|
Shingwedzi Camp Hiding In The Trees (214134022)
View of Shingwedzi's office building with the Shingwedzi River in the foreground Visitor accommodation at Shingwedzi Alexander Merensky's map of 1881 shows the unhealthy malarial flats and the range of the tsetse fly (in blue) encompassing much of the region. Shingwedzi (also Xingwedzi in modern Tsonga orthography) is a rest camp (i.e. tourist camp) and ranger's post situated in the northern section of the Kruger National Park. They are located on the southern bank of the Shingwedzi River, for which they were named, in Limpopo province, South Africa. The surrounding country formerly constituted the Singwitsi Reserve, proclaimed in 1903, which encompassed over 5,000 square kilometers. The region was over-hunted by the end of the 19th century, its big game depleted and its elephant population completely decimated. The name "Shingwedzi" is of Tsonga origin, and was perhaps derived from "Shing-xa-goli", perhaps a local chieftain, and "njwetse", the sound of iron rubbing against iron. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingwedzi Camp Hiding In The Trees (214134022)
View of Shingwedzi's office building with the Shingwedzi River in the foreground Visitor accommodation at Shingwedzi Alexander Merensky's map of 1881 shows the unhealthy malarial flats and the range of the tsetse fly (in blue) encompassing much of the region. Shingwedzi (also Xingwedzi in modern Tsonga orthography) is a rest camp (i.e. tourist camp) and ranger's post situated in the northern section of the Kruger National Park. They are located on the southern bank of the Shingwedzi River, for which they were named, in Limpopo province, South Africa. The surrounding country formerly constituted the Singwitsi Reserve, proclaimed in 1903, which encompassed over 5,000 square kilometers. The region was over-hunted by the end of the 19th century, its big game depleted and its elephant population completely decimated. The name "Shingwedzi" is of Tsonga origin, and was perhaps derived from "Shing-xa-goli", perhaps a local chieftain, and "njwetse", the sound of iron rubbing against iron. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoutpansberg
Zoutpansberg was the north-eastern division of the Transvaal, South Africa, encompassing an area of 25,654 square miles. The chief towns at the time were Pietersburg and Leydsdorp. It was divided into two districts (west and east) prior to the first general election of the Union of South Africa in 1910. Since 2005 the area is divided into the Capricorn, Vhembe and Mopani district municipalities of Limpopo province. Voortrekkers This was the district to which Louis Tregardt and Hans van Rensburg, the forerunners of the Great Trek, journeyed in 1835. In 1845 Hendrik Potgieter, a prominent leader of the Voortrekkers, moved there. The Zoutpansberg Boers formed a semi-independent community, and in 1857 Stephanus Schoeman, their commandant-general, sided against Marthinus Pretorius and Paul Kruger when they invaded the Orange Free State. South African Republic It was not until 1864 that Zoutpansberg was definitively incorporated in the South African Republic as a result of the Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Xanthophloea
''Vachellia xanthophloea'' is a tree in the family Fabaceae, commonly known in English as the fever tree. This species of ''Vachellia'' is native to eastern and southern Africa (Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Somalia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe). It has also become a landscape tree in other warm climates, outside of its natural range. Description The trees grow to a height of . The characteristic bark is smooth, powdery and greenish yellow, although new twigs are purple, flaking later to reveal the characteristic yellow. It is one of the few trees where photosynthesis takes place in the bark. Straight, white spines grow from the branch nodes in pairs. The leaves are twice compound, with small leaflets (). The flowers are produced in scented pale cream spherical inflorescences, clustered at the nodes and towards the ends of the branches. The pale brown pods contain 5–10 elliptical, flattened green seeds and are long, straight, flat and rather pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphaene Coriacea
''Hyphaene coriacea'', the lala palm or ilala palm is a species of palm tree native to the eastern Afrotropics. It occurs in eastern Africa from Somalia to Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa, and is also found in the coastal flats of Madagascar and on Juan de Nova Island in the Mozambique Channel Islands. Uses The spongy pulp of the hard, brown fruit is edible and the fruit is eaten and sold in Madagascar. The flavour has been compared to raisins A raisin is a dried grape. Raisins are produced in many regions of the world and may be eaten raw or used in cooking, baking, and brewing. In the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, and Australia, the word ''raisin'' is reserved for the dar ... and raisin bran. See also * Fan palm References coriacea Flora of Ethiopia Flora of Somalia Flora of Kenya Flora of Tanzania Flora of Mozambique Flora of KwaZulu-Natal Flora of the Northern Provinces Flora of the Mozambique Channel Islands Flora of Madagascar Trees of Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mopane
''Colophospermum mopane'', commonly called mopane, mopani, balsam tree, butterfly tree, or turpentine tree, is a tree in the legume family (Fabaceae), that grows in hot, dry, low-lying areas, in elevation, in the far northern parts of southern Africa. The tree only occurs in Africa and is the only species in genus ''Colophospermum''. Its distinctive butterfly-shaped (bifoliate) leaf and thin seed pod make it easy to identify. In terms of human use it is, together with camel thorn and leadwood, one of the three regionally important firewood trees. Range and habit It is native to Southern Africa, including Southern Angola, Zambia, Southern Malawi, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Mozambique and northern South Africa. It grows in alkaline (high lime content) soils which are shallow and not well drained. It also grows in alluvial soils (soil deposited by rivers). Where it occurs, it is often the dominant tree species, frequently forming homogeneous stands. In Northern South Africa and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanner Gorge
The Lanner Gorge is located in the far North of the Kruger National Park. It forms the boundary between the Kruger National Park to the South and the Makuleke Concession to the North. It was carved by the Luvuvhu River and is at some points more than 150 m deep. Description Lanner Gorge is approximately 11 km long and is carved into sandstones and shales. Geology The uppermost rocks are gravels which are thought to be Cretaceous in age while the basal shales are thought to be Permian in age. The majority of the walls appear to be composed of Triassic and Jurassic aged sandstones formed under arid conditions. The Luvuvhu river has eroded through the sandstones and shales and formation is still active as is evidenced by the many collapsed boulders in the river bed. Dinosaur fossils have been discovered in the walls of Lanner Gorge and rocks in the surrounding region. Desert roses are also common in the Triassic and Jurassic-aged rocks. The precise geological age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adansonia Digitata
''Adansonia digitata'', the African baobab, is the most widespread tree species of the genus ''Adansonia'', the baobabs, and is native to the African continent and the southern Arabian Peninsula (Yemen, Oman). These are long-lived pachycauls; radiocarbon dating has shown some individuals to be over 2,000 years old. They are typically found in dry, hot savannas of sub-Saharan Africa, where they dominate the landscape and reveal the presence of a watercourse from afar. They have traditionally been valued as sources of food, water, health remedies or places of shelter and are a key food source for many animals. They are steeped in legend and superstition. In recent years, many of the largest, oldest trees have died, possibly due to climate change. Common names for the baobab include monkey-bread tree, upside-down tree, and cream of tartar tree. Description African baobabs are trees that often grow as solitary individuals, and are large and distinctive elements of savanna or scrubla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letaba River
The Letaba River ( af, Letabarivier), also known as Leţaba, Lehlaba or Ritavi, is a river located in eastern Limpopo Province, South Africa. It is one of the most important tributaries of the Olifants River. Course It starts at the confluence of the Groot Letaba River and Klein Letaba River, whence they continue their journey eastwards through the Lowveld as the Letaba River. It joins the Olifants River in the foothills of the Lebombo Mountains, near South Africa's border with Mozambique. In Mozambique the latter river is called the Rio Elefantes. Tributaries include the Middle Letaba River, Nharhweni River, Ngwenyeni River, Nwanedzi River, Molototsi River, Nsama River and Makhadzi River. Dams in the basin * Ebenezer Dam *Tzaneen Dam * Modjaji Dam, in the Molototsi River * Hudson Ntsanwisi Dam, in the Nsama River * Middle Letaba Dam, in the Middle Letaba River * Engelhard Dam none, 450px, Game animals along its banks, near Letaba camp, central Kruger Park See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
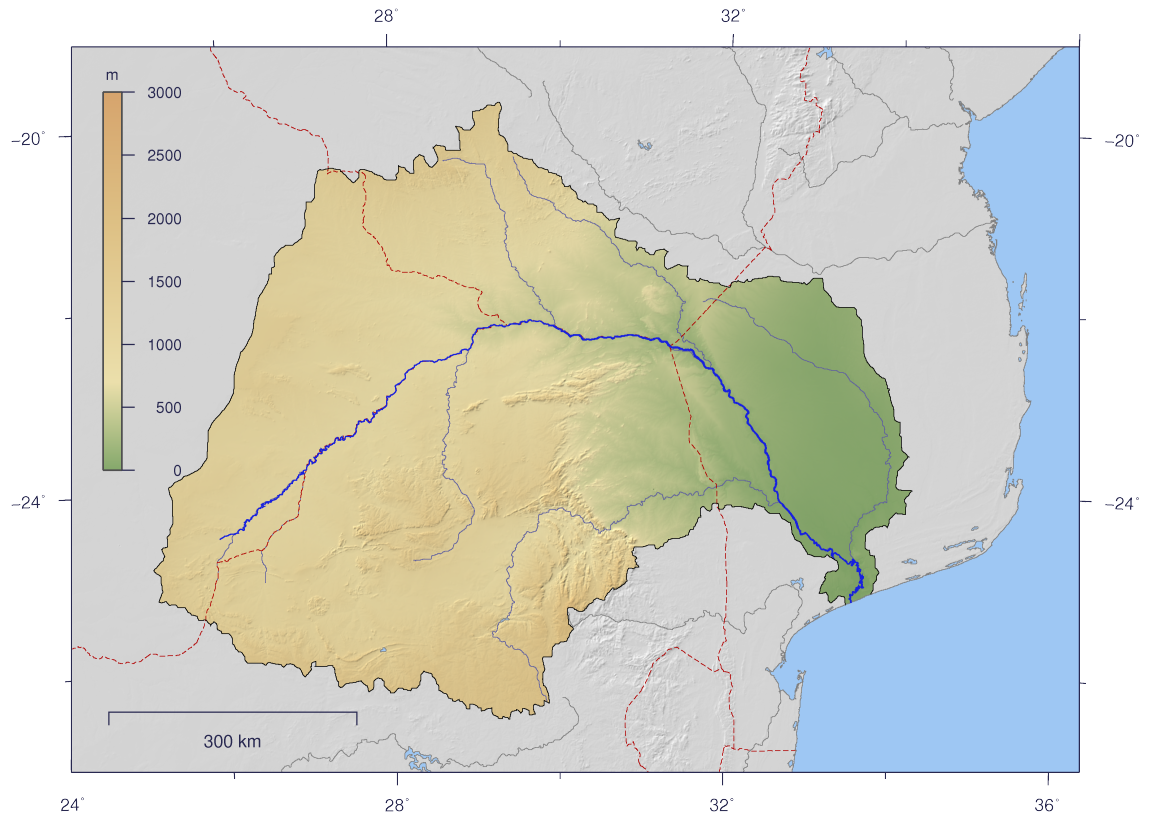
Olifants River (Limpopo)
The Olifants River, Lepelle, iBhalule or Obalule ( af, Olifantsrivier; pt, Rio dos Elefantes) is a river in South Africa and Mozambique, a tributary of the Limpopo River. It falls into the Drainage Area B of the Drainage basins of South Africa. The historical area of the Pedi people, Sekhukhuneland, is located between the Olifants River and one of its largest tributaries, the Steelpoort River. Course The Olifants River has its origin between Breyten and Bethal, Mpumalanga Province. It flows north towards Limpopo Province through Witbank Dam and then the Loskop Dam and is forced east by the Transvaal Drakensberg, cutting through at the Abel Erasmus Pass and then flowing east further across the Lowveld to join with the Letaba River. It crosses into Gaza Province, Mozambique, after cutting through the Lebombo Mountains by way of the Olifants Gorge, becoming the ''Rio dos Elefantes'', and finally joining the Limpopo River after 40 km before it enters the Indian Ocean at Xa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozambique–South Africa Border
The border between Mozambique and South Africa is divided into two segments, separated by the kingdom of Eswatini. The northern segment, which is long, runs north–south along the Lebombo Mountains from Zimbabwe to Eswatini. The southern segment, which is long, runs east–west across Maputaland from Eswatini to the Indian Ocean. Geography The tripoint with Zimbabwe is located at Crooks' Corner, in the Limpopo River either at or very close to its confluence with the Luvuvhu River. The border runs in a straight line from this tripoint to the Shingwedzi River, and then along a series of straight lines joining beacons generally along the top of the eastern slope of the Lebombo Mountains. It crosses the Olifants, Sabie and Komati rivers. This segment of the border terminates at the northern Eswatini tripoint at Mpundweni Beacon near Namaacha. The southern Eswatini tripoint is situated at Abercorn Drift in the Usutu River (Maputo River), where the Mozambique–Eswatini border ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levuvhu River
The Levubu River or Levuvhu ( ts, Rivubye; ve, Luvuvhu) is located in the northern Limpopo province of South Africa. Some of its tributaries, such as the Mutshindudi River and Mutale River rise in the Soutpansberg Mountains. The Luvuvhu River flows for about 200 km through a diverse range of landscapes before it joins the Limpopo River in the Fever Tree Forest area, near Pafuri in the Kruger National Park. A Zambezi shark (''Carcharhinus leucas'') was caught at the confluence of the Limpopo and Luvuvhu Rivers in July 1950. Zambezi sharks tolerate fresh water and can travel far up rivers like the Limpopo. The river's crocodile population extends to its upper reaches at Thohoyandou. Dams * Albasini Dam * Mambedi Dam * Tshakhuma Dam * Damani Dam * Nandoni Dam, previously known as the Mutoti Dam, in the middle section of the Luvuvhu River east of the confluence with the Dzindi River tributary and east of the town Thohoyandou * Vondo Dam in the Mutshindudi River, a tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klein Letaba River
Klein Letaba River is a tributary of the Letaba River, situated in Limpopo, South Africa. After its confluence with the Groot Letaba River on the western boundary of the Kruger National Park it forms the Letaba River flowing through the whole width of the park. The Klein Letaba tributaries like the Soeketse River and Koedoes River are wide, dry and sandy ditches for most of the year. See also *Letaba River *Groot Letaba River *List of reservoirs and dams in South Africa The following is a partial list of dams in South Africa. __NOTOC__ In South African English (as well as Afrikaans), a dam refers to both the wall as well as the reservoir or lake that builds up as a consequence. List of dams (reservoirs) ... Rivers of Limpopo {{SouthAfrica-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |