|
Shogi Notation
Shogi notation is the set of various abbreviatory notational systems used to describe the piece movements of a shogi game record or the positions of pieces on a shogi board. A game record is called a ''kifu'' in Japanese. Recording moves Western notation The system used in English language texts to express shogi moves was established by George Hodges and Glyndon Townhill in 1976 by the second issue of ''Shogi'' magazine. A slightly modified version was used in . It is derived from the algebraic notation used for chess, but differs in several respects. A typical move might be notated P86 or P-8f. The notation format has the following 5 part structure: : An example using all 5 parts is S72x83+ or S7bx8c+. All parts are obligatory except for the ''origin'' and ''promotion'' parts. (Thus, most notation strings only contain 3 parts.) The ''origin'' part is only indicated when needed to resolve ambiguity. The ''promotion'' part is only needed when there is the possibility of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shorthand
Shorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed and brevity of writing as compared to longhand, a more common method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Greek ''stenos'' (narrow) and ''graphein'' (to write). It has also been called brachygraphy, from Greek ''brachys'' (short), and tachygraphy, from Greek ''tachys'' (swift, speedy), depending on whether compression or speed of writing is the goal. Many forms of shorthand exist. A typical shorthand system provides symbols or abbreviations for words and common phrases, which can allow someone well-trained in the system to write as quickly as people speak. Abbreviation methods are alphabet-based and use different abbreviating approaches. Many journalists use shorthand writing to quickly take notes at press conferences or other similar scenarios. In the computerized world, several autocomplete programs, standalone or integrated in text editors, based on w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hifumi Katoh
Hifumi (written: 一二三) is a unisex Japanese given name, as well as a family name. Notable people with the given name include: *, Japanese judoka *, Japanese shogi player *, Japanese classical composer *Hifumi Suzuki (born 1957), Japanese Paralympic archer Notable people with the family name include:https://myoji-yurai.net/searchResult.htm?myojiKanji=%E4%B8%80%E4%BA%8C%E4%B8%89 *, Japanese baseballer *, Japanese educator Fictional characters *, a character in the manga series ''Koi Koi Seven'' *, a character in the multimedia project ''Hypnosis Mic: Division Rap Battle'' *, a character in the manga series ''New Game!'' *, a character in the video game ''Persona 5 is a 2016 role-playing video game developed by Atlus. It takes place in modern-day Tokyo and follows a high school student known by the pseudonym Joker who transfers to a new school after being falsely accused of assault and put on probation ...'' *Hifumi Yamada (山田 一二三), a character in the visual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Exchange Climbing Silver
In shogi, Bishop Exchange Climbing Silver (角換わり棒銀 ''kakugawari bōgin'') is a Bishop Exchange (Double Static Rook) opening that uses a Climbing Silver attacking formation with the left silver. See also * Bishop Exchange * Climbing Silver * Bishop Exchange Reclining Silver * Bishop Exchange Rushing Silver * Tempo Loss Bishop Exchange * Wrong Diagonal Bishop Exchange * Static Rook Static Rook (居飛車 ''ibisha'') openings in shogi typically have the player's rook at its start position, which is the second file (on the 28 square) for Black and the eighth file (on the 82 square) for White. Explanation Static Rook is a ... Bibliography * * External links * HIDETCHI's YouTube videos: *Shogi Openings: Bishop Exchange #1 · Climbing Silver played by Black in Bishop Exchange (from 11 min 58 sec to 19 min 40 sec) *Shogi Openings: Bishop Exchange #2 · Merits of Climbing Silver vs other silver strategies in Bishop Exchange *Shogi Openings: Bishop Exchange #4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshiharu Habu
is a professional shogi player and a chess FIDE Master. His master is Tatsuya Futakami. He is the only person to simultaneously hold seven major professional shogi titles at the same time and is also the only person to qualify as a lifetime title holder for seven major titles. In January 2018, Habu became the first professional shogi player to be awarded Japan's People's Honour Award. Early life Yoshiharu Habu was born in Tokorozawa, Saitama in 1970 and moved to Hachioji, Tokyo before entering kindergarten. Habu first encountered shogi in his first year of elementary school, when his classmates taught him how the shogi pieces move. He was so fascinated by the game that his mother entered him in a shogi tournament held at the Hachioji Shogi Club in the summer of 1978. Although Habu was eliminated during the preliminary rounds with a record of 1 win and 2 losses, his parents took him to the shogi club every weekend from October 1978. Habu improved so rapidly that he was promote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Notation
Shogi notation is the set of various abbreviatory notational systems used to describe the piece movements of a shogi game record or the positions of pieces on a shogi board. A game record is called a ''kifu'' in Japanese. Recording moves Western notation The system used in English language texts to express shogi moves was established by George Hodges and Glyndon Townhill in 1976 by the second issue of ''Shogi'' magazine. A slightly modified version was used in . It is derived from the algebraic notation used for chess, but differs in several respects. A typical move might be notated P86 or P-8f. The notation format has the following 5 part structure: : An example using all 5 parts is S72x83+ or S7bx8c+. All parts are obligatory except for the ''origin'' and ''promotion'' parts. (Thus, most notation strings only contain 3 parts.) The ''origin'' part is only indicated when needed to resolve ambiguity. The ''promotion'' part is only needed when there is the possibility of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are , which severely limited its scope. All modern computer systems instead use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) prefers the name US-ASCII for this character encoding. ASCII is one of the List of IEEE milestones, IEEE milestones. Overview ASCII was developed from telegraph code. Its first commercial use was as a seven-bit teleprinter code promoted by Bell data services. Work on the ASCII standard began in May 1961, with the first meeting of the American Standards Association's (ASA) (now the American Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
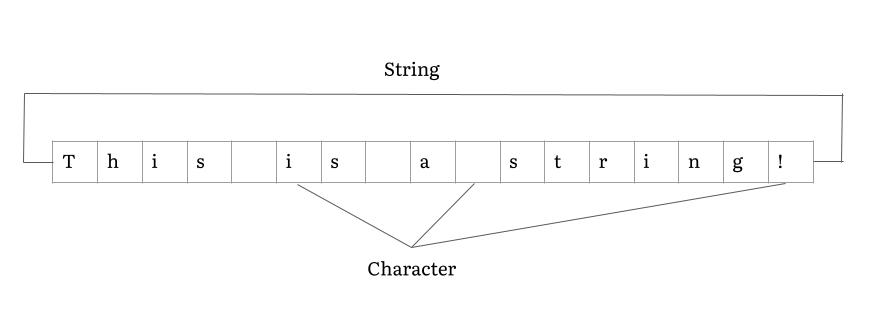
Text String
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathematical l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forsyth–Edwards Notation
Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN) is a standard notation for describing a particular board position of a chess game. The purpose of FEN is to provide all the necessary information to restart a game from a particular position. FEN is based on a system developed by Scottish newspaper journalist David Forsyth. His system became popular in the 19th century; Steven J. Edwards extended it to support use by computers. FEN is defined in the "Portable Game Notation Specification and Implementation Guide". In the Portable Game Notation for chess games, FEN is used to define initial positions other than the standard one. FEN does not provide sufficient information to decide whether a draw by threefold repetition may be legally claimed or a draw offer may be accepted; for that, a different format such as Extended Position Description is needed. Definition A FEN record defines a particular game position, all in one text line and using only the ASCII character set. A text file with only FEN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishida (shogi)
The ''Ishida'' Opening (石田流三間飛車 ''ishida-ryū sankenbisha'' or shorter form 石田流 ''ishida-ryū'') is a major variation in Third File Rook openings of the Japanese game of '' shōgi''. In the Ishida Opening, in contrast to other Third File Rook openings, the seventh file pawn is advanced to the fifth rank if played by Black (P-75), or the third file pawn if played by White (P-35). This allows the rook to move up to the 76 square (Black) or 34 square (White). History The variation is said to have originated with a blind ''shōgi'' player named Kengyo Ishida in the early Edo period. Although records of Ishida's actual games still exist, all of them end in Ishida's loss. An extant game record of a Double Ranging Rook game in 1649 featuring an Ishida position played by Kengyo Ishida is shown in the diagram. A renaissance of the Ishida variation occurred in the 1970s through the development of an original strategy by the well-known ''shōgi'' master Kōzō Masud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempo Loss Bishop Exchange
In shogi, Tempo Loss Bishop Exchange or One-Move-Loss Bishop Exchange or Bishop Exchange With Tempo Loss (一手損角換わり ''ittezon kakugawari'') is a Bishop Exchange (Static Rook) opening that has White trading the bishops very early in the game before Black's bishop moves up to the 77 square. Overview The Tempo Loss Bishop Exchange opening was developed by retired player Hitoshige Awaji 9-dan for which he was awarded the prestigious Masuda award in 2006. This opening became popular among professional players around 2004 and was even played in two of the seven matches for the title of Meijin between Toshiyuki Moriuchi and Yoshiharu Habu in 2005. Before the emergence of the Tempo Loss Bishop Exchange, some professional players had considered that Bishop Exchange openings led White to be pushed into defensive positions and to be unable to launch more powerful attacks, hence reducing the amount of possibilities available to the White player. Since the Tempo Loss varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madoka Kitao
is a Japanese retired women's professional shogi player who achieved the rank of women's professional 2-dan. Women's shogi professional Promotion history Kitao has been promoted as follows: * 2-kyū: October 1, 2000 * 1-kyū: April 1, 2001 * 1-dan: April 1, 2003 * 2-dan: August 1, 2013 * Retired: July 10, 2023 Note: All ranks are women's professional ranks. Retirement On April 3, 2023, the Japan Shogi Association (JSA) posted on its official website that Kitao had met the criteria for mandatory retirement for women's professionals, but that her retirement would not take effect until the completion of her last official game. On July 11, 2023, the JSA posted that Kitao's retirement became official on July 10, 2023, upon the completion of her game against Saori Shimai. Kitao finised her career with a record of 110 wins and 187 losses for a winning percentage of 37%. Shogi-related business and promotion activities Kitao, together with former women's professional created the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |