|
Shorewall
Shorewall is an open source firewall tool for Linux that builds upon the Netfilter (iptables/ipchains) system built into the Linux kernel, making it easier to manage more complex configuration schemes by providing a higher level of abstraction for describing rules using text files. Its documentation is hosted on shorewall.org, while the latest code is hosted at https://gitlab.com/shorewall/code. Configuration It is not a daemon since it does not run continuously, but rather configures rules in the kernel allowing and disallowing traffic through the system. Shorewall is configured through a group of plain-text configuration files and does not have a graphical user interface, though a Webmin module is available separately. A monitoring utility packaged with Shorewall can be used to watch the status of the system as it operates and to assist in testing. Use Shorewall is mainly used in network installations (as opposed to a personal computer firewall), since most of its stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iptables
iptables is a user-space utility program that allows a system administrator to configure the IP packet filter rules of the Linux kernel firewall, implemented as different Netfilter modules. The filters are organized in a set of tables, which contain chains of rules for how to treat network traffic packets. Different kernel modules and programs are currently used for different protocols; ''iptables'' applies to IPv4, ''ip6tables'' to IPv6, ''arptables'' to ARP, and ' to Ethernet frames. iptables requires elevated privileges to operate and must be executed by user root, otherwise it fails to function. On most Linux systems, iptables is installed as and documented in its man pages, which can be opened using man iptables when installed. It may also be found in /sbin/iptables, but since iptables is more like a service rather than an "essential binary", the preferred location remains . The term ''iptables'' is also commonly used to inclusively refer to the kernel-level compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Though Perl is not officially an acronym, there are various backronyms in use, including "Practical Extraction and Reporting Language". Perl was developed by Larry Wall in 1987 as a general-purpose Unix scripting language to make report processing easier. Since then, it has undergone many changes and revisions. Perl originally was not capitalized and the name was changed to being capitalized by the time Perl 4 was released. The latest release is Perl 5, first released in 1994. From 2000 to October 2019 a sixth version of Perl was in development; the sixth version's name was changed to Raku. Both languages continue to be developed independently by different development teams which liberally borrow ideas from each other. Perl borrows features from other programming languages including C, sh, AWK, and sed. It provides text processing facilities without the arbitrary data-length limits of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based user interface, text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation interface, direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and Distributed control system, industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks that consists of Private network, private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, Wireless network, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and Web application, applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), email, electronic mail, internet telephony, streaming media and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
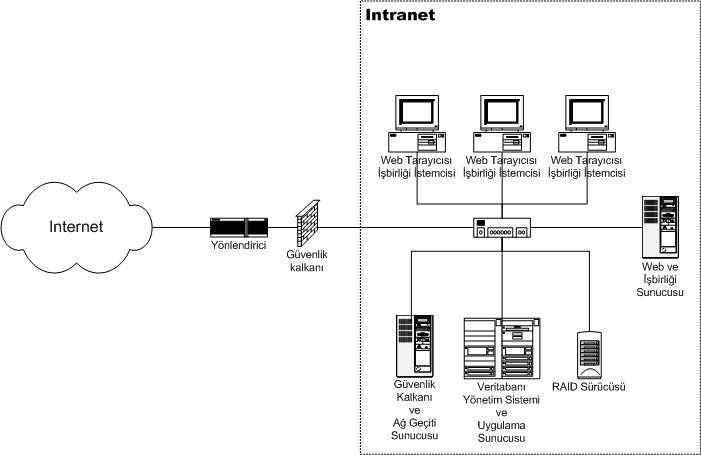
Intranet
An intranet is a computer network for sharing information, easier communication, collaboration tools, operational systems, and other computing services within an organization, usually to the exclusion of access by outsiders. The term is used in contrast to public networks, such as the Internet, but uses the same technology based on the Internet protocol suite. An organization-wide intranet can constitute an important focal point of internal communication and collaboration, and provide a single starting point to access internal and external resources. In its simplest form, an intranet is established with the technologies for local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs). Many modern intranets have Web search engine, search engines, user profiles, blogs, mobile apps with notifications, and events planning within their infrastructure. An intranet is sometimes contrasted to an extranet. While an intranet is generally restricted to employees of the organization, extranets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demilitarized Zone (computing)
In computer security, a DMZ or demilitarized zone (sometimes referred to as a perimeter network or screened subnet) is a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes an organization's external-facing services to an untrusted, usually larger, network such as the Internet. The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization's local area network (LAN): an external network node can access only what is exposed in the DMZ, while the rest of the organization's network is protected behind a firewall. The DMZ functions as a small, isolated network positioned between the Internet and the private network. This is not to be confused with a DMZ host, a feature present in some home routers that frequently differs greatly from an ordinary DMZ. The name is from the term ''demilitarized zone'', an area between states in which military operations are not permitted. Rationale The DMZ is seen as not belonging to either network bordering it. This metaphor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Firewall
A personal firewall is an application which controls network traffic to and from a computer, permitting or denying communications based on a security policy. Typically it works as an application layer firewall. A personal firewall differs from a conventional firewall in terms of scale. A personal firewall will usually protect only the computer on which it is installed, as compared to a conventional firewall which is normally installed on a designated interface between two or more networks, such as a router or proxy server. Hence, personal firewalls allow a security policy to be defined for individual computers, whereas a conventional firewall controls the policy between the networks that it connects. The per-computer scope of personal firewalls is useful to protect machines that are moved across different networks. For example, a laptop computer may be used on a trusted intranet at a workplace where minimal protection is needed as a conventional firewall is already in place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Webmin
Webmin is a web-based server management control panel for Unix-like systems. Webmin allows the user to configure operating system internals, such as users, disk quotas, services and configuration files, as well as modify and control open-source apps, such as BIND, Apache HTTP Server, PHP, and MySQL. History Webmin, developed by Jamie Cameron, was first released as version 0.1 in October 1997. It was initially created while Cameron was administering a DNS server and needed a user-friendly interface that would allow users to modify DNS records without granting them root access to the server. Over time, various themes, a dashboard that displays CPU, RAM, and disk space usage with visual gauges, and a sidebar with a search function were also added. Financial support for the Webmin project came from the Linux distribution companies Caldera and MSC Linux, as well as many user contributions of code patches, hundreds of modules, language translations, and user suggestions. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system (OS) which was created to be a free software, free replacement for Unix. Since the late 1990s, it has been included in many Linux distributions, operating system distributions, many of which are called Linux. One such Linux kernel operating system is Android (operating system), Android which is used in many mobile and embedded devices. Most of the kernel code is written in C (programming language), C as supported by the GNU compiler collection (GCC) which has extensions beyond standard C. The code also contains assembly language, assembly code for architecture-specific logic such as optimizing memory use and task execution. The kernel has a Modular programming, modular design such that modules can be inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daemon (computing)
In computing, a daemon is a program that runs as a background process, rather than being under the direct control of an interactive user. Customary convention is to name a daemon process with the letter ''d'' as a suffix to indicate that it's a daemon. For example, is a daemon that implements system logging facility, and is a daemon that serves incoming SSH connections. Even though the concept can apply to many computing systems, the term ''daemon'' is used almost exclusively in the context of Unix-based systems. In other contexts, different terms are used for the same concept. Systems often start daemons at boot time that will respond to network requests, hardware activity, or other programs by performing some task. Daemons such as cron may also perform defined tasks at scheduled times. Terminology In the context of computing, the word is generally pronounced either as or . The term was coined by the programmers at MIT's Project MAC. According to Fernando J. Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipchains
Linux IP Firewalling Chains, normally called ipchains, is free software to control the packet filter or firewall capabilities in the 2.2 series of Linux kernels. It superseded ipfirewall (managed by ipfwadm command), but was replaced by iptables in the 2.4 series. Unlike iptables, ipchains is stateless. History It is a rewrite of Linux's previous IPv4 firewall, ipfirewall. This newer ipchains was required to manage the packet filter in Linux kernels starting with version 2.1.102 (which was a 2.2 development release). Patches are also available to add ipchains to 2.0 and earlier 2.1 series kernels. Improvements include larger maxima for packet counting, filtering for fragmented packets and a wider range of protocols, and the ability to match packets based on the inverse of a rule. The ipchains suite also included some shell scripts for easier maintenance and to emulate the behavior of the old ipfwadm command. The ipchains software was superseded by the iptables system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |