|
Sheffield Bridgehouses Railway Station
Bridgehouses railway station was the terminal station of the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway from its opening in 1845 until the opening of the Wicker Arches, a long viaduct across the Don Valley, which supported the new Sheffield Victoria railway station, Sheffield Victoria opened on 15 September 1851. On 1 January 1847 a half-mile connecting line to the Sheffield Wicker railway station, Wicker station of the Midland Railway had been constructed in order to increase goods traffic and enable wagon transfers. This short steeply graded line, enclosed within a tunnel for almost its entire length was known locally as the ''Fiery Jack.'' By this time the railway operating company had become the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway, which in 1899 became the Great Central Railway. From 1851 Bridgehouses became the company's terminal for goods and cattle traffic. It remained open for freight until 1965. The station was approached by a ramp from Nursery Stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burngreave
Burngreave is an inner city district of Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England lying north of the city centre. The population of the ward taken at the 2011 census was 27,481. It started to develop in the second half of the 19th century. Prior to this, this area was mostly covered by Burnt Greave wood. Most of the area of the wood is covered by Burngreave Cemetery which was built in 1860 (consecrated 1861) and extended in the early 1900s. Grimesthorpe Lane, which runs through Burngreave, is a very old road that follows the course of the Roman Rig, a man-made defensive ridge—probably built by the Celtic Brigantes tribe—that used to run from near the Wicker to Mexborough. History Prehistory Although there is not much physical evidence of early settlement in Burngreave, we do know that an Iron Age fort was discovered in Roe Woods. The people who built this may have been from a Celtic tribe, the Brigantes. In the early 20th century you could still see the circular banks o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Closed In 1851
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1845
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Great Central Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
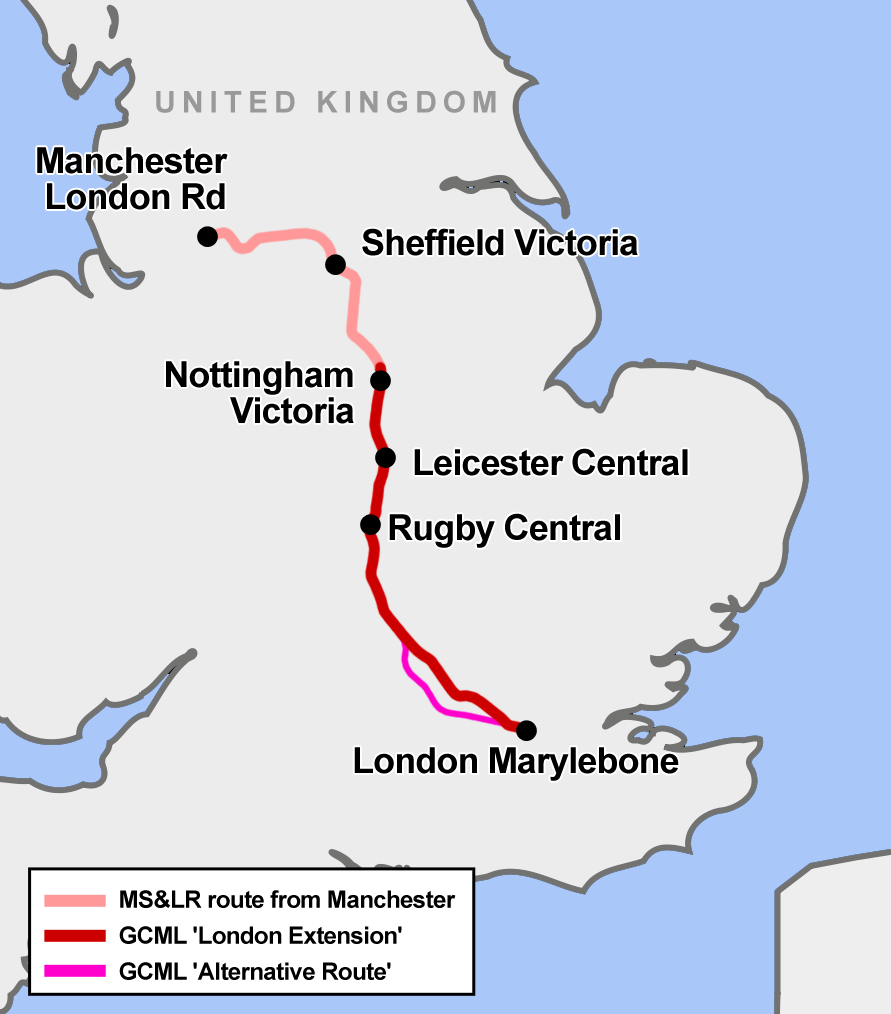
Great Central Main Line
The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railway running from Sheffield in the North of England, southwards through Nottingham and Leicester to Marylebone in London. The GCML was the last main line railway to be built in Britain during the Victorian period. Built by the railway entrepreneur Edward Watkin with the aim to run as a fast trunk route from the North and the East Midlands to London and the south of England. Initially not a financial success, it recovered under the leadership of Sam Fay. Although initially planned for long-distance passenger services, in practice the line's most important function became to carry goods traffic, notably coal. In the 1960s, the line was considered by Dr Beeching as an unnecessary duplication of other lines that served the same places, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neepsend Railway Station
Neepsend railway station was a railway station on the former Great Central Railway in England. History Neepsend railway station was opened on 1 July 1888 to serve the industrial suburb of Neepsend, to the north west of Sheffield city centre. It was situated on the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway's (latterly the Great Central Railway) Woodhead line which connected Sheffield Victoria and Manchester London Road stations and was located to the northwest of Neepsend engine shed. There had been much local pressure over a long period of time to get a station at Neepsend; in December 1857 the mayor of Sheffield was told that it would be too expensive. Four years later, local activists were informed that their latest petition would be granted if they could raise £211, this being half the cost of providing the station. The building of the station was further delayed when a dispute arose about who should pay the cost of constructing a road bridge across the River Don to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheffield
Sheffield is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in South Yorkshire, England, whose name derives from the River Sheaf which runs through it. The city serves as the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is Historic counties of England, historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire and some of its southern suburbs were transferred from Derbyshire to the city council. It is the largest settlement in South Yorkshire. The city is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines and the valleys of the River Don, Yorkshire, River Don with its four tributaries: the River Loxley, Loxley, the Porter Brook, the River Rivelin, Rivelin and the River Sheaf, Sheaf. Sixty-one per cent of Sheffield's entire area is green space and a third of the city lies within the Peak District national park. There are more than 250 parks, woodlands and gardens in the city, which is estimated to contain around 4.5 million trees. The city is south of Leeds, east of Manchester, and north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Sheffield Flood
The Great Sheffield Flood was a flood that devastated parts of Sheffield, England, on 11 March 1864, when the Dale Dyke Dam broke as its reservoir was being filled for the first time. At least 240 people died and more than 600 houses were damaged or destroyed by the flood. The immediate cause was a crack in the embankment, the cause of which was never determined. The dam's failure led to reforms in engineering practice, setting standards on specifics that needed to be met when constructing such large-scale structures. The dam was rebuilt in 1875. Dale Dyke Dam Sheffield is a city and subdivision of South Yorkshire, England. As the town industrialised, its population grew from 45,478 in 1801 to 185,157 in 1861. This rapid population growth resulted in greatly increased demand for water, which led to the construction of the Dale Dyke Dam for the purpose of providing a more efficient source of clean water. It was created by the Sheffield Waterworks Company (SWWC). During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art UK
Art UK is a cultural, education charity in the United Kingdom, previously known as the Public Catalogue Foundation. Since 2003, it has digitised more than 220,000 paintings by more than 40,000 artists and is now expanding the digital collection to include UK public sculpture. It was founded for the project, completed between 2003 and 2012, of obtaining sufficient rights to enable the public to see images of all the approximately 210,000 oil paintings in public ownership in the United Kingdom. Originally the paintings were made accessible through a series of affordable book catalogues, mostly by county. Later the same images and information were placed on a website in partnership with the BBC, originally called ''Your Paintings'', hosted as part of the BBC website. The renaming in 2016 coincided with the transfer of the website to a stand-alone site. Works by some 40,000 painters held in more than 3,000 collections are now on the website. The catalogues and website allow readers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



