|
Shitik Na Lene
Shitik () is a small, broad-bottomed vessel in which parts of the hull have been sewed with belts or juniper and fir-tree rods called ''vinya'' (). Etymology There are two proposed origins for the name of this boat. The first is that it comes from the verb , meaning 'to sew'. This explains some of the design features of the boat. The second is that the shape of the boat is similar to that of larvae of Trichoptera, which are also called (''shitik''). Types The term Shitik refers to two different vessel types: Sea Cargo Ship The Shitik was a keeled vessel, powered by sail and oars. It was used as a sea trade and transport ship. The ship has a rounded-off bottom and, therefore, features a considerable expansion of the hull and disorder of boards. This design improves the ship's performance. Shitik had a single mast with a direct sail, oars, and a hinged wheel. The vessel had a canopy to protect the cargo from the rain although there is also a bunkhouse below the deck. The und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shitik Na Lene
Shitik () is a small, broad-bottomed vessel in which parts of the hull have been sewed with belts or juniper and fir-tree rods called ''vinya'' (). Etymology There are two proposed origins for the name of this boat. The first is that it comes from the verb , meaning 'to sew'. This explains some of the design features of the boat. The second is that the shape of the boat is similar to that of larvae of Trichoptera, which are also called (''shitik''). Types The term Shitik refers to two different vessel types: Sea Cargo Ship The Shitik was a keeled vessel, powered by sail and oars. It was used as a sea trade and transport ship. The ship has a rounded-off bottom and, therefore, features a considerable expansion of the hull and disorder of boards. This design improves the ship's performance. Shitik had a single mast with a direct sail, oars, and a hinged wheel. The vessel had a canopy to protect the cargo from the rain although there is also a bunkhouse below the deck. The und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tikhvinka
The Tikhvinka () is a river in Boksitogorsky and Tikhvinsky Districts of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, a right and the biggest tributary of the Syas. The town of Tikhvin is located on its banks. It is long, and the area of its basin . The main tributaries of the Tikhvinka are the Ryadan (left) and the Shomushka (right). The source of the Tikhvinka is in Lake Yeglino in Boksitogorsky District, several kilometers northwest of the urban-type settlement of Yefimovsky. The river flows northwest, through Lake Ozerskoye, turns west and eventually southwest. Upstream of the village of Astrachi the Tikhvinka accepts the Ryadan from the left and turns west. Downstream of Astrachi, the Tikhvinka enters Tikhvinsky District and flows through the town of Tikhvin. The mouth of the Tikhvinka is located between the villages of Ovino and Khalezevo. The drainage basin of the Tikhvinka include the western part of Boksitogorsky District and areas in the southeast of Tikhvinsky District. The tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may be made from a combination of woven materials—including canvas or polyester cloth, laminated membranes or bonded filaments—usually in a three- or four-sided shape. A sail provides propulsive force via a combination of lift and drag, depending on its angle of attack—its angle with respect to the apparent wind. Apparent wind is the air velocity experienced on the moving craft and is the combined effect of the true wind velocity with the velocity of the sailing craft. Angle of attack is often constrained by the sailing craft's orientation to the wind or point of sail. On points of sail where it is possible to align the leading edge of the sail with the apparent wind, the sail may act as an airfoil, generating propulsive force as air p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lena (river)
The Lena (russian: Ле́на, ; evn, Елюенэ, ''Eljune''; sah, Өлүөнэ, ''Ölüöne''; bua, Зүлхэ, ''Zülkhe''; mn, Зүлгэ, ''Zülge'') is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean (the other two being the Ob and the Yenisey). Permafrost underlies most of the catchment, 77% of which is continuous. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . The Lena is the eleventh-longest river in the world, and the longest river entirely within Russia. Course Originating at an elevation of at its source in the Baikal Mountains south of the Central Siberian Plateau, west of Lake Baikal, the Lena flows northeast across the Lena-Angara Plateau, being joined by the Kirenga, Vitim and Olyokma. From Yakutsk it enters the Central Yakutian Lowland and flows north until joined by its right-hand tributary the Aldan and its most important left-hand tributary, the Vilyuy. After that, it bends westward and northward, flowing between the K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiga
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga or boreal forest has been called the world's largest land biome. In North America, it covers most of inland Canada, Alaska, and parts of the northern contiguous United States. In Eurasia, it covers most of Sweden, Finland, much of Russia from Karelia in the west to the Pacific Ocean (including much of Siberia), much of Norway and Estonia, some of the Scottish Highlands, some lowland/coastal areas of Iceland, and areas of northern Kazakhstan, northern Mongolia, and northern Japan (on the island of Hokkaidō). The main tree species, depending on the length of the growing season and summer temperatures, vary across the world. The taiga of North America is mostly spruce, Scandinavian and Finnish taiga consists of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). Lumber has many uses beyond home building. Lumber is sometimes referred to as timber as an archaic term and still in England, while in most parts of the world (especially the United States and Canada) the term timber refers specifically to unprocessed wood fiber, such as cut logs or standing trees that have yet to be cut. Lumber may be supplied either rough- sawn, or surfaced on one or more of its faces. Beside pulpwood, ''rough lumber'' is the raw material for furniture-making, and manufacture of other items requiring cutting and shaping. It is available in many species, including hardwoods and softwoods, such as white pine and red pine, because of their low cost. ''Finished lumber'' is supplied in standard sizes, mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in British and American shipbuilding traditions the construction is dated from this event. Etymology The word "keel" comes from Old English , Old Norse , = "ship" or "keel". It has the distinction of being regarded by some scholars as the first word in the English language recorded in writing, having been recorded by Gildas in his 6th century Latin work ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', under the spelling ''cyulae'' (he was referring to the three ships that the Saxons first arrived in). is the Latin word for "keel" and is the origin of the term careen (to clean a keel and the hull in general, often by rolling the ship on its side). An example of this use is Careening Cove, a suburb of Sydney, Australia, where careening was carried out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty (russian: Под высочайшим Его Императорского Величества покровительством Российская-Американская Компания, Pod vysochayshim Yego Imperatorskogo Velichestva pokrovitelstvom Rossiyskaya-Amerikanskaya Kompaniya) was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the United American Company. Emperor Paul I of Russia chartered the company in the Ukase of 1799. It had the mission of establishing new settlements in Russian America, conducting trade with natives, and carrying out an expanded colonization program. Russia's first joint-stock company, it came under the direct authority of the Ministry of Commerce of Imperial Russia. Count Nikolai Petrovich Rumyantsev (Minister of Commerce from 1802 to 1811; Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1808 to 1814) exercised a pivotal influence upon the early activities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but also included small outposts in California, including Fort Ross, and three forts in Hawaii, including Russian Fort Elizabeth. Russian Creole settlements were concentrated in Alaska, including the capital, Novo-Arkhangelsk (''New Arkhangelsk''), which is now Sitka. After first landing in Alaska in 1741, Vitus Bering claimed the Alaskan country for the Russian Empire. Russia later confirmed its rule over the territory with the ''Ukase'' of 1799 which established the southern border of Russian America along the 55th parallel north.United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland''Text of Ukase of 1779''in ''Behring sea arbitration'' (London: Harrison and Sons, 1893), pp. 25-27 The decree also provided monopolistic privileges to the state-sponsor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing 180th meridian, longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude (Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
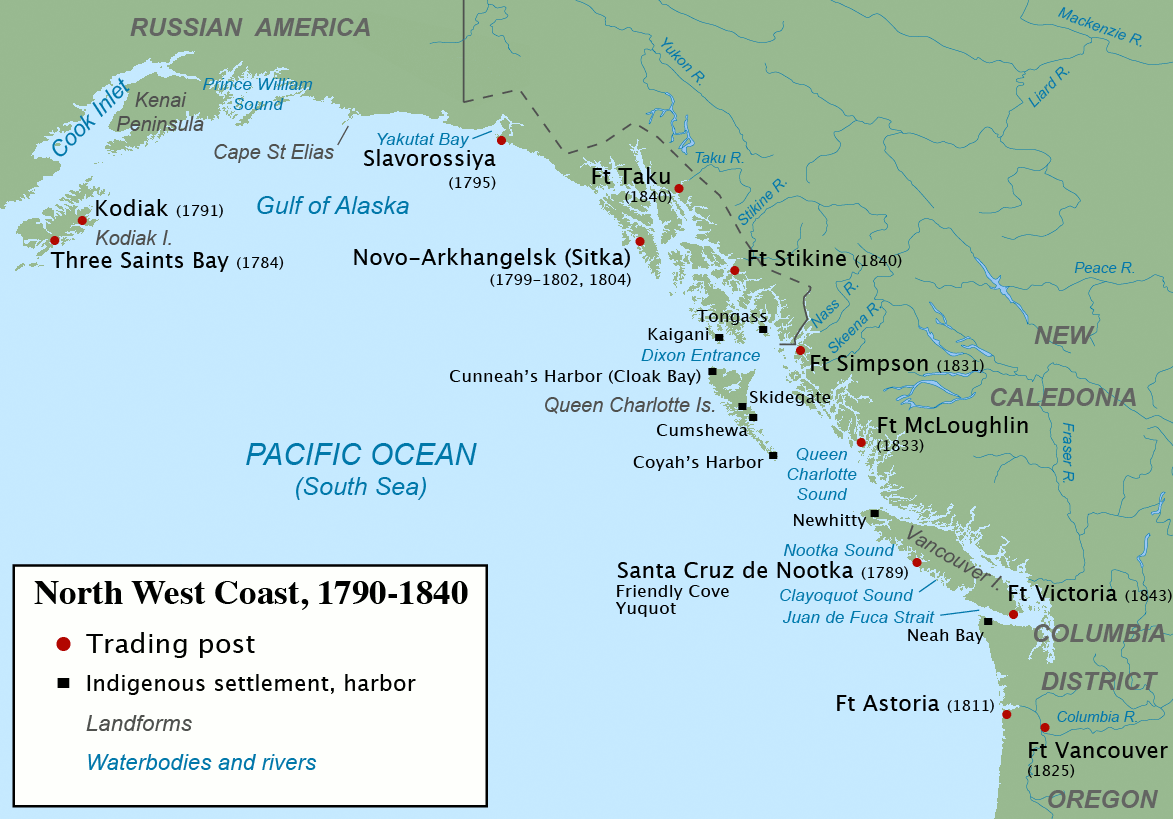
Maritime Fur Trade
The maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in exchange for tea, silks, porcelain, and other Chinese goods, which were then sold in Europe and the United States. The maritime fur trade was pioneered by Russians, working east from Kamchatka along the Aleutian Islands to the southern coast of Alaska. British and Americans entered during the 1780s, focusing on what is now the coast of British Columbia. The trade boomed around the beginning of the 19th century. A long period of decline began in the 1810s. As the sea otter population was depleted, the maritime fur trade diversified and transformed, tapping new markets and commodities, while continuing to focus on the Northwest Coast and China. It lasted until the middle to late 19th century. Russians controlled most of the coast of present-da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |