|
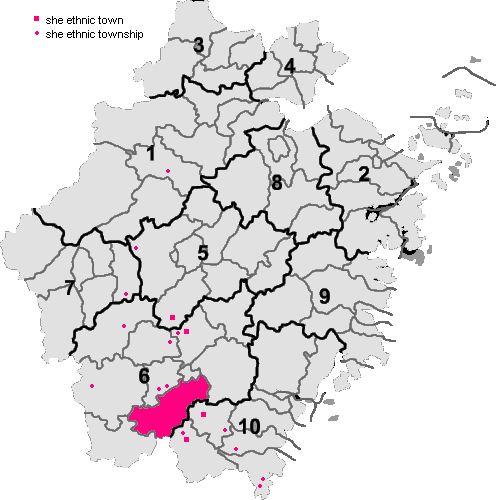
Shehua
Shehua (, ''Shēhuà'', meaning 'She speech') is an unclassified Sinitic language spoken by the She people of Southeastern China. It is also called Shanha, San-hak () or Shanhahua (). Shehua speakers are located mainly in Fujian and Zhejiang provinces of Southeastern China, with smaller numbers of speakers in a few locations of Jiangxi (in Guixi and Yanshan County), Guangdong (in Chaozhou and Fengshun County) and Anhui (in Ningguo) provinces. ''Shēhuà'' () is not to be confused with Shēyǔ (, also known as Ho Ne), which is a Hmong–Mien language spoken in East-Central Guangdong. Shehua and Sheyu speakers have separate histories and identities, although both are officially classified by the Chinese government as She people. The Dongjia of Majiang County, Guizhou are also officially classified as She people, but speak a Western Hmongic language closely related to Chong'anjiang Miao (). History During the Tang dynasty, Shehua speakers lived in the Jiangxi-Guangdong-Fuji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
She People
The She people (; Shehua: ; Cantonese: , Fuzhou: ) are an ethnic group in China. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. The She are the largest ethnic minority in Fujian, Zhejiang, and Jiangxi Provinces. They are also present in the provinces of Anhui and Guangdong. Some descendants of the She also exist amongst the Hakka minority in Taiwan. Languages Today, over 400,000 She people of Fujian, Zhejiang, and Jiangxi provinces speak Shehua, an unclassified Chinese variety that has been heavily influenced by Hakka Chinese. There are approximately 1,200 She people in Guangdong province who speak a Hmong–Mien language called She, also called ''Ho Ne'' meaning "mountain people" (). Some said they were descendants of Dongyi, Nanman or Yue peoples. '' Shēhuà'' () should not be confused with (), also known as Ho Ne, which is a Hmong-Mien language spoken in east-central Guangdong. Shehua and Sheyu speakers have separate h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
She Language
The She language (Mandarin: 畲語, ''Shēyǔ'', Hakka 山客話, ''san ha ue'', ), autonym Ho Ne, or Ho Nte, is a critically endangered Hmong–Mien language spoken by the She people. Most of the over 709,000 She people today speak ''Shehua'' (probably a variety of Hakka Chinese). Those who speak Sheyu—approximately 1,200 individuals in Guangdong Province—call themselves ''Ho Ne'', "mountain people" (). Dialects There are two main dialects of She, both of which are highly endangered. They are spoken in two small pockets to the west and east of Huizhou City, Guangdong. *Luofu 罗浮 (Western She dialect), spoken in Luofu Mountain District 罗浮山区, Boluo County and in Zengcheng District. 580 speakers according to ''Ethnologue''. *Lianhua 莲花 (Eastern She dialect), spoken in Lianhua Mountain District 莲花山区, Haifeng County. 390 speakers according to ''Ethnologue''. External relationships She has been difficult to classify due to the heavy influence of Chines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hmong–Mien Languages
The Hmong–Mien languages (also known as Miao–Yao and rarely as Yangtzean) are a highly tonal language family of southern China and northern Southeast Asia. They are spoken in mountainous areas of southern China, including Guizhou, Hunan, Yunnan, Sichuan, Guangxi, and Hubei provinces; the speakers of these languages are predominantly "hill people", in contrast to the neighboring Han Chinese, who have settled the more fertile river valleys. Relationships Hmong (Miao) and Mien (Yao) are closely related, but clearly distinct. For internal classifications, see Hmongic languages and Mienic languages. The largest differences are due to divergent developments in their phonological systems. The Hmongic languages appear to have kept the large set of initial consonants featured in the protolanguage but greatly reduced the distinctions in the syllable finals, in particular losing all glides and stop codas. The Mienic languages, on the other hand, have largely preserved syllable finals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinitic Languages
The Sinitic languages (漢語族/汉语族), often synonymous with "Chinese languages", are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is a primary split between the Sinitic languages and the rest of the family (the Tibeto-Burman languages). This view is rejected by a number of researchers but has found phylogenetic support among others. The Greater Bai languages, whose classification is difficult, may be an offshoot of Old Chinese and thus Sinitic; otherwise Sinitic is defined only by the many varieties of Chinese unified by a common writing system, and usage of the term "Sinitic" may reflect the linguistic view that Chinese constitutes a family of distinct languages, rather than variants of a single language. Population The total speakers of the Chinese macrolanguage is 1,521,943,700, of which about 73.5% (1,118,584,040) speak a Mandarin variety. The estimated number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakka Chinese
Hakka (, , ) forms a language group of varieties of Chinese, spoken natively by the Hakka people throughout Southern China and Taiwan and throughout the diaspora areas of East Asia, Southeast Asia and in overseas Chinese communities around the world. Due to its primary usage in scattered isolated regions where communication is limited to the local area, Hakka has developed numerous Variety (linguistics), varieties or dialects, spoken in different provinces, such as Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Fujian, Sichuan, Hunan, Jiangxi and Guizhou, as well as in Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand and Indonesia. Hakka is not Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible with Yue Chinese, Yue, Wu Chinese, Wu, Southern Min, Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin or other branches of Chinese, and itself contains a few mutually unintelligible varieties. It is most closely related to Gan Chinese, Gan and is sometimes classified as a variety of Gan, with a few northern Hakka varieties even being partiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Chinese
The Wu languages (; Romanization of Wu Chinese, Wu romanization and Romanization of Wu Chinese#IPA, IPA: ''wu6 gniu6'' [] (Shanghainese), ''ng2 gniu6'' [] (Suzhounese), Mandarin pinyin and IPA: ''Wúyǔ'' []) is a major group of Sinitic languages spoken primarily in Shanghai, Zhejiang, Zhejiang Province, and the part of Jiangsu, Jiangsu Province south of the Yangtze River, which makes up the cultural region of Wu (region), Wu. The Suzhou dialect was the prestige dialect of Wu as of the 19th century, and formed the basis of Wu's koiné dialect, Shanghainese, at the History of Shanghai, turn of the 20th century. Speakers of various Wu languages sometimes inaccurately labelled their mother tongue as "Shanghainese" when introduced to foreigners. The languages of #subdivision, Northern Wu are mutually intelligible with each other, while those of #subdivision, Southern Wu are not. Historical linguistics, Historical linguists view Wu of great significance because it distinguished itse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substratum
In linguistics, a stratum (Latin for "layer") or strate is a language that influences or is influenced by another through contact. A substratum or substrate is a language that has lower power or prestige than another, while a superstratum or superstrate is the language that has higher power or prestige. Both substratum and superstratum languages influence each other, but in different ways. An adstratum or adstrate is a language that is in contact with another language in a neighbor population without having identifiably higher or lower prestige. The notion of "strata" was first developed by the Italian linguist Graziadio Isaia Ascoli (1829–1907), and became known in the English-speaking world through the work of two different authors in 1932. Thus, both concepts apply to a situation where an intrusive language establishes itself in the territory of another, typically as the result of migration. Whether the superstratum case (the local language persists and the intrusive languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gan Chinese
Gan, Gann or Kan is a group of Sinitic languages spoken natively by many people in the Jiangxi province of China, as well as significant populations in surrounding regions such as Hunan, Hubei, Anhui, and Fujian. Gan is a member of the Sinitic languages of the Sino-Tibetan language family, and Hakka is the closest Chinese variety to Gan in terms of phonetics. Different dialects of Gan exist; the Nanchang dialect is usually taken as representative. Classification Like all other varieties of Chinese, there is a large amount of mutual unintelligibility between Gan Chinese and other varieties. Within the variation of Chinese dialects, Gan has more similarities with Mandarin than with Yue or Min. However, Gan clusters more with Xiang than Mandarin. Name * ''Gan'': the most common name. Also spelled ''Gann'' to reflect the falling tone of the name in Mandarin. Scholars in mainland China use ''Gan'' or ''Gan dialect.'' * ''Jiāngxīhuà'' ("Jiangxi language") is commonly used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fu'an
(; Foochow Romanized: Hók-ăng-chê; sometimes ''Fu An'') is a county-level city of Ningde prefecture level city, in northeast Fujian province, PRC, some away from the provincial capital Fuzhou. History Found Fu'an county was found in 1245 AD in the Southern Song. Modern In civil war of China, Fu'an was occupied by People's Liberation Army on July, 1949. In November 1989, Fu'an county was abolished, at the same time Fu'an city was established. Geography Fu'an is surrounded by hills and the sea. It covers an area of . Climate Demographics By December of 2021, Fu'an has 676,624 residents. With 199031 households. Fu'an City is mainly composed of three ethnic groups: Han Chinese, She and Hui. The She population accounts for about 11% of the city's population, and the Han population accounts for about 88.4% of the total population. The Han include the Tanka people of which there currently are about 7,400. Fu'an dialect in Eastern Min is commonly spoken in the city, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Min Chinese
Min (; BUC: ''Mìng-ngṳ̄'') is a broad group of Sinitic languages spoken by about 30 million people in Fujian province as well as by the descendants of Min speaking colonists on Leizhou peninsula and Hainan, or assimilated natives of Chaoshan, parts of Zhongshan, three counties in southern Wenzhou, Zhoushan archipelago, and Taiwan. The name is derived from the Min River in Fujian, which is also the abbreviated name of Fujian Province. Min varieties are not mutually intelligible with one another nor with any other variety of Chinese (such as Mandarin, Cantonese, Wu, Gan, Xiang, or Hakka). There are many Min speakers among overseas Chinese in Southeast Asia. The most widely spoken variety of Min outside Fujian is Southern Min (Min Nan), also known as Hokkien-Taiwanese (which includes Taiwanese and Amoy). Many Min languages have retained notable features of the Old Chinese language, and there is linguistic evidence that not all Min varieties are directly descended from Midd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Hmongic
The West Hmongic languages, also known as Chuanqiandian Miao (川黔滇苗: Sichuan–Guizhou–Yunnan Miao) and Western Miao, is the major branch of the Hmongic languages of China and Southeast Asia. The name ''Chuanqiandian'' is used both for West Hmongic as a whole and for one of its branches, the ''Chuanqiandian cluster'' Hmong. Writing The Miao languages were traditionally written with various adaptations of Chinese characters. Around 1905, Samuel Pollard introduced a Romanized script, the Pollard script, for the A-Hmao language, and this came to be used for Hmong Daw (Chuanqiandian) as well. In the United States, the Romanized Popular Alphabet is often used for White and Green Hmong (also Chuanqiandian). In China, pinyin-based Latin alphabets have been devised for Chuanqiandian (variety of Dananshan 大南山, Yanzikou 燕子口镇, Bijie) and A-Hmao. Wu and Yang (2010) report attempts at writing Mashan in 1985 and an improvement by them; they recommend that standards s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |