|
Sibawayh The Phonologist
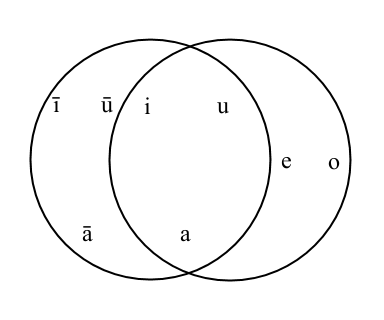
''Sibawayh the phonologist: A critical study of the phonetic and phonological theory of Sibawayh as presented in his treatise Al-Kitab'' is a 1993 book by A. A. Al-Nassir in which the author examines the views of Sibawayh on phonology. The book is based on Al-Nassir's doctoral dissertation (1985) at the University of York under the supervision of John Kelly. Reception The book was reviewed by John McCarthy, Yasir Suleiman Yasir Suleiman CBE is the Sultan Qaboos Bin Said Professor of Modern Arabic Studies at the University of Cambridge. He is a Palestinian Arab living in the diaspora. Suleiman holds degrees from Amman University, the University of St Andrews, and ... and M. G. Carter. References External links Sibawayh the Phonologist 1993 non-fiction books Phonology books Books on linguistic typology Arabic grammar books History of linguistics Theses {{ling-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but may now relate to any linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The building blocks of signs are specifications for movement, location, and handshape. At first, a separate terminology was used for the study of sign phonology ('chereme' instead of 'phoneme', etc.), but the concepts are now considered to apply universally to all human languages. Terminology The word 'phonology' (as in 'phonology of English') can refer either to the field of study or to the phonological system of a given language. This is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibawayh
Sibawayh ( ar, سِيبَوَيْهِ ' or ; fa, سِیبُویه ' ; c. 760–796), whose full name is Abu Bishr Amr ibn Uthman ibn Qanbar al-Basri (, '), was a Persian leading grammarian of Basra and author of the earliest book on Arabic grammar. His famous unnamed work, referred to as ''Al-Kitāb'', or "The Book", is a five-volume seminal discussion of the Arabic language. Ibn Qutaybah, the earliest extant source, in his biographical entry under ''Sibawayh'' simply wrote: He is Amr ibn Uthman, and he was mainly a grammarian. He arrived in Baghdad, fell out with the local grammarians, was humiliated and went back to some town in Persia, and died there while still a young man. The tenth-century biographers Ibn al-Nadim and Abu Bakr al-Zubaydi, and in the 13th-century Ibn Khallikan, attribute Sibawayh with contributions to the science of the Arabic language and linguistics that were unsurpassed by those of earlier and later times. He has been called the greatest of all A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of York
, mottoeng = On the threshold of wisdom , established = , type = Public research university , endowment = £8.0 million , budget = £403.6 million , chancellor = Heather Melville , vice_chancellor = Charlie Jeffery , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Heslington, York , country = England , campus = Heslington West, Heslington East, and King's Manor , colours = Dark blue and dark green , website = , logo = UoY_logo_with_shield_2016.png , logo_size = 250px , administrative_staff = 3,091 , affiliations = The University of York (abbreviated as or ''York'' for post-nominals) is a collegiate research university, located in the city of York, England. Established in 1963, the university has expanded to more than thirty departments and centres, covering a wide range of subjects. Situated to the south-east of the city of York, the university campus is about in size. The original campus, Campus West, incorporates the York Scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John McCarthy (linguist)
John Joseph McCarthy (born 1953) is an American linguist and the Provost and Senior Vice Chancellor for Academic Affairs at the University of Massachusetts Amherst since July 2017. In July 2018, he assumed office as the Provost. McCarthy is best-known for his work on Optimality Theory in phonology: with Alan Prince, he devised Correspondence Theory and alignment constraints, although he has subsequently renounced the latter.McCarthy, John. OT Constraints are Categorical. ''Phonology'' 20 75--138. 2003 He has since written textbooks like '' Doing Optimality Theory: Applying Theory to Data''. Earlier in his career, McCarthy was responsible, along with Prince, for extending autosegmental phonology, and later Optimality Theory, to morphology, in particular to solve the problem of nonconcatenative morphology in Semitic languages. Career HHe completed his A.B. in linguistics and Near Eastern languages at Harvard College and obtained his Ph.D. from MIT in 1979. He was a professor at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yasir Suleiman
Yasir Suleiman CBE is the Sultan Qaboos Bin Said Professor of Modern Arabic Studies at the University of Cambridge. He is a Palestinian Arab living in the diaspora. Suleiman holds degrees from Amman University, the University of St Andrews, and Durham University. He lectures nationally and internationally on various topics related to the Middle East. He was selected to be a trustee of the International Prize for Arabic Fiction (2007—2009). He was appointed Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE) in the 2011 Birthday Honours for his services to scholarship. Bibliography In addition to authoring books, Yasir Suleiman was an editor of a number of monographs is Arabic studies. * ''Arabic in the Fray: Language Ideology and Cultural Politics'' (2013) '' Edinburgh University Press'', * ''A War of Words: Language and Conflict in the Middle East'' (2004) ''Cambridge University Press Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambrid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1993 Non-fiction Books
File:1993 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Oslo I Accord is signed in an attempt to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict; The Russian White House is shelled during the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis; Czechoslovakia is peacefully dissolved into the Czech Republic and Slovakia; In the United States, the ATF besieges a compound belonging to David Koresh and the Branch Davidians in a search for illegal weapons, which ends in the building being set alight and killing most inside; Eritrea gains independence; A major snow storm passes over the United States and Canada, leading to over 300 fatalities; Drug lord and narcoterrorist Pablo Escobar is killed by Colombian special forces; Ramzi Yousef and other Islamic terrorists detonate a truck bomb in the subterranean garage of the North Tower of the World Trade Center in the United States., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 Oslo I Accord rect 200 0 400 200 1993 Russian constitutional crisis rect 400 0 600 200 Dissol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology Books
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but may now relate to any linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The building blocks of signs are specifications for movement, location, and handshape. At first, a separate terminology was used for the study of sign phonology ('chereme' instead of 'phoneme', etc.), but the concepts are now considered to apply universally to all human languages. Terminology The word 'phonology' (as in 'phonology of English') can refer either to the field of study or to the phonological system of a given language. This is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books On Linguistic Typology
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physical arrangement is ''codex'' (plural, ''codices''). In the history of hand-held physical supports for extended written compositions or records, the codex replaces its predecessor, the scroll. A single sheet in a codex is a leaf and each side of a leaf is a page. As an intellectual object, a book is prototypically a composition of such great length that it takes a considerable investment of time to compose and still considered as an investment of time to read. In a restricted sense, a book is a self-sufficient section or part of a longer composition, a usage reflecting that, in antiquity, long works had to be written on several scrolls and each scroll had to be identified by the book it contained. Each part of Aristotle's ''Physics'' is called a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Grammar Books
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal written med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language, involving analysis of language form, language meaning, and language in context. Language use was first systematically documented in Mesopotamia, with extant lexical lists of the 3rd to the 2nd Millenia BCE, offering glossaries on Sumerian cuneiform usage and meaning, and phonetical vocabularies of foreign languages. Later, Sanskrit would be systematically analysed, and its rules described, by Pāṇini ( fl. 6-4th century BCE), in the Indus Valley. François & Ponsonnet (2013). Beginning around the 4th century BCE, Warring States period China also developed its own grammatical traditions. Aristotle laid the foundation of Western linguistics as part of the study of rhetoric in his ''Poetics'' ca. 335 BC. Traditions of Arabic grammar and Hebrew grammar developed during the Middle Ages in a religious context like Pānini's Sanskrit grammar. Modern approaches began to develop in the 18th century, eventually being regarded in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |