|
Sharia Board
A Sharia Board (also Sharia Supervisory Board, Advisory Board or Religious Board) certifies Islamic financial products as being Sharia-compliant (i.e. in accordance with Islamic law). Because compliance with Sharia law is the underlying reason for the existence of Islamic finance, Islamic banks (and conventional banking institutions that offer Islamic banking products and services) should establish a Sharia Supervisory Board (SSB) to advise them on whether their products comply, and to ensure that their operations and activities comply with Sharia principles. Jamaldeen, ''Islamic Finance For Dummies'', 2012:265 There are also national Sharia boards in many Muslim majority countries that regulate Islamic financial institutions nationwide. History Some of the first Islamic financial institutions to have a Sharia Boards were the Faisal Islamic Bank of Egypt, (founded in 1976); the Jordan Islamic Bank, (founded in 1978); the Sudanese Faisal Islamic Bank (founded in 1978); the Kuwaiti H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, █śž¦┘ä┘Éžźž│┘ä┘Äž¦┘ģ, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "All─üh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) "[T]he Muslims' understanding of All─üh is based...on the Qur╩┐─ün's public witness. All─üh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is All─üh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and MußĖźammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the Major religious groups, world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Indonesia
Bank Indonesia (BI) is the central bank of the Republic of Indonesia. It replaced in 1953 the Bank of Java ( nl, De Javasche Bank, DJB), which had been created in 1828 to serve the financial needs of the Dutch East Indies. History Bank of Java King William I of the Netherlands granted the right to create a private bank in the Indies in 1826, which was named . It was founded on 24 January 1828 and later became the bank of issue of the Dutch East Indies. The bank regulated and issued the Netherlands Indies gulden. In 1881, an office of the Bank of Java was opened in Amsterdam. Later followed the opening of an office in New York. By 1930 the bank owned sixteen office branches in the Dutch East Indies: Bandung, Cirebon, Semarang, Yogyakarta, Surakarta, Surabaya, Malang, Kediri, Banda Aceh, Medan, Padang, Palembang, Banjarmasin, Pontianak, Makassar, and Manado. The Bank of Java was operated as a private bank and individuals as well as industries etc. could get help in the bank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia Investments
Banking or banking activity that complies with Sharia (Islamic law)ŌĆöknown as Islamic banking and finance, or Sharia-compliant financeŌĆöhas its own products, services and contracts that differ from conventional banking. Some of these include ''Mudharabah'' (profit sharing), ''Wadiah'' (safekeeping), ''Musharakah'' (joint venture), ''Murabahah'' (cost plus finance), ''Ijar'' (leasing), ''Hawala'' (an international fund transfer system), ''Takaful'' (Islamic insurance), and ''Sukuk'' (Islamic bonds). Sharia prohibits ''riba'', or usury, defined as interest paid on all loans of money (although some Muslims dispute whether there is a consensus that interest is equivalent to ''riba''). Farooq, ''Riba-Interest Equation and Islam'', 2005: pp. 3ŌĆō6 Khan, ''What Is Wrong with Islamic Economics?'', 2013: pp. 216ŌĆō226 Investment in businesses that provide goods or services considered contrary to Islamic principles (e.g. pork or alcohol) is also ''haraam'' ("sinful and prohibited"). By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ar, ┘ü┘é┘ć ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh. The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and examples of the Prophet passed down as hadith). The first Muslims (the Sahabah or Companions) heard and obeyed, and passed this essence of Islam to succeeding generations (''Tabi'un'' and ''Tabi' al-Tabi'in'' or successors/followers and successors of successors), as Muslims and Islam spread from West Arabia to the conquered lands north, east, and west, Hoyland, ''In God's Path'', 2015: p.223 where it was systematized and elaborated Hawting, "John Wansbrough, Islam, and Monotheism", 2000: p.513 The history of Islamic jurisprudence is "customarily divided into eight periods": El-Gamal, ''Islamic Finance'', 2006: pp. 30ŌĆō31 *the first period ending with the death of Muhammad in 11 AH. *second period "characterized by personal interp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulema
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, ž╣┘ä┘ģž¦žĪ ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam, including Islamic doctrine and law. By longstanding tradition, ulama are educated in religious institutions ''(madrasas)''. The Quran and sunnah (authentic hadith) are the scriptural sources of traditional Islamic law. Traditional way of education Students do not associate themselves with a specific educational institution, but rather seek to join renowned teachers. By tradition, a scholar who has completed his studies is approved by his teacher. At the teacher's individual discretion, the student is given the permission for teaching and for the issuing of legal opinions ''( fatwa)''. The official approval is known as the '' ijazat at-tadris wa 'l-ifta'' ("license to teach and issue legal opinions"). Through time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lease
A lease is a contractual arrangement calling for the user (referred to as the ''lessee'') to pay the owner (referred to as the ''lessor'') for the use of an asset. Property, buildings and vehicles are common assets that are leased. Industrial or business equipment are also leased. Basically a lease agreement is a contract between two parties: the lessor and the lessee. The lessor is the legal owner of the asset, while the lessee obtains the right to use the asset in return for regular rental payments. The lessee also agrees to abide by various conditions regarding their use of the property or equipment. For example, a person leasing a car may agree to the condition that the car will only be used for personal use. The term rental agreement can refer to two kinds of leases: * A lease in which the asset is tangible property. Here, the user '' rents'' the asset (e.g. land or goods) ''let out'' or ''rented out'' by the owner (the verb ''to lease'' is less precise because it can r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
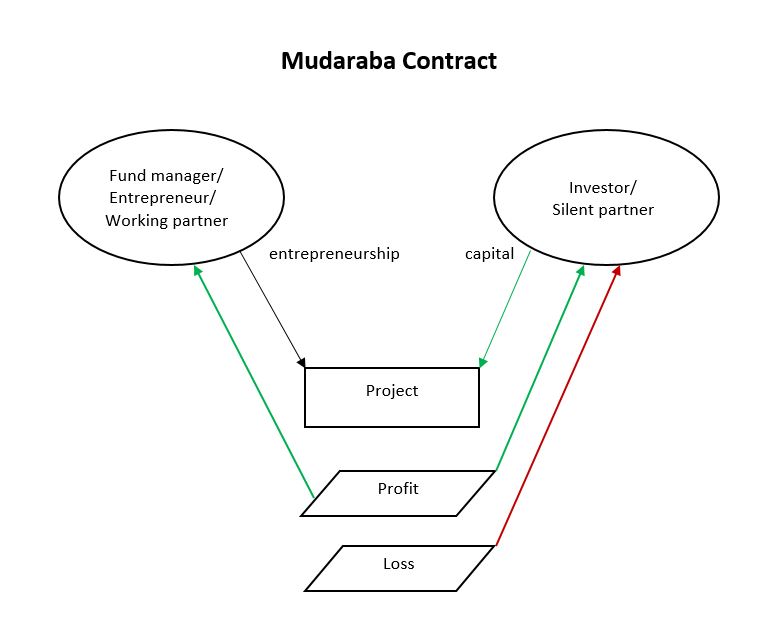
Profit And Loss Sharing
Profit and Loss Sharing (also called PLS or participatory banking) refers to Sharia-compliant forms of equity financing such as mudarabah and musharakah. These mechanisms comply with the religious prohibition on interest on loans that most Muslims subscribe to. ''Mudarabah'' (┘ģžČž¦ž▒ž©ž®) refers to "trustee finance" or passive partnership contract, while ''Musharakah'' (┘ģž┤ž¦ž▒┘āž® or ┘ģž┤ž▒┘āž®) refers to equity participation contract. Other sources include sukuk (also called "Islamic bonds") and direct equity investment (such as purchase of common shares of stock) as types of PLS. Khan, ''Islamic Banking in Pakistan'', 2015: p.91 The profits and losses shared in PLS are those of a business enterprise or person which/who has obtained capital from the Islamic bank/financial institution (the terms "debt", "borrow", "loan" and "lender" are not used). As financing is repaid, the provider of capital collects some agreed upon percentage of the profits (or deducts if there are losses) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortgage
A mortgage loan or simply mortgage (), in civil law jurisdicions known also as a hypothec loan, is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged. The loan is " secured" on the borrower's property through a process known as mortgage origination. This means that a legal mechanism is put into place which allows the lender to take possession and sell the secured property ("foreclosure" or " repossession") to pay off the loan in the event the borrower defaults on the loan or otherwise fails to abide by its terms. The word ''mortgage'' is derived from a Law French term used in Britain in the Middle Ages meaning "death pledge" and refers to the pledge ending (dying) when either the obligation is fulfilled or the property is taken through foreclosure. A mortgage can also be described as "a borrower giving consideration in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shari'ah
Sharia (; ar, ž┤ž▒┘Ŗž╣ž®, shar─½╩┐a ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the Hadith. In Arabic, the term ''shar─½╩┐ah'' refers to God's immutable divine law and is contrasted with ''fiqh'', which refers to its human scholarly interpretations. In the historical course, fiqh sects have emerged that reflect the preferences of certain societies and state administrations on behalf of people who are interested in the theoretical (method) and practical application (Ahkam / fatwa) studies of laws and rules, but sharia has never been a valid legal system on its own. It has been used together with " customary (Urf) law" since Omar or the Umayyads. It may also be wrong to think that the Sharia, as a religious argument or belief, is entirely within or related to Allah's commands and prohibitions. Several non-graded crimes ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatwa
A fatw─ü ( ; ar, ┘üž¬┘ł┘ē; plural ''fat─üw─ü'' ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (''sharia'') given by a qualified '' Faqih'' (Islamic jurist) in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', and the act of issuing fatwas is called ''ift─ü╩Š''. Fatwas have played an important role throughout Islamic history, taking on new forms in the modern era. Resembling ''jus respondendi'' in Roman law and rabbinic ''responsa'', privately issued fatwas historically served to inform Muslim populations about Islam, advise courts on difficult points of Islamic law, and elaborate substantive law. In later times, public and political fatwas were issued to take a stand on doctrinal controversies, legitimize government policies or articulate grievances of the population. During the era of European colonialism, fatwas played a part in mobilizing resistance to foreign domination. Muftis acted as independent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murabaha
''MurabaßĖźah'', ''murabaßĖźa'', or ''mur├óbaßĖźah'' ( ar, ┘ģž▒ž¦ž©žŁž®, derived from ''ribh'' ar, ž▒ž©žŁ, meaning profit) was originally a term of ''fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence) for a sales contract where the buyer and seller agree on the markup (profit) or "cost-plus" price for the item(s) being sold. In recent decades it has become a term for a very common form of Islamic (i.e., "shariah compliant") financing, where the price is marked up in exchange for allowing the buyer to pay over timeŌĆöfor example with monthly payments (a contract with deferred payment being known as ''bai-muajjal''). ''Murabaha'' financing is similar to a rent-to-own arrangement in the non-Muslim world, with the intermediary (e.g., the lending bank) retaining ownership of the item being sold until the loan is paid in full. There are also Islamic investment funds and ''sukuk'' (Islamic bonds) that use ''murabahah'' contracts. Jamaldeen, ''Islamic Finance For Dummies'', 2012:188-9, 220-1 The purpose o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ßĖźiyal
''ßĖżiyal'' (žŁ┘Ŗ┘ä, singular ''ßĖź─½la'' žŁ┘Ŗ┘äž® "contortion, contrivance; device, subterfuge") is "legalistic trickery" in Islamic jurisprudence. The main purpose of ''ßĖźiyal'' is to avoid straightforward observance of Islamic law in difficult situations while still obeying the letter of the law. An example of ''hiyal'' is the practice of "dual purchase" (''bai╩┐at─ün f─½ bai╩┐a'') to avoid the prohibition of usury by making two contracts of purchase and re-purchase (at a higher price), similar to the modern futures contract. A special sub-field of ''ßĖźiyal'' is "oath-trickery" (''ma╩┐─ür─½ßĖŹ'') dedicated to the formulation of ambiguous statements designed to be interpreted as an oath or promise while leaving open loopholes to avoid perjury. Views on its admissibility in Islam have varied by schools of Islamic jurisprudence (''Madhhab''), by time period, and by type of ''ßĖźiyal''. A substantial literature on such tricks has developed in the Hanafi school of jurisprudence in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_001.jpg)