|
Shikha (hairstyle)
A ''shikha'' ( sa, शिखा, translit=śikhā) is a tuft of hair kept at the back of the head by a Hindu following tonsure. Though traditionally considered to be an essential mark of a Hindu, today it is primarily worn among Brahmins, especially those serving as temple priests. Nomenclature ''Śikhā'' literally means "crest" or "tuft" in Sanskrit. The hairstyle is referred to as the ''juṭṭu'' or ''śikhe'' in Kannada, ''choti'' in Hindi, ''tiki'' in Bengali, ''kudumi'' in Malayalam and Tamil, "chôin" in Odia and ''shendi'' in Marathi. Description The ''shikha'' signifies a one-pointed (''ekanta'') focus on a spiritual goal, and devotion to God. It is also an indication of cleanliness, as well as personal sacrifice to God. According to Smriti texts, it is mandatory for all Hindus to wear a ''shikha'', especially for the twice-born (initiated by the sacred thread called the ''yajnopavita''). A man not keeping a tuft is regarded not to gain the full merit of religious ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Gospel In South India - Or The Religious Life, Experience, And Character Of The Hindu Christians (1880) (14586684050)
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeannine Auboyer
Jeannine Auboyer (1912 - 1990) was a French curator of the Musée Guimet (1965–1980) in Paris, who made several archaeological expeditions to India and Cambodia Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand t ... and wrote numerous French titles on history. She is known for ''Daily Life in Ancient India'' (French: ''La Vie quotidienne dans l'Inde ancienne)'', a record of the ancient Indian rituals and customs, many of which are preserved in Indian society today. References 1912 births 1990 deaths French curators 20th-century French archaeologists French women archaeologists 20th-century French historians French women historians 20th-century French women writers French women curators {{France-archaeologist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khokhol
Oseledets ( uk, оселедець, p=ɔsɛˈl ɛdɛt͡sʲ, IPA: �sɛ'lɛdɛt͡sʲ, hohol in Russian or chub ( uk, чуб, translit=chub, p=t͡ɕup, IPA: ͡ɕup is a traditional Ukrainian style of haircut that features a long lock of hair left on the otherwise completely shaved head, commonly sprouting from the top or the front of an otherwise closely shaven head. Most commonly it is associated with the Ukrainian cossacks, although first mentions of the haircut go back to Sviatoslav I. A Russian name for oseledets, ''khokhol'', is commonly used as an ethnic slur for Ukrainians. History Halfshaven haircuts have been worn by the inhabitants of Ukraine since the early Middle Ages. The Viking rulers of Kyivan Rus imitated the traditional costume and hairstyles of their Slavic subjects. Many of these Russified Vikings joined the Varangian guard of the Roman Empire in Constantinople, and introduced the haircut to their comrades from Denmark. Subsequent generations of Viking colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
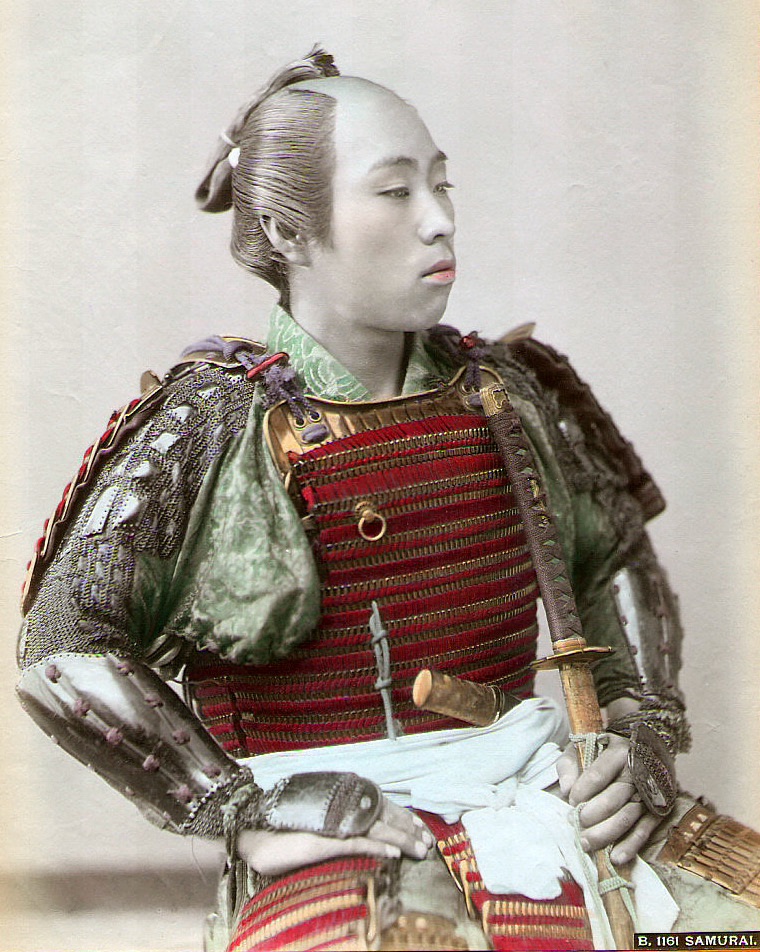
Chonmage
The is a type of traditional Japanese topknot haircut worn by men. It is most commonly associated with the Edo period (1603–1867) and samurai, and in recent times with sumo wrestlers. It was originally a method of using hair to hold a samurai kabuto helmet steady atop the head in battle, and became a status symbol among Japanese society. In a traditional Edo-period , the top of the head is shaved. The remaining hair was oiled and waxed before being tied into a small tail folded onto the top of the head in the characteristic topknot. History The origins of the can be traced back to the Heian period. During this period, aristocrats wore special cap like crowns as part of their official clothing. To secure the crown in place, the hair would be tied near the back of the head. Between the 1580s (towards the end of the Warring States period, 1467–1615) and the 1630s (the beginning of the Edo period, 1603–1867), Japanese cultural attitudes to men's hair shifted; where a fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Society For Krishna Consciousness
The International Society for Krishna Consciousness (ISKCON), known Colloquialism, colloquially as the Hare Krishna movement or Hare Krishnas, is a Gaudiya Vaishnavism, Gaudiya Vaishnava Hinduism, Hindu religious organization. ISKCON was founded in 1966 in New York City by A. C. Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada. Its core beliefs are based on Hindu texts, Hindu scriptures, particularly the ''Bhagavad Gita'' and the ''Bhagavata Purana''. ISKCON is "the largest and, arguably, most important branch" of Gaudiya Vaishnava tradition, which has had adherents in India since the early 16th century and American and European Hindu devotional movements, devotees since the early 1900s. ISKCON was formed to spread the practice of Bhakti yoga, the practice of love of God in which those involved (''bhaktas'') dedicate their thoughts and actions towards pleasing Krishna, whom they consider the Svayam Bhagavan, Supreme Lord. Its most rapid expansion in membership have been within India and (after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chidambaram
Chidambaram is a town and municipality in Cuddalore district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, on the banks of the Vellar River where it meets the Bay of Bengal. It is the headquarters of the Chidambaram taluk. The town is believed to be of significant antiquity and has been ruled, at different times, by the Pallavas until ninth century, Medieval Cholas, Later Cholas, Later Pandyas, Vijayanagar Empire, Thanjavur Nayakas, Marathas and the British. The town is known for the Thillai Nataraja Temple and Thillai Kali Temple, and the annual chariot festival held in the months of December–January (In the Tamil month of Marghazhi known as "Margazhi Urchavam") and June to July (In the Tamil month of Aani known as "Aani Thirumanjanam"). One of the Divya Desams Divya Sri Govindaraja Perumal Temple (Thiruchitrakoodam) is a part of Thillai Nataraja Temple complex. Thiruvetkalam Shiva Temple, Vadakiruppu, Thirunelvayil Shiva Temple, Sivapuri and Tirukkazhippalai Palvannanathar Temple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dikshitar
Dīkṣitars (Tamil: தீக்ஷிதர்) or Thillai Vazh Anthaanar are a Vedic Shaiva Brahmin servitor community of Tamil Nadu who are based mainly in the town of Chidambaram. Smartha (especially the Vadamas), Sri Vaishnava and other Brahmins in South India also carry the surname Dikshitars, but are different from the Chidambaram Dishitar. They are an exclusive group of Brahmins learned in the Vedas and ''Yagnas'' (sacrifices) who also serve as the hereditary trustees of the Nataraja temple in Chidambaram. They are also called ''Thillai Muvayiravar'' or the ''Three Thousand of Thillai'' Every Dikshitar once he is married becomes as of right a trustee and ''archaka'' of the Nataraja temple. A practice unique to the community is that the priests wear the tuft of hair in front of the head similar to the Nambuthiri Brahmans of Kerala. History The Dikshithars might be traced back to the first line of Brahmanas who migrated to South India from the north, this migration ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
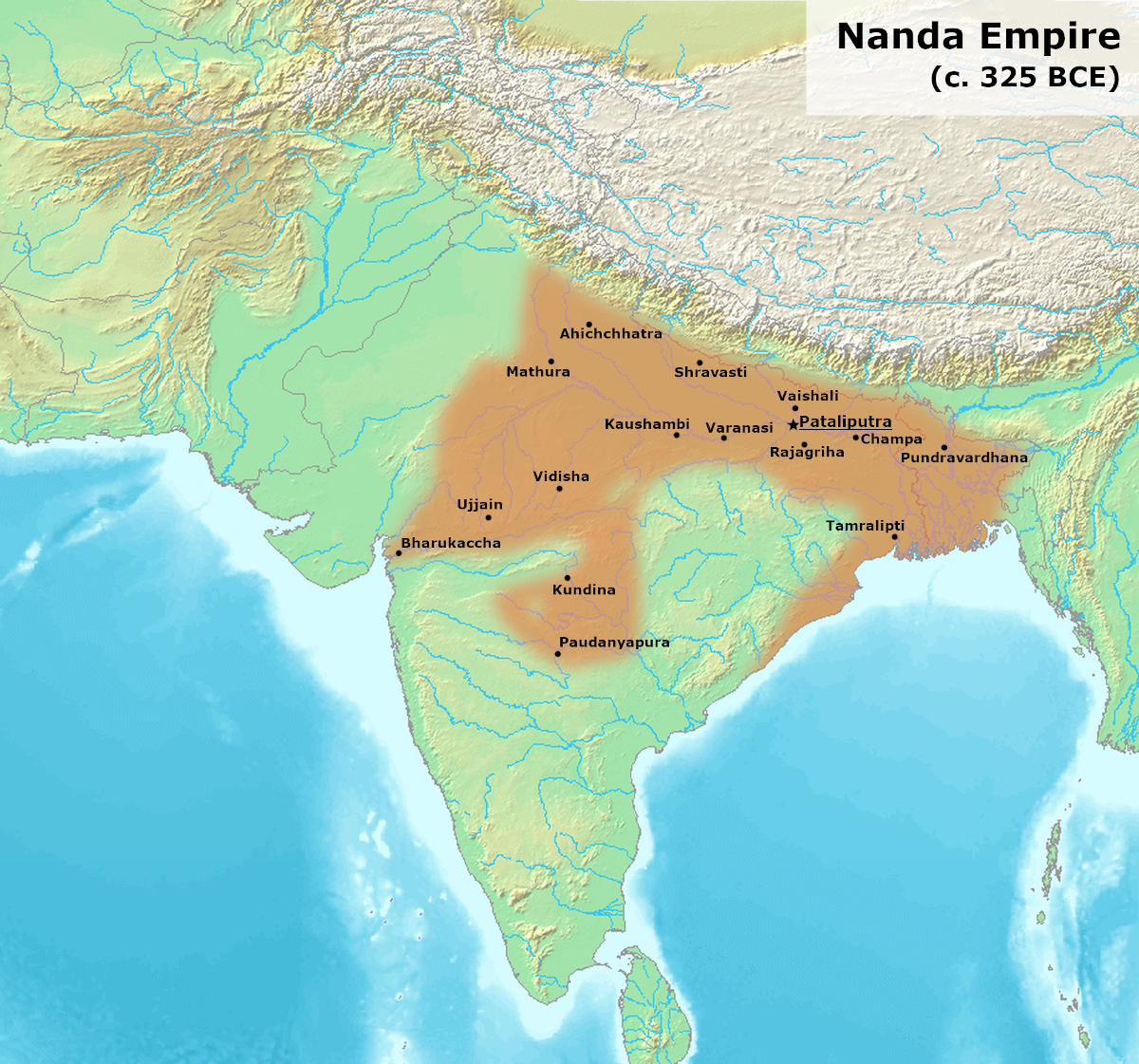
Nanda Empire
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded their empire to include a larger part of northern India. Ancient sources differ considerably regarding the names of the Nanda kings and the duration of their rule, but based on the Buddhist tradition recorded in the '' Mahavamsa'', they appear to have ruled during ''circa'' 345–322 BCE, although some theories date the start of their rule to fifth century BCE. The Nandas built on the successes of their Haryanka and Shaishunaga predecessors, and instituted a more centralised administration. Ancient sources credit them with amassing great wealth, which was probably a result of introduction of new currency and taxation system. Ancient texts also suggest that the Nandas were unpopular among their subjects because of their low status birth, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhana Nanda
Dhana Nanda (died c. 321 BCE), according to the Buddhist text '' Mahabodhivamsa'', was the last ruler of the Nanda dynasty of ancient India. He was the youngest son of Mahapadma Nanda. Chandragupta Maurya raised an army that eventually conquered the Nanda capital Pataliputra and defeated him. This defeat marked the fall of the Nanda Empire and the birth of the Maurya Empire. The Jain tradition presents a similar legend about the last Nanda emperor, although it simply calls the emperor "Nanda", and states that the emperor was allowed to leave his capital alive after being defeated. The Puranas give a different account, describing the last Nanda emperor as one of eight sons of the dynasty's founder, whom they call Mahapadma. The Greco-Roman accounts name Alexander's contemporary ruler in India as Agrammes or Xandrames, whom modern historians identify as the last Nanda emperor. According to these accounts, Alexander's soldiers mutinied when faced with the prospect of a war with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanakya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭilya or Vishnugupta, who authored the ancient Indian political treatise, the ''Arthashastra'', a text dated to roughly between the fourth century BCE and the third century CE. As such, he is considered the pioneer of the field of political science and economics in India, and his work is thought of as an important precursor to classical economics.Waldauer, C., Zahka, W.J. and Pal, S. 1996Kauṭilya's Arthashastra: A neglected precursor to classical economics ''Indian Economic Review'', Vol. XXXI, No. 1, pp. 101–108. His works were lost near the end of the Gupta Empire in the sixth century CE and not rediscovered until the early 20th century. Around 321 BCE, Chanakya assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta in his rise to power and is wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swami Shraddhanand
Swami Shraddhanand (22 February 1856 – 23 December 1926), also known as Mahatma Munshi Ram Vij, was an Arya Samaj sannyasi and an Indian Independence activist who propagated the teachings of Dayananda Saraswati. This included the establishment of educational institutions, like the Gurukul Kangri University, and played a key role on the ''Sangathan'' (consolidation and organization) and the ''Shuddhi'' (purification), a Hindu reform movement in the 1920s. Early life and education He was born on 22 February 1856 in the village of Talwan in the Jalandhar District of the Punjab Province of India. He was the youngest child in the family of Lala Nanak Chand, who was a Police Inspector in the United Provinces (now Uttar Pradesh), then administered by the East India Company. His given name was Brihaspati Vij, but later he was called Munshi Ram Vij by his father, a name that stayed with him till he took sanyas in 1917, variously as Lala Munshi Ram Vij and Mahatma Munshi Ram. He adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohandas K
Mohandas may refer to: People * Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi or Mahatma Gandhi (1869–1948), major political and spiritual leader of India * Achuth Mohandas, Indian writer in both English and Malayalam and a radio jockey * Geetu Mohandas (born 1981), Indian actress * Mamta Mohandas (born 1985), Indian actress * P. M. K. Mohandas Ponnambath Mambally Krishnan Mohandas (31 January 1948 – 17 October 2004) was an Indian cricketer who played at first-class level for Kerala during the 1972–73 season. He was a right-handed batsman and right-arm medium-fast bowler. Mohandas ... (1948–2004), Indian cricketer * P. V. A. Mohandas, Indian orthopedic surgeon Other uses * ''Mohandas'' (2008 film), a Hindi drama film by Mazhar Kamran * ''Mohandas'' (2019 film), Indian biographical film about the childhood of Mahatma Gandhi in English, Hindi and Kannada and directed by P. Sheshadri * '' Mohandas B.A.L.L.B.'', Indian TV show broadcast on Zee TV in 1997-1998 See also * Muhandes (disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)