|
Siddaganga Matha
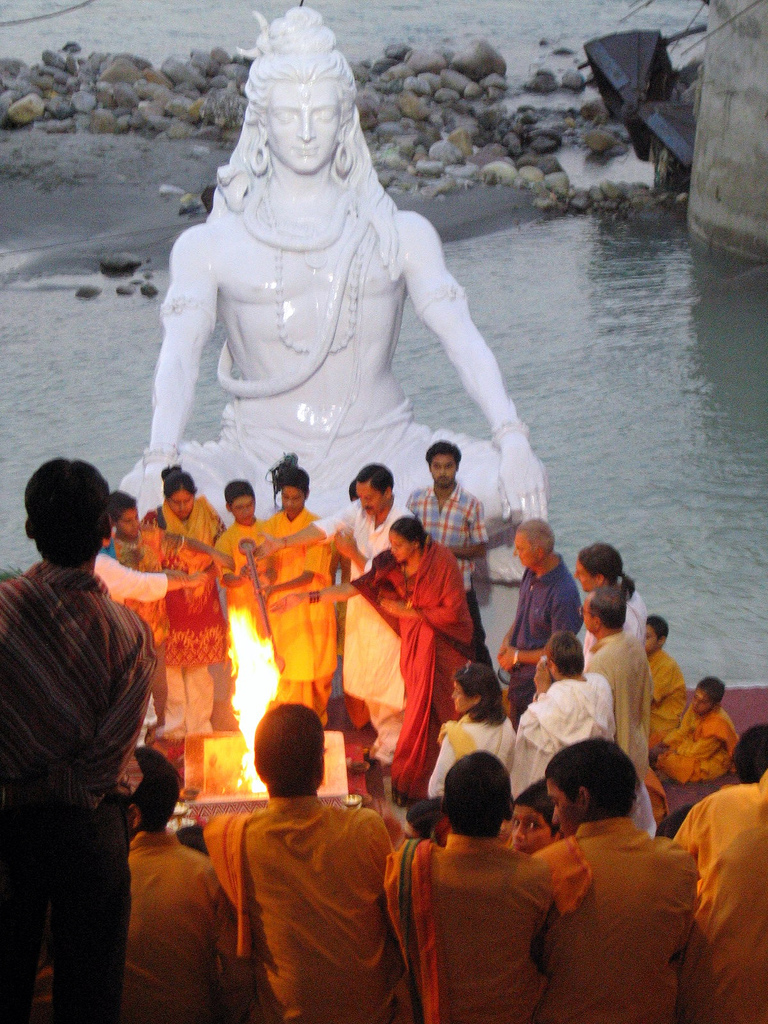
Sree Siddaganga Matha (also called Siddaganga Kshetra) is a Lingayat matha with an attached educational institution. The matha was established by Sri Haradanahally Gosala Siddeshwara Swamigalu in the 15th century in a village in the southern state of Karnataka, India.Village code= 1562300 Siddaganga Matha, Tumkur, Karnataka It is located in the Tumkur taluk of Tumkur district in Karnataka. Demographics As of the 2001 India census, Siddaganga Matha had a population of 6335 with 6284 males and 51 females. Matha The matha or monastery is said to be established by Thontada Siddalingeswara to spread Lingayatism (a sampradaya of Shaivism). The Matha (also called as Mutt) has established schools, a junior college and an engineering college, Medical College, School for Special Needs Children. It's a Gurukul for many poor people who cannot afford expensive educations. No Caste, No Religion questions are asked and only criteria needed here is hunger to learn. Every day it provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddaganga Institute Of Technology
Sports The college has facilities for encouraging sports and games. Has well equipped gymnasium, basketball, volleyball court, cricket ground, race track, badminton court, and an indoor stadium. Ranking Siddaganga Institute of Technology is ranked 101 among engineering colleges by the National Institutional Ranking Framework The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) is a methodology adopted by the Ministry of Education (India), Ministry of Education, Government of India, to rank institutions of higher education in India. The Framework was approved by the ... (NIRF) in 2021. References External links * Siddaganga Mutt {{Coord missing, Karnataka Affiliates of Visvesvaraya Technological University Educational institutions established in 1963 Universities and colleges in Tumkur district Education in Tumkur 1963 establishments in Mysore State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumkur District
Tumakuru District is an administrative district in the state of Karnataka in India. It is the third largest district in Karnataka by land area with an area of 10,598 km2, and fourth largest by Population. It is a one-and-a-half-hour drive from Bengaluru, the state capital. The district is known for the production of coconuts and is also called as 'Kalpataru Nadu'. It is the only discontiguous district in Karnataka (Pavagada Taluk has no geographical continuity with the rest of the district). As of census of 2011, the district has a population of 2,678,980, with a population density of 253 people /km2, the district has the literary rate of 75.14% and a sex ratio of 984 women/ 1000 men. Tumakuru district is surrounded by Chikkaballapura district and Bengaluru Rural in East, Ramanagara District in South-East, Mandya and Hassan Districts in South-West, Chikmagalur District in west, Chitradurga district in north-west and Sri Sathya Sai district and Anantapur district of Andhra Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
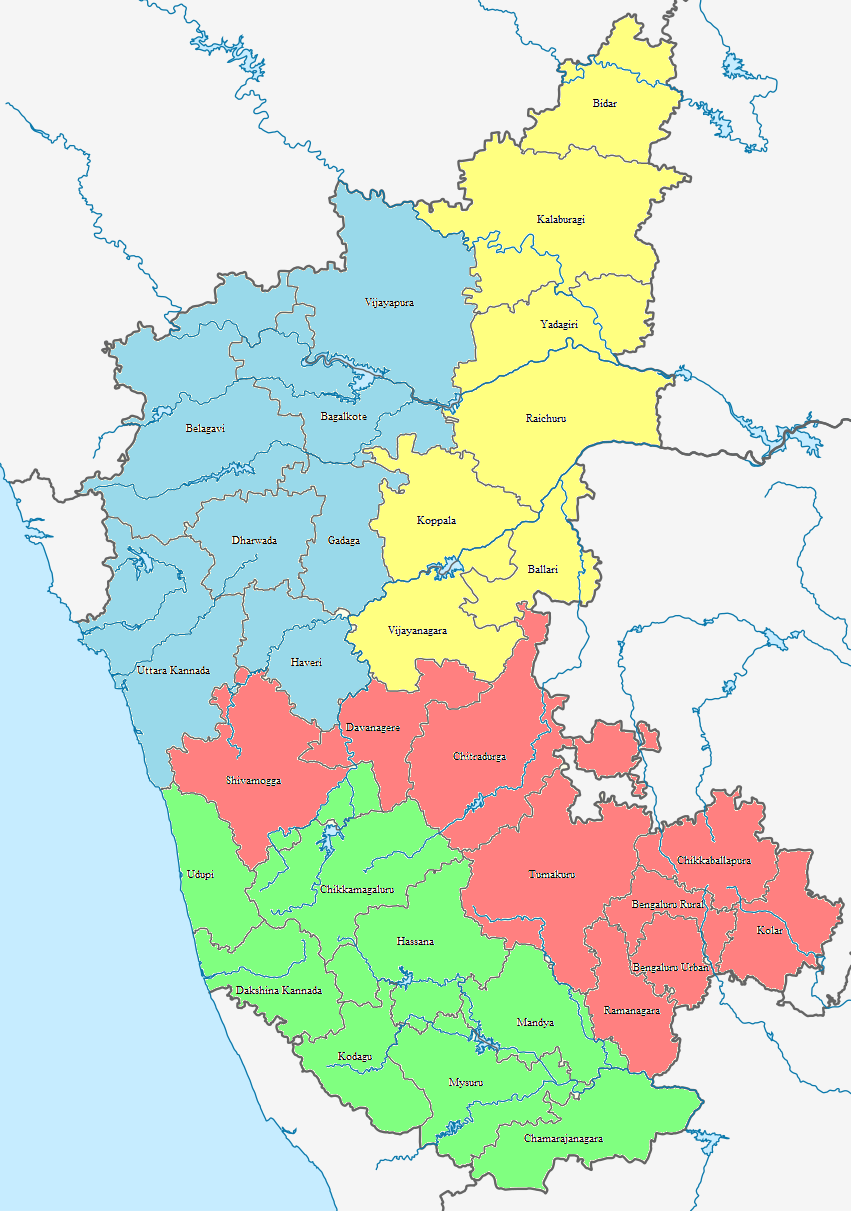
Districts Of Karnataka
The Indian State of Karnataka consists of 31 districts grouped into 4 administrative divisions. The state geographically has 3 principal regions: the coastal region of Karavali, the hilly Malenadu region comprising the Western Ghats, and the Bayaluseeme region, comprising the plains of the Deccan plateau. History It took its present shape in 1956, when the former states of Mysore and Coorg were merged with the Kannada-speaking districts of the former states of Bombay, Hyderabad, and Madras. Unified Mysore state was made up of ten districts, Bengaluru, Kolar, Tumakuru, Mandya, Mysuru, Hassana, Chikkamagaluru , Shivamogga, Chitradurga, and Ballari which had been transferred from Madras state to Mysore in 1953, when the new state of Andhra Pradesh was created out of Madras' northern districts. Coorg State became a district known as Kodagu, Dakshina Kannada was transferred from Madras State, Uttara Kannada, Dharwad, Belagavi, and Vijayapura from Bombay State. Bidar, Kalaburagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivakumara Swami
Shivakumara Swami (born Shivanna; 1 April 1907 – 21 January 2019) was an Indian humanitarian, spiritual leader, educator and supercentenarian. He was a Veerashaiva Lingayat religious figure, he joined the Siddaganga Matha in 1930 Karnataka and became head seer from 1941. He also founded the Sri Siddaganga Education Society. Described as the most esteemed adherent of Lingayatism(Veerashaivism), he was referred to as ''Nadedaaduva Devaru'' (walking God) in the state. In 2015, he was awarded by the Government of India the Padma Bhushan, India's third highest civilian award. Early life Shivanna was born on 1 April 1907 in Veerapura, a village near Magadi in the erstwhile Kingdom of Mysore (in present-day Ramanagara district of Karnataka state) in a Vokkaliga family. He was the youngest of thirteen children of Gangamma and Honne Gowda. Having been devoted followers of the deities Gangadhareshwara and Honnadevi, Shivanna's parents took him to the shrines in Shivagange, alongside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaivism
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions ranging from devotional dualistic theism such as Shaiva Siddhanta to yoga-orientated monistic non-theism such as Kashmiri Shaivism.Ganesh Tagare (2002), The Pratyabhijñā Philosophy, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 16–19 It considers both the Vedas and the Agama texts as important sources of theology.Mariasusai Dhavamony (1999), Hindu Spirituality, Gregorian University and Biblical Press, , pages 31–34 with footnotesMark Dyczkowski (1989), The Canon of the Śaivāgama, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 43–44 Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Vedic religions and traditions derived from the southern Tamil Shaiva Siddhanta traditions and philosophies, which were assimilated in the non-Vedic Shiva-tradition. In the process of Sanskritisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampradaya
''Sampradaya'' ( sa, सम्प्रदाय; ), in Indian origin religions, namely Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism, can be translated as 'tradition', 'spiritual lineage', 'sect', or 'religious system'. To ensure continuity and transmission of dharma, various ''sampradayas'' have the Guru-shishya parampara in which parampara or lineage of successive ''gurus'' (masters) and '' shishyas'' (disciples) serves as a spiritual channel and provides a reliable network of relationships that lends stability to a religious identity. Shramana is vedic term for seeker or shishya. Identification with and followership of ''sampradayas'' is not static, as ''sampradayas'' allows flexibility where one can leave one ''sampradaya'' and enter another or practice religious syncretism by simultaneously following more than one ''sampradaya''. '' Samparda'' is a punjabi language term, used in Sikhism, for ''sampradayas''. Guru-shishya parampara Sampradayas are living traditions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingayatism
Lingayatism or Veera Saivism is a Hindu denomination based on Shaivism. Initially known as ''Veerashaivas'', since the 12th-century adherents of this faith are known as ''Lingayats''. The terms ''Lingayatism'' and '' Veerashaivism'' have been used synonymously, but ''Veerashaivism'' may refer to the broader ''Veerashaiva'' philosophy which predates Lingayatism, to the historical community now called ''Lingayats'', and to a contemporary (sub)tradition within Lingayatism with Vedic influences. Veerashaiva Lingayatism was revived, by the 12th-century philosopher and statesman Basava in Karnataka. ''Lingayatism'' may refer to the whole Veerashaiva Lingayat community, but also to a contemporary sub-tradition dedicated to Basava's original thought, and to a movement within this community which strives toward recognition as an independent religion. Lingayat scholars thrived in northern Karnataka during the Vijayanagara Empire (14th–18th century). In the 21st century, some Lingayats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices. The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, covering th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taluk
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administrative centre, with possible additional towns, and usually a number of villages. The terms in India have replaced earlier terms, such as '' pargana'' (''pergunnah'') and ''thana''. In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, a newer unit called mandal (circle) has come to replace the system of tehsils. It is generally smaller than a tehsil, and is meant for facilitating local self-government in the panchayat system. In West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, community development blocks are the empowered grassroots administrative unit, replacing tehsils. As an entity of local government, the tehsil office (panchayat samiti) exercises certain fiscal and administrative power over the villages and municipalities within its jurisdiction. It is the ultimate execu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15th Century
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 ( MCDI) to 31 December 1500 ( MD). In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period. Many technological, social and cultural developments of the 15th century can in retrospect be seen as heralding the "European miracle" of the following centuries. The architectural perspective, and the modern fields which are known today as banking and accounting were founded in Italy. The Hundred Years' War ended with a decisive French victory over the English in the Battle of Castillon. Financial troubles in England following the conflict resulted in the Wars of the Roses, a series of dynastic wars for the throne of England. The conflicts ended with the defeat of Richard III by Henry VII at the Battle of Bosworth Field, establishing the Tudor dynasty in the later part of the century. Constantinople, known as the capital of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumkur
Tumkur, officially renamed as Tumakuru, is a city located in the southern part of Indian state of Karnataka. Tumkur is situated at a distance of northwest of Bangalore, the state capital along NH 48 and NH 73. It is the headquarters of the Tumkur district. It is located at an altitude of 835 m (2739.5 ft). Tumkur hosts India's first mega food park, a project of the ministry of food processing. The India Food Park was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in September 2014. Tumkur is also included in the Smart Cities Mission list and is among the 100 smart cities to be developed in India. Since 28 August 2010, Tumkur has been accorded the status of a city corporation. Etymology Etymologically, the name of the city is believed to have been mutated possibly from "Tumbe ooru" because of the abundance of thumbe hoovu, a kind of flower, or thamate ooru because of the folk musical percussion instrument thamate, that might have been used most here. It is also calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |