulgaria, part of Plovdiv Province. It is the largest town in Bulgaria that is not a province center. Previously known as ''Stanimaka'' (; ), it was renamed in 1934 after the 13th-century tsar Ivan Asen II. Asenovgrad also includes the districts of Gorni Voden and Dolni Voden, which until 1986 were separate villages. According to the census data of 2021, the population of the city is 47 815 people. Above the town are the remains of the Asen Fortress, an old fortress that was strengthened under Tsar Ivan Asen II and turned into an important military post in the defense of the southern borders of the Second Bulgarian Kingdom.The city is known for its many churches, monasteries and chapels and is often called Little Jerusalem. It is also known as the "City of Bridal Gowns" because of the large number of ateliers and shops for wedding dresses and accessories. The majority of Asenovgrad residents are Bulgarians, with representatives of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
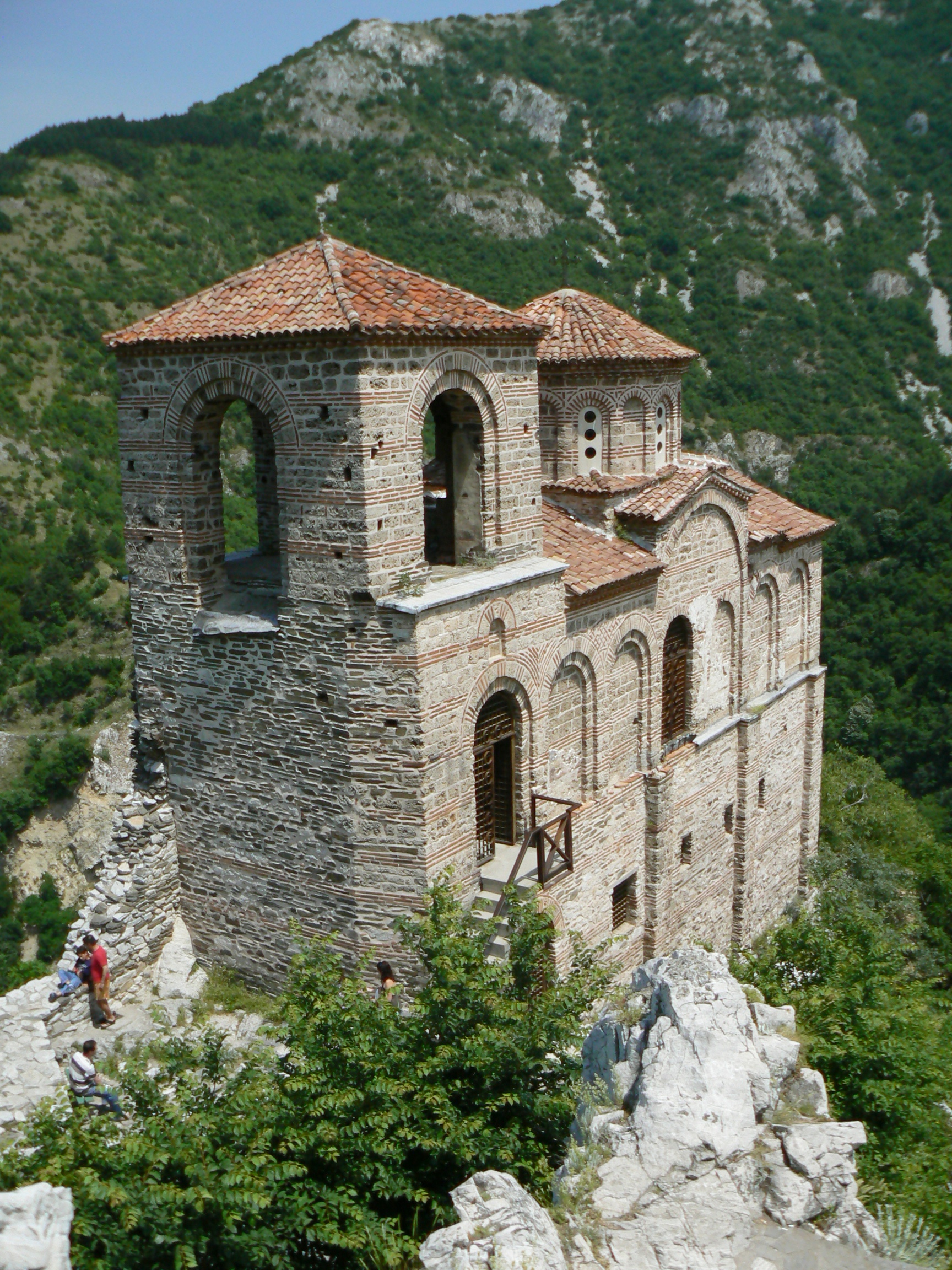
Bachkovo Monastery
The Bachkovo Monastery of the Dormition of the Theotokos ( "Успение Богородично", ''Bachkovski manastir'', ka, პეტრიწონის მონასტერი, ''Petritsonis Monasteri''), archaically the Petritsoni Monastery or Monastery of the Mother of God Petritzonitissa is a major Eastern Orthodox monastery in Southern Bulgaria. It is located on the right bank of the Chepelare River, 189 km from Sofia and 10 km south of Asenovgrad, and is directly subordinate to the Holy Synod of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. The monastery is known and appreciated for the unique combination of Byzantine, Georgian people, Georgian and Bulgarian culture, united by the common faith. History The monastery was founded in 1083 by Prince Gregory Pakourianos, a prominent statesman and military commander in the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine service, as a Georgian-dominated Orthodox monastery. He set up a seminary(school) for the youth at the monastery. The cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Described In 2022
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars from carbon dioxide and water, using the green pigment chlorophyll. Exceptions are parasitic plants that have lost the genes for chlorophyll and photosynthesis, and obtain their energy from other plants or fungi. Most plants are multicellular, except for some green algae. Historically, as in Aristotle's biology, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi. Definitions have narrowed since then; current definitions exclude fungi and some of the algae. By the definition used in this article, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (green plants), which consists of the green algae and the embryophytes or land plants (hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, conifers and other gymnosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |