|
Si J'étais Roi
''Si j'étais roi'' (English: ''If I Were King'') is an opéra comique in three acts by Adolphe Adam. The libretto was written by Adolphe d'Ennery and Jules-Henri Brésil. It was first performed in Paris at the Théâtre Lyrique (Théâtre-Historique, Boulevard du Temple) on 4 September 1852, opening with a dual cast to allow performance on successive evenings (it made up half of all performances at the Théâtre Lyrique in the last four months of the year and reached over 170 performances in its first ten years). The production was considered lavish, with expensive costumes and jewels being worn by the cast. It was then staged in Brussels (1853), New Orleans (1856), Turin (1858) and Soerabaya (1864).Loewenberg A. Annals of Opera. London, John Calder, 1978. Though less popular than ''Le postillon de Lonjumeau ''Le postillon de Lonjumeau'' (''The Postillion of Lonjumeau'') is an opéra-comique in three acts by Adolphe Adam to a French libretto by Adolphe de Leuven and Lé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
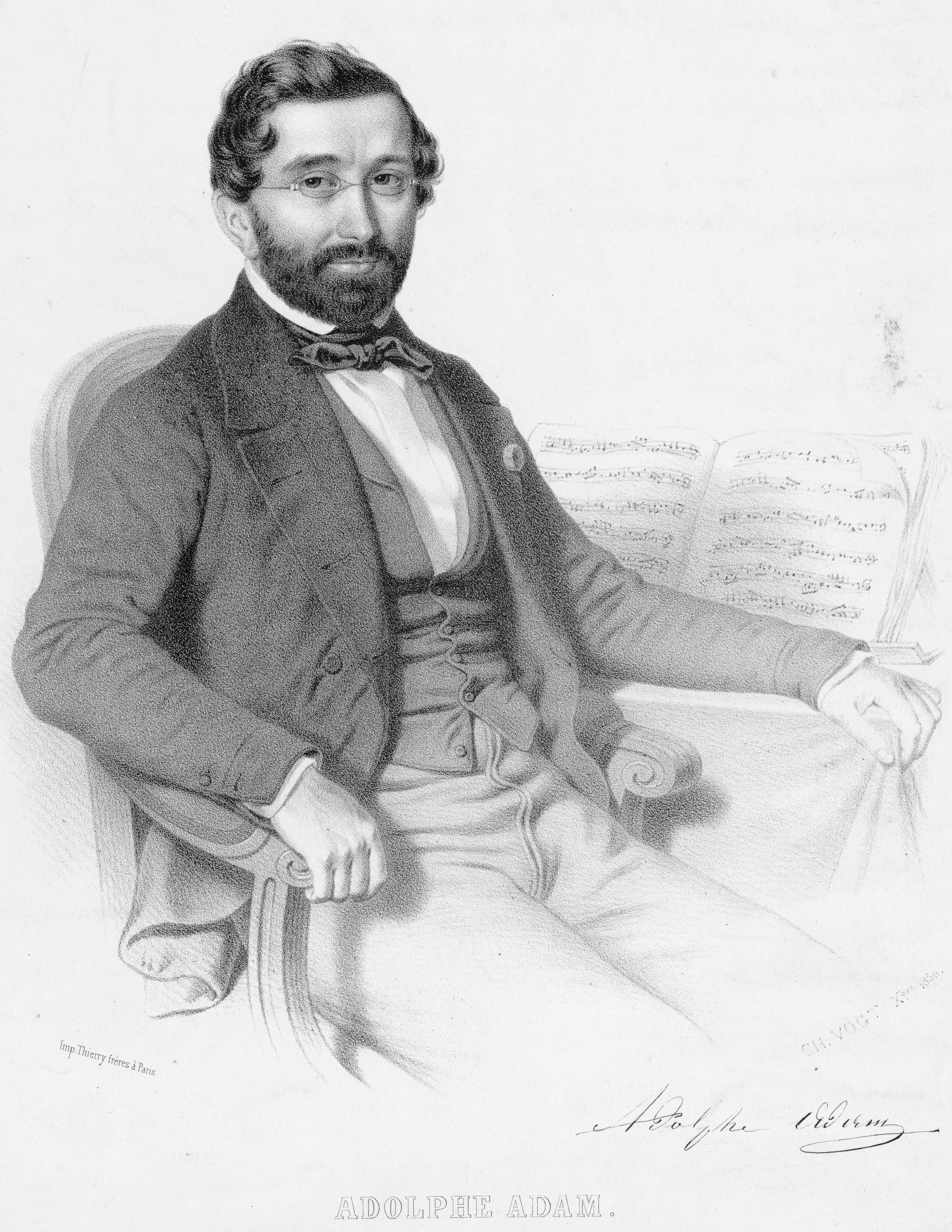
Adolphe Adam 1850 - Charles Vogt - Gallica
''Adolphe'' is a classic French novel by Benjamin Constant, first published in 1816. It tells the story of an alienated young man, Adolphe, who falls in love with an older woman, Ellénore, the Polish mistress of the Comte de P***. Their illicit relationship serves to isolate them from their friends and from society at large. The book eschews all conventional descriptions of exteriors for the sake of detailed accounts of feelings and states of mind. Constant began the novel on 30 October 1806, and completed it some time before 1810. While still working on it he read drafts to individual acquaintances and to small audiences, and after its first publication in London and Paris in June 1816 it went through three further editions: in July 1816 (new preface), July 1824 in Paris (restorations to Ch. 8, third preface), and in 1828. Many variants appear, mostly alterations to Constant's somewhat archaic spelling and punctuation. Plot summary Adolphe, the narrator, is the son of a go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soprano
A soprano () is a type of classical female singing voice and has the highest vocal range of all voice types. The soprano's vocal range (using scientific pitch notation) is from approximately middle C (C4) = 261 Hz to "high A" (A5) = 880 Hz in choral music, or to "soprano C" (C6, two octaves above middle C) = 1046 Hz or higher in operatic music. In four-part chorale style harmony, the soprano takes the highest part, which often encompasses the melody. The soprano voice type is generally divided into the coloratura, soubrette, lyric, spinto, and dramatic soprano. Etymology The word "soprano" comes from the Italian word '' sopra'' (above, over, on top of),"Soprano" '' |
1852 Operas
Year 185 ( CLXXXV) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lascivius and Atilius (or, less frequently, year 938 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 185 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Nobles of Britain demand that Emperor Commodus rescind all power given to Tigidius Perennis, who is eventually executed. * Publius Helvius Pertinax is made governor of Britain and quells a mutiny of the British Roman legions who wanted him to become emperor. The disgruntled usurpers go on to attempt to assassinate the governor. * Tigidius Perennis, his family and many others are executed for conspiring against Commodus. * Commodus drains Rome's treasury to put on gladiatorial spectacles and confiscates property to suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operas
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another. Opera is a key part of the Western classical music tradition. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include numerous genres, including some that include spoken dialogue such as ''Singspiel'' and ''Opéra comique''. In traditional number opera, singers employ two styles of singing: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French-language Operas
French opera is one of Europe's most important operatic traditions, containing works by composers of the stature of Rameau, Berlioz, Gounod, Bizet, Massenet, Debussy, Ravel, Poulenc and Messiaen. Many foreign-born composers have played a part in the French tradition as well, including Lully, Gluck, Salieri, Cherubini, Spontini, Meyerbeer, Rossini, Donizetti, Verdi and Offenbach. French opera began at the court of Louis XIV of France with Jean-Baptiste Lully's ''Cadmus et Hermione'' (1673), although there had been various experiments with the form before that, most notably '' Pomone'' by Robert Cambert. Lully and his librettist Quinault created ''tragédie en musique'', a form in which dance music and choral writing were particularly prominent. Lully's most important successor was Rameau. After Rameau's death, the German Gluck was persuaded to produce six operas for the Paris, Parisian stage in the 1770s. They show the influence of Rameau, but simplified and with greater foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operas By Adolphe Adam
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another. Opera is a key part of the Western classical music tradition. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include numerous genres, including some that include spoken dialogue such as '' Singspiel'' and '' Opéra comique''. In traditional number opera, singers employ two styles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Médus
Henri Médus (21 October 1904 – 11 November 1985) was a French operatic bass. A member of the troupe of the Opéra Garnier from 1933, he distinguished himself particularly in the roles of : ''The Magic Flute'' (Sarastro), ''Samson et Dalila'' (the old Hebrew man), ''Aida'' (Ramfis), ''Rigoletto'' (Sparafucile), ''La Juive'' (Cardinal de Brogni), ''Les Huguenots'' (Marcel), ''Die Entführung aus dem Serail'' (Osmin), ''Boris Godunov'' (Pimen, Varlaam), ''Die Walküre'' (Hunding), and ''Der Rosenkavalier'' (Baron Ochs). Biography Medus was born in Guelma (Algeria) where he spent his childhood before his family settled in Algiers. He took singing lessons from Rose Elsie (soprano of the Opéra-Comique) After an audition for conductor Désiré-Émile Inghelbrecht (1880–1965), then musical director of the Algiers Opera, he was hired for the role of Colline in ''La Bohème''. He made his stage debut on 16 October 1929 in Puccini's opera in French. After two seasons of experienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Mallabrera
André Mallabrera (15 June 1934 – 2 October 2017) was a French tenor. Born in Oran, (then in French Algeria), he was the son of singer José Mallabrera. After following his father into the watchmaker trade, Mallabrera undertook vocal studies at the Conservatoire d'Alger and in 1958 joined the Réunion des Théâtres Lyriques Nationaux.André Mallabrera page on artlyriquefr.fr accessed 27 February 2018. His career was based at both the Opéra Comique (where he made his debut in December 1958 as Almaviva), and the Opéra in Paris (his debut being Hylas in ''Les Troyens'' in May 1962). His voice, described as 'light, with immaculate French' was particularly at home at the former house in '' |
Liliane Berton
Liliane Berton (11 July 1924, Bully-les-Mines, Pas-de-Calais - Paris, 22 April 2009) was a French soprano, known principally on the opera stage, but also active in radio recordings and as a teacher. Career Although considering a dramatic career, after vocal studies at the Conservatoire de Lille and the Conservatoire de Paris she made her debut at the Opéra de Marseille as Blonde in ''Die Entführung aus dem Serail''. Berton was taken on by the RTLN, and made her Paris debut at the Opéra as Siebel in ''Faust'' on 8 September 1952, before appearing in the premiere of ''Dolorès'' by Michel-Maurice Lévy at the Opéra-Comique on 7 November 1952.Wolff S. ''Un demi-siècle d'Opéra Comique (1900-1950).'' André Bonne, Paris, 1953. Her career encompassed many lighter soprano roles in the repertoire: l’Amour, Fatime (''Les Indes galantes''), Sophie (''Werther''), Poussette (''Manon''), Xenia (''Boris Godunov''), Rosina (''The Barber of Seville'', in French), Eurydice ('' Orphée''), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass (voice Type)
A bass is a type of classical male singing voice and has the lowest vocal range of all voice types. According to ''The New Grove Dictionary of Opera'', a bass is typically classified as having a vocal range extending from around the second E below middle C to the E above middle C (i.e., E2–E4).; ''The Oxford Dictionary of Music'' gives E2–E4/F4 Its tessitura, or comfortable range, is normally defined by the outermost lines of the bass clef. Categories of bass voices vary according to national style and classification system. Italians favour subdividing basses into the ''basso cantante'' (singing bass), ''basso buffo'' ("funny" bass), or the dramatic ''basso profondo'' (low bass). The American system identifies the bass-baritone, comic bass, lyric bass, and dramatic bass. The German ''Fach'' system offers further distinctions: Spielbass (Bassbuffo), Schwerer Spielbass (Schwerer Bassbuffo), Charakterbass (Bassbariton), and Seriöser Bass. These classification systems can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baritone
A baritone is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the bass and the tenor voice-types. The term originates from the Greek (), meaning "heavy sounding". Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second F below middle C to the F above middle C (i.e. F2–F4) in choral music, and from the second A below middle C to the A above middle C (A2 to A4) in operatic music, but the range can extend at either end. Subtypes of baritone include the baryton-Martin baritone (light baritone), lyric baritone, ''Kavalierbariton'', Verdi baritone, dramatic baritone, ''baryton-noble'' baritone, and the bass-baritone. History The first use of the term "baritone" emerged as ''baritonans'', late in the 15th century, usually in French sacred polyphonic music. At this early stage it was frequently used as the lowest of the voices (including the bass), but in 17th-century Italy the term was all-encompassing and used to describe the averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |