|
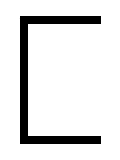
Sho (letter)
The letter (sometimes called sho or san) was a letter added to the Greek alphabet in order to write the Bactrian language.Everson, M. and Sims-Williams, N. (2002) �Proposal to add two Greek letters for Bactrian to the UCS��,ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2 N2411. It was similar in appearance to the Anglo-Saxon and Icelandic letter thorn (þ), which has typically been used to represent it in modern print, although they are historically unrelated. It probably represented a sound similar to English "sh" (). Its conventional transliteration in Latin is . Its original name and position in the Bactrian alphabet, if it had any, are unknown. Some authors have called it "san", on the basis of the hypothesis that it was a survival or reintroduction of the archaic Greek letter San. This letter closely resembles, perhaps coincidentally, the letter of the Greek-based Carian alphabet which may have also stood for . The name "sho" was coined for the letter for purposes of modern computer encod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorn (letter)
Thorn or þorn (Þ, þ) is a letter in the Old English Latin alphabet, Old English, Old Norse alphabet, Old Norse, Old Swedish and modern Icelandic orthography, Icelandic alphabets, as well as modern transliterations of the Gothic language, Gothic alphabet, Middle Scots, and some dialects of Middle English. It was also used in Middle Ages, medieval Scandinavia but was later replaced with the Digraph (orthography), digraph ''Th (digraph), th,'' except in Iceland, where it survives. The letter originated from the runic alphabet, rune in the Elder Futhark and was called ''thorn'' in the Anglo-Saxon and ''thorn'' or ''Jötunn, thurs'' in the Scandinavian rune poems. It is similar in appearance to the archaic Greek letter Sho (letter), sho (ϸ), although the two are historically unrelated. The only language in which þ is currently in use is Icelandic language, Icelandic. It represented a voiceless dental fricative or its voiced dental fricative, voiced counterpart . However, in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypriot Greek Dialect
Cypriot Greek (, or ) is the variety of Modern Greek that is spoken by the majority of the Cypriot populace and Greek Cypriot diaspora. It is considered a divergent dialect as it differs from Standard Modern Greek in various aspects of its lexicon, phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax and even pragmatics, not only for historical reasons but also because of geographical isolation, and extensive contact with typologically distinct languages. Classification Cypriot Greek is not an evolution of ancient Arcadocypriot Greek, but derives from Byzantine Medieval Greek. It has traditionally been placed in the southeastern group of Modern Greek varieties, along with the dialects of the Dodecanese and Chios (with which it shares several phonological phenomena). As Cypriot Greek tends to be regarded as a dialect by its speakers, it remains largely understandable to speakers of Standard Modern Greek, though it can be challenging without prior exposure. Greek-speaking Cypriot soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Letters
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic and early Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BC, the Ionic-based Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard throughout the Greek-speaking world and is the version that is still used for Greek writing today. The uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are: : , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of several scripts, such as the Latin, Gothic, Coptic, and Cyrillic scripts. Throughout antiquity, Greek had only a single uppercase form of each letter. It was written without diacritics and with little punctuation. By the 9th century, Byzantine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanasis Costakis
Thanasis Costakis (, 1907–2009) was a Greek linguist and lexicographer best known for his work on the critically endangered Tsakonian language spoken in the eastern Peloponnese. Costakis was born in Pera Melana in Arcadia, a Tsakonian-speaking village. Costakis taught at several gymnasia and lycea in Athens before affiliating with the Academy of Athens, where he contributed to the composition of the Historical Lexicon of Modern Greek. In addition to his linguistic works, he also published a volume on the traditional architecture of Tsakonia. Costakis also developed a writing system for the Tsakonian language, which included orthography using dots, ''spiritus asper'', and caron A caron or háček ( ), is a diacritic mark () placed over certain letters in the orthography of some languages, to indicate a change of the related letter's pronunciation. Typographers tend to use the term ''caron'', while linguists prefer ... for use in his works, which has been used in hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsakonian Language
Tsakonian or Tsaconian (also Tzakonian or Tsakonic, and Tsakonian: , ) is a highly divergent modern variety of Greek, spoken in the Tsakonian region of the Peloponnese, Greece Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th .... Unlike all other extant varieties of Greek, Tsakonian derives from Doric Greek rather than from the Attic Greek, Attic–Ionic Greek, Ionic branch. Although it is conventionally treated as a dialect of Greek, some compendia treat it as a separate language. Tsakonian is Critically endangered language, critically endangered, with only a few hundred or a few thousand, mostly elderly, fluent speakers left. Although Tsakonian and standard Modern Greek are related, they are not mutually intelligible. Etymology The term Tsakonas or Tzakonas first emerges in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, or , ), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the language sometimes referred to as Varieties of Modern Greek#Standard Modern Greek, Standard Modern Greek. The end of the Medieval Greek period and the beginning of Modern Greek is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic features of the modern language arose centuries earlier, having begun around the fourth century AD. During most of the Modern Greek period, the language existed in a situation of diglossia, with regional spoken dialects existing side by side with learned, more archaic written forms, as with the vernacular and learned varieties (''Dimotiki'' and ''Katharevousa'') that co-existed in Greece throughout much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mashallah
Mashallah or Ma Sha Allah or Masha Allah or Ma Shaa Allah () is an Arabic phrase generally used to positively denote something of greatness or beauty and to express a feeling of awe. It is often used to convey a sense of respect and to protect against the evil eye, suggesting that the speaker is acknowledging something positive without invoking jealousy. It is a common expression used throughout the Arabic-speaking and Muslim world, as well as among non-Muslim Arabic speakers, especially Arabic-speaking Christians and others who refer to God by the Arabic name Allah. Etymology The triconsonantal root of ' is šīn- yāʼ-hamza 'to will', a doubly weak root. The literal English translation of ''Mashallah'' is 'God has willed it',MashAllah meaning Islamic-dictionary.com the |
University Of Cyprus
The University of Cyprus (Greek language, Greek: Πανεπιστήμιο Κύπρου, Turkish language, Turkish: Kıbrıs Üniversitesi) is a public university, public research institute, research university established in Cyprus in 1989. It admitted its first students in 1992 and has approximately 7000 students. History The University of Cyprus was established in 1989 and admitted its first students in 1992. Admission for the majority of undergraduate students is by entrance examinations organised by the Ministry of Education and Culture of the Republic of Cyprus. A number of places are reserved for students with special needs or circumstances. When the University of Cyprus opened, the incoming class consisted of 486 undergraduate students. During the academic year 2010–2011, 4691 undergraduate students attended courses offered by the 21 departments. At the same time, there were 1549 postgraduate students. Academic reputation Based in the capital of Cyprus, Nicosia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caron
A caron or háček ( ), is a diacritic mark () placed over certain letters in the orthography of some languages, to indicate a change of the related letter's pronunciation. Typographers tend to use the term ''caron'', while linguists prefer the Czech word '. The symbol is common in the Baltic, Slavic, Finnic, Samic and Berber language families. Its use differs according to the orthographic rules of a language. In most Slavic and other European languages it indicates present or historical palatalization (e → ě; [] → []), iotation, or postalveolar consonant, postalveolar articulation (c → č; → ). In Salishan languages, it often represents a uvular consonant (x → x̌; [] → ). When placed over vowel symbols, the caron can indicate a contour tone, for instance the falling and then rising tone in the Pinyin romanization of Standard Chinese, Mandarin Chinese. It is also used to decorate symbols in mathematics, where it is often pronounced ("check"). The caro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Character (computing), characters and 168 script (Unicode), scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts. Unicode has largely supplanted the previous environment of a myriad of incompatible character sets used within different locales and on different computer architectures. The entire repertoire of these sets, plus many additional characters, were merged into the single Unicode set. Unicode is used to encode the vast majority of text on the Internet, including most web pages, and relevant Unicode support has become a common consideration in contemporary software development. Unicode is ultimately capable of encoding more than 1.1 million characters. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic Greece, Archaic and early Classical Greece, Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in Archaic Greek alphabets, many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BC, the Ionia, Ionic-based Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard throughout the Greek-speaking world and is the version that is still used for Greek writing today. The letter case, uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are: : , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of several scripts, such as the Latin script, Latin, Gothic alphabet, Gothic, Coptic script, Coptic, and Cyrillic scripts. Throughout antiquity, Greek had only a single uppercas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carian Alphabet
The Carian alphabets are a number of regional scripts used to write the Carian language of western Anatolia. They consisted of some 30 alphabetic letters, with several geographic variants in Caria and a homogeneous variant attested from the Nile delta, where Carian mercenaries fought for the Egyptian pharaohs. They were written left-to-right in Caria (apart from the Carian–Lydian city of Tralleis) and right-to-left in Egypt. Carian was deciphered primarily through Egyptian–Carian bilingual tomb inscriptions, starting with John Ray in 1981; previously only a few sound values and the alphabetic nature of the script had been demonstrated. The readings of Ray and subsequent scholars were largely confirmed with a Carian–Greek bilingual inscription discovered in Kaunos in 1996, which for the first time verified personal names, but the identification of many letters remains provisional and debated, and a few letters are wholly unknown. The Carian alphabet resembles the Greek alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |