|
Shikhara
''Shikhara'' (IAST: '), a Sanskrit word translating literally to "mountain peak", refers to the rising tower in the Hindu temple architecture of North India, and also often used in Jain temples. A ''shikhara'' over the ''garbhagriha'' chamber where the presiding deity is enshrined is the most prominent and visible part of a Hindu temple of North India. In South India, the equivalent term is ''vimana''; unlike the ''shikhara'', this refers to the whole building, including the sanctum beneath. In the south, ''shikhara'' is a term for the top stage of the vimana only, which is usually a dome capped with a finial; this article is concerned with the northern form. The southern ''vimana'' is not to be confused with the elaborate gateway-towers of south Indian temples, called ''gopuram'', which are often taller and more prominent features in large temples. Forms ''Shikhara'' can be classified into three main forms: *''Latina''. The ''shikhara'' has four faces, which may include proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabodhi Temple
The Mahabodhi Temple (literally: "Great Awakening Temple") or the Mahābodhi Mahāvihāra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an ancient, but rebuilt and restored Buddhist temple in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India, marking the location where the Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment. Bodh Gaya is 15 km from Gaya and is about from Patna. The site contains a descendant of the Bodhi Tree under which Buddha gained enlightenment, and has been a major pilgrimage destination of Buddhists for well over two thousand years, and some elements date to the period of Ashoka (died c. 232 BCE). What is now visible on the ground essentially dates from the 5th century CE, or possibly earlier, as well as several major restorations since the 19th century. But the structure now may well incorporate large parts of earlier work, possibly from the 2nd or 3rd century CE.Harle, 201; Michell, 228–229 Archaeological finds from the site however, indicate that the place was a site of veneration for Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
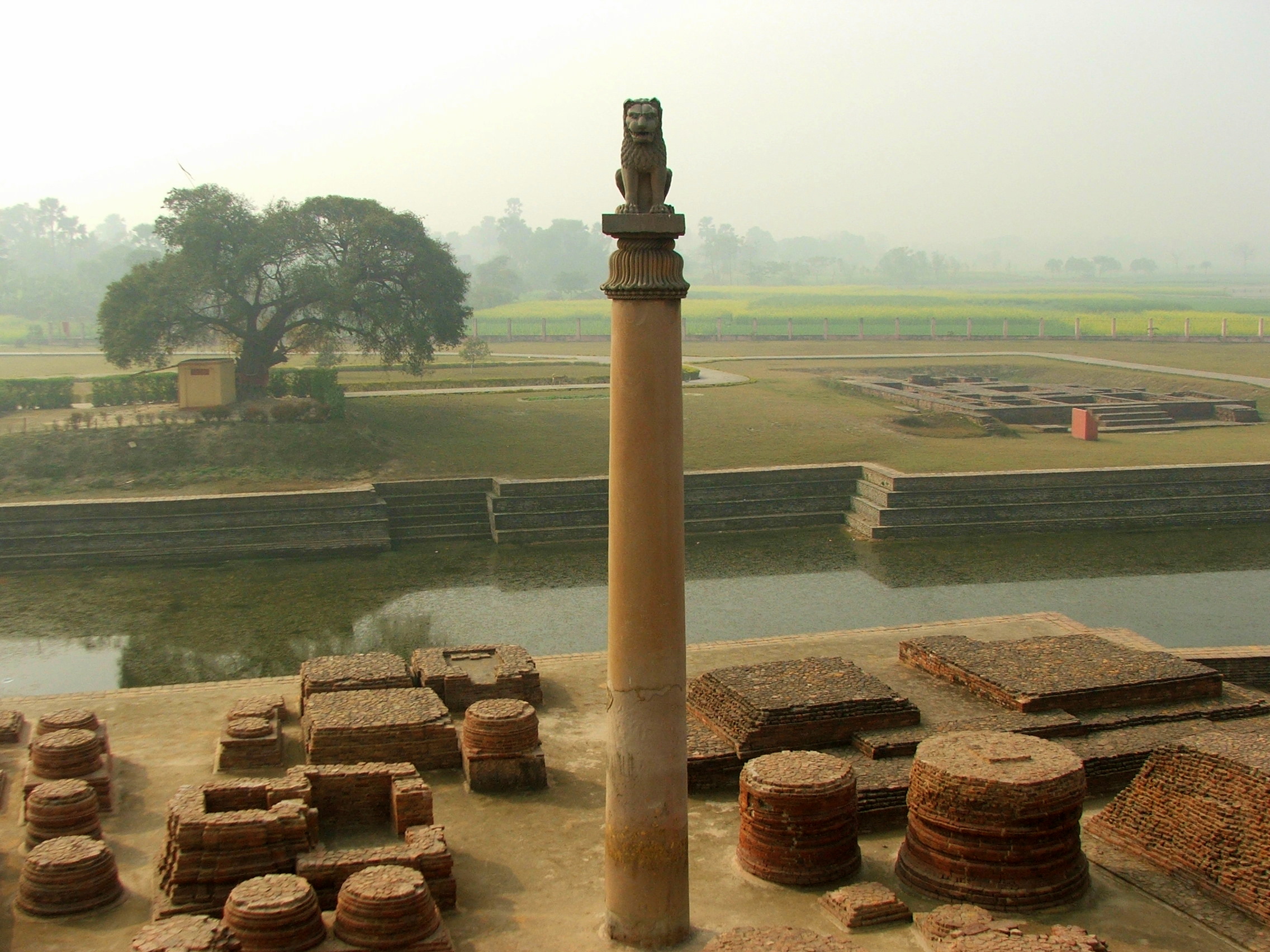
Pillar Of Ashoka
The pillars of Ashoka are a series of monolithic columns dispersed throughout the Indian subcontinent, erected or at least inscribed with edicts by the Mauryan Emperor Ashoka during his reign from c. 268 to 232 BCE. Ashoka used the expression ''Dhaṃma thaṃbhā'' (Dharma stambha), i.e. "pillars of the Dharma" to describe his own pillars. These pillars constitute important monuments of the architecture of India, most of them exhibiting the characteristic Mauryan polish. Of the pillars erected by Ashoka, twenty still survive including those with inscriptions of his edicts. Only a few with animal capitals survive of which seven complete specimens are known. Two pillars were relocated by Firuz Shah Tughlaq to Delhi. Several pillars were relocated later by Mughal Empire rulers, the animal capitals being removed.Krishnaswamy, 697-698 Averaging between in height, and weighing up to 50 tons each, the pillars were dragged, sometimes hundreds of miles, to where they were erected. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but Great Renunciation, renounced his Householder (Buddhism), home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a Sangha, monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana (Buddhism), Nirvana, that is, Vimutti, freedom from Avidyā (Buddhism), ignorance, Upādāna, craving, Saṃsāra (Buddhism), rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation. In Buddhism, circumambulation or ''pradakhshina'' has been an important ritual and devotional practice since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate or drum with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have or had ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of the dome is a thin vertical element, with one of more horizontal discs spreadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huvishka
Huvishka ( Kushan: Οοηϸκι, ''Ooēški'', Brahmi: ', '; Kharosthi: 𐨱𐨂𐨬𐨅𐨮𐨿𐨐 ', ') was the emperor of the Kushan Empire from the death of Kanishka (assumed on the best evidence available to be in 150 CE) until the succession of Vasudeva I about thirty years later. His rule was a period of consolidation for the Empire. Huvishka's territory encompassed Balkh in Bactria to Mathura in India, locations where it is known that he minted his coinage. Gold coins and amulets in his effigy were found as far as Pataliputra and Bodh Gaya, including one such amulet as an offering under the Enlightenment Throne of the Buddha in Bodh Gaya, suggesting with other finds of Kushan coins in the area that Kushan rule may have extended this far east. His reign seems to have been essentially peaceful, consolidating Kushan power in northern India, and moving the centre of the Kushan Empire to the southern capital city of Mathura. Religion Huvishka was the son of Kanishka. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharoshthi
The Kharoṣṭhī script, also spelled Kharoshthi (Kharosthi: ), was an ancient Indo-Iranian script used by various Aryan peoples in north-western regions of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely around present-day northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan. It was used in Central Asia as well. An abugida, it was introduced at least by the middle of the 3rd century BCE, possibly during the 4th century BCE, and remained in use until it died out in its homeland around the 3rd century CE. It was also in use in Bactria, the Kushan Empire, Sogdia, and along the Silk Road. There is some evidence it may have survived until the 7th century in Khotan and Niya, both cities in East Turkestan. Form Kharosthi (, from right to left ''Kha-ro-ṣṭhī'') is mostly written right to left (type A). Each syllable includes the short /a/ sound by default, with other vowels being indicated by diacritic marks. Recent epigraphic evidence has shown that the order of letters in the Kharosthi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
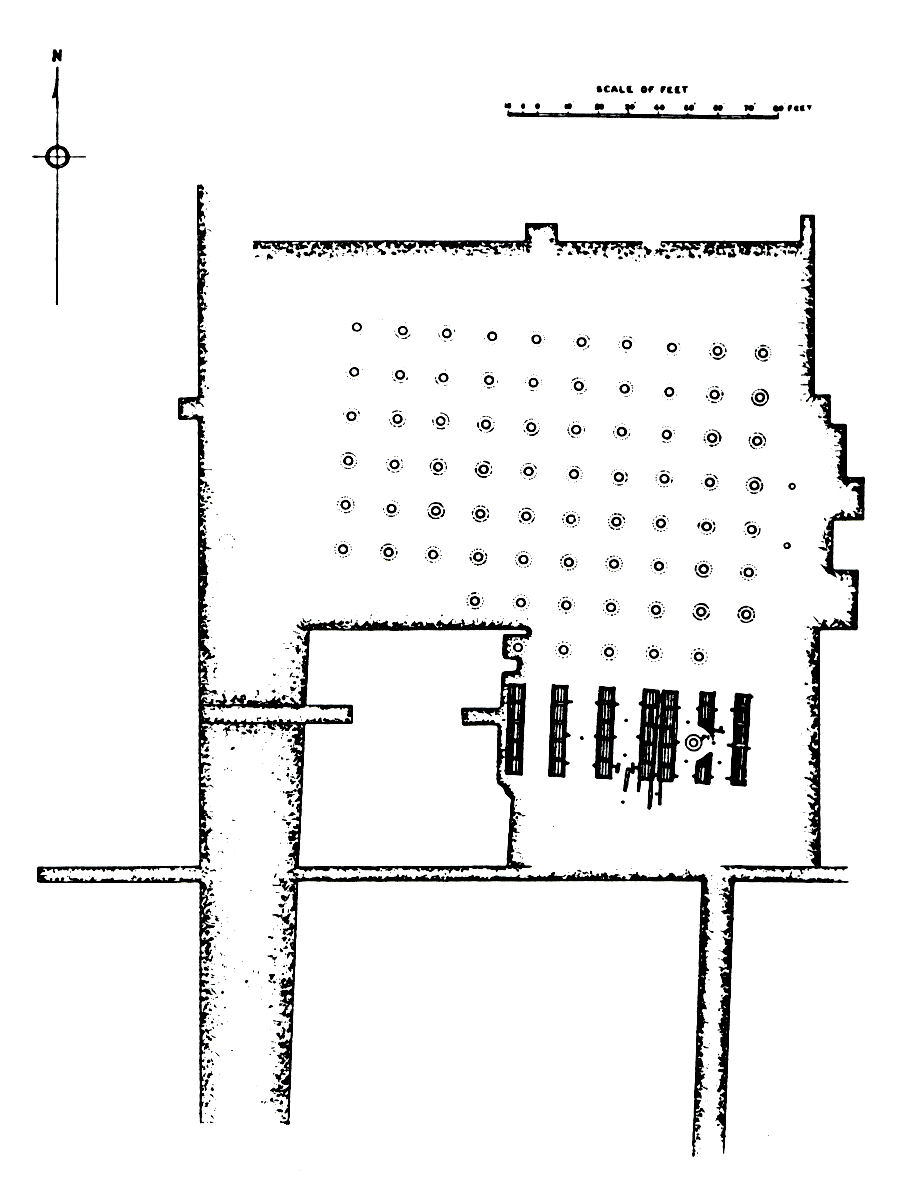
Kumrahar
Kumhrar or Kumrahar is the area of Patna where remains of the ancient city of Pataliputra were excavated by the Archaeological Survey of India starting from 1913. It is located 5 km east of Patna Railway Station. Archaeological remains of the Mauryan period (322–185 BCE) have been discovered here, this include the ruins of a hypostyle 80-pillared hallDevise plan to save Kumhrar site:HC , 1 February 2002. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran, Syria and Turkey. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history () to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (). Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Binfield Havell
Ernest Binfield Havell (16 September 1861 – 31 December 1934), who published under the name E.B. Havell, was an influential English arts administrator, art historian and author of numerous books about Indian art and architecture. He was a member of the Havell family of artists and art educators. He was the principal of the Government School of Art, Calcutta from 1896 to 1905, where, along with Abanindranath Tagore, he developed a style of art and art education based on Indian rather than Western models, which led to the foundation of the Bengal school of art. Early life Ernest was born at Jesse Terrace, Reading in the English county of Berkshire in 1861, the son of an artist Charles Richard Havell and his wife, Charlotte Amelia Lord. The family had several artists and publishers. He went to Reading School and learned art at the Royal College of Art and in Paris and Italy. Art history In India, Havell initially served the Madras School of Art as Superintendent for a decade fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Temple
A Hindu temple, or ''mandir'' or ''koil'' in Indian languages, is a house, seat and body of divinity for Hindus. It is a structure designed to bring human beings and gods together through worship, sacrifice, and devotion.; Quote: "The Hindu temple is designed to bring about contact between man and the gods" (...) "The architecture of the Hindu temple symbolically represents this quest by setting out to dissolve the boundaries between man and the divine". The symbolism and structure of a Hindu temple are rooted in Vedic traditions, deploying circles and squares. It also represents recursion and the representation of the equivalence of the macrocosm and the microcosm by astronomical numbers, and by "specific alignments related to the geography of the place and the presumed linkages of the deity and the patron". A temple incorporates all elements of the Hindu cosmos — presenting the good, the evil and the human, as well as the elements of the Hindu sense of cyclic time and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Golden Age of India by historians. The ruling dynasty of the empire was founded by the king Sri Gupta; the most notable rulers of the dynasty were Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Skandagupta. The 5th-century CE Sanskrit poet Kalidasa credits the Guptas with having conquered about twenty-one kingdoms, both in and outside India, including the kingdoms of Parasikas, the Hunas, the Kambojas, tribes located in the west and east Oxus valleys, the Kinnaras, Kiratas, and others.Raghu Vamsa v 4.60–75 The high points of this period are the great cultural developments which took place primarily during the reigns of Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Kumaragupta I. Many Hindu epics and literary sources, such as Mahabharata and Ramay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)