|
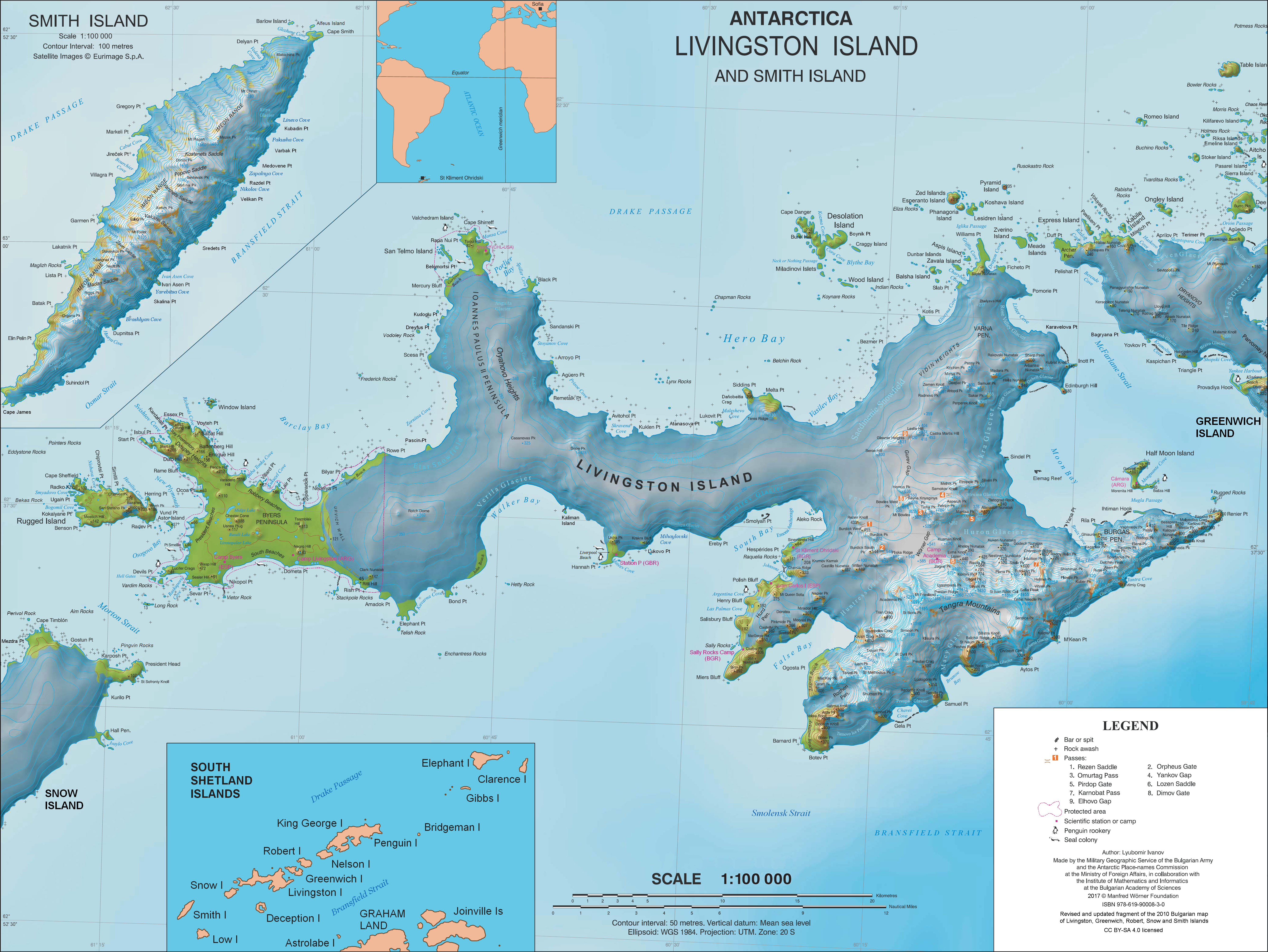
Shipka Saddle
Shipka Saddle (Shipchenska Sedlovina \'ship-chen-ska se-dlo-vi-'na\) is a deep ice-covered saddle in Tangra Mountains, Livingston Island, Antarctica between Friesland Ridge to the west and Levski Ridge to the east. The feature is 250 m long, with an elevation ca. 1,200 m. It forms part of the divide between the glacial catchments of Huron Glacier to the north and Macy Glacier to the south. Shipka is the name of a pass in the Stara Planina (Balkan Mountains) in central Bulgaria. Location The saddle midpoint is located at , which is 2.99 km east of Mount Friesland, 3.52 km south-southeast of Kuzman Knoll, 3.91 km west of Great Needle Peak and 3.95 km north of Peshev Peak (UK Directorate of Overseas Surveys mapping in 1968; rough Argentine mapping in 1980, and Bulgarian mapping in 2005 and 2009. Co-ordinates, elevation and distances given according to a 1995-96 Bulgarian topographic survey and the Tangra 2004/05 survey. Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Committee On Antarctic Research
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scientific work is administered through several discipline-themed ''science groups''. The organisation has observer status at, and provides independent advice to Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings, and also provides information to other international bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). History At the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU)’s Antarctic meeting held in Stockholm from 9–11 September 1957, it was agreed that a committee should be created to oversee scientific research in Antarctica. At the time there were 12 nations actively conducting Antarctic research and they were each invited to nominate one delegate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangra 2004/05
The Tangra 2004/05 Expedition was commissioned by the Antarctic Place-names Commission at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria, managed by the Manfred Wörner Foundation, and supported by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute, the Institute of Mathematics and Informatics at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Bulgarian Posts, Uruguayan Antarctic Institute, Peregrine Shipping (Australia), and Petrol Ltd, TNT, Mtel, Bulstrad, Polytours, B. Bekyarov and B. Chernev (Bulgaria). Expedition team Dr. Lyubomir Ivanov (team leader), senior research associate, Institute of Mathematics and Informatics at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences; chairman, Antarctic Place-names Commission; author of the 1995 Bulgarian Antarctic ''Toponymic Guidelines'' introducing in particular the present official system for the Romanization of Bulgarian; participant in four Bulgarian Antarctic campaigns, and author of the first Bulgarian Antarctic topographic maps. Doychin Vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directorate Of Overseas Surveys
The Ordnance Survey International or Ordnance Survey Overseas Directorate its predecessors built an archive of air photography, map and survey records for the United Kingdom from 1946 to 1999. The Ordnance Survey International Collection (formerly the Ordnance Survey International Library) held mapping records that were acquired outside the UK. Although the international division opened in 1946, the OS had been involved in overseas work for almost a century (notably the 1864-65 Ordnance Survey of Jerusalem). The agency was closed in 2001. History The agency In 1946 the ''Directorate of Colonial Surveys'' (DCS) was established by the Colonial Office to provide a central survey and mapping organisation for British colonies and protectorates. In 1957, with the imminent decolonisation of many British territories, it was renamed the ''Directorate of Overseas Surveys'' (DOS). Government reviews during the 1970s led to it being merging into the Ordnance Survey (OS) in 1984 whence it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peshev Ridge
Peshev Ridge (Peshev Rid \'pe-shev 'rid\) is a crescent-shaped ridge in central Tangra Mountains extending along the northeast coast of Brunow Bay and southeast of Macy Glacier, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Its east extremity is formed by the summit St. Naum Peak (), separated from Balchik Ridge to the east by Starosel Gate. The ridge was named in honour of Dimitar Peshev (1894–1973), who led the nationwide campaign that kept Bulgaria’s Jews safe during the Holocaust. Location The central peak, named Peshev Peak in association, is located at , which is southwest of Great Needle Peak (Falsa Aguja), south of Lyaskovets Peak, east by south of Simeon Peak and northeast of Needle Peak (Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05, and mapping in 2005 and 2009). Maps South Shetland Islands.Scale 1:200000 topographic map. DOS 610 Sheet W 62 60. Tolworth, UK, 1968. * Islas Livingston y Decepción. Mapa topográfico a escala 1:100000. Madrid: S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Needle Peak
Great Needle Peak ( bg, Голям Иглен връх, Golyam Iglen vrah, ; variant name in es, pico Falsa Aguja, lit=False Needle Peak) is the summit of the central Levski Ridge in Tangra Mountains on Livingston Island, Antarctica. Rising to 1,679.5 m, it is the third highest peak of both the mountains and the island after Mount Friesland (1700.2 m) and St. Boris Peak (1685 m). Great Needle Peak surmounts Huron Glacier and its tributary draining Devnya Valley to the north, Magura Glacier to the east, Srebarna Glacier to the south, and Macy Glacier to the southwest. History The peak's name derives from the Spanish name form ''pico Falsa Aguja'' (False Needle Peak) that probably dates back to 1957, with ‘great’ becoming established in usage and considered more suitable than ‘false’ as this heavily glaciated, major peak could hardly be associated with the ‘true’ Needle Peak (''pico Aguja''), a sharp rocky peak of elevation just 370 m situated near S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuzman Knoll
Kuzman Knoll (Kuzmanova Mogila \'kuz-ma-no-va mo-'gi-la\) is a solitary ice-covered knoll rising to 620 m in eastern Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The knoll forms a conspicuous landmark in Wörner Gap area, overlooking Huron Glacier and upper Perunika Glacier. It was named after Kuzman Tuhchiev, participant in the 1993/94 Bulgarian Antarctic campaign and base commander at St. Kliment Ohridski during the 1994-96 seasons. The feature is named ''‘Tukhchiev Knoll’'' by the U.S. and British Antarctic naming committees; "Kuzman Knoll" is the official Bulgarian name, which is established among the Spanish and Bulgarian scientists working in the area. First ascent by the Bulgarians Kuzman Tuhchiev and Vasil Gurev from St. Kliment Ohridski Base during the 1994/95 season. Location The knoll is located at which is 1.1 km north-northeast of Camp Academia site, 1.1 km east of the midpoint of Wörner Gap, 3.68 km east-northeast of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Friesland
Mount Friesland is a mountain rising to in the homonymous Friesland Ridge, the summit of Tangra Mountains and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Its north rib is connected to Pliska Ridge by Nesebar Gap on the west, and to Bowles Ridge by Wörner Gap on the north. On the east Mount Friesland is connected to Presian Ridge and further on to Catalunyan Saddle and Lyaskovets Peak. On the south-southwest it is connected by a short saddle to ‘ The Synagogue’ a sharp-peaked rock-cored ice formation abutting neighbouring St. Boris Peak. The peak is heavily glaciated and crevassed, surmounting Huntress Glacier to the west, Perunika Glacier to the north-northwest, Huron Glacier to the northeast and Macy Glacier to the southeast. The local weather is notoriously unpleasant and challenging; according to the seasoned Antarctic mountaineer Damien Gildea who climbed in the area, 'just about the worst weather in the world'. History The feature was known to Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stara Planina
The Balkan mountain range (, , known locally also as Stara planina) is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border between Bulgaria and Serbia. It then runs for about , first in a south-easterly direction along the border, then eastward across Bulgaria, forming a natural barrier between the northern and southern halves of the country, before finally reaching the Black Sea at Cape Emine. The mountains reach their highest point with Botev Peak at . In much of the central and eastern sections, the summit forms the watershed between the drainage basins of the Black Sea and the Aegean. A prominent gap in the mountains is formed by the sometimes narrow Iskar Gorge, a few miles north of the Bulgarian capital, Sofia. The karst relief determines the large number of caves, including Magura, featuring the most important and extended European post-Palaeolithic cave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |