|
Shared Socio-Economic Pathways
Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) are scenarios of projected socioeconomic global changes up to 2100. They are used to derive greenhouse gas emissions scenarios with different climate policies.. The scenarios are: *SSP1: Sustainability (Taking the Green Road) *SSP2: Middle of the Road *SSP3: Regional Rivalry (A Rocky Road) *SSP4: Inequality (A Road divided) *SSP5: Fossil-fueled Development (Taking the Highway) They have been used to help produce the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report on climate change, published on 9 August 2021. The SSPs provide narratives describing alternative socio-economic developments. These storylines are a qualitative description of logic relating elements of the narratives to each other. In terms of quantitative elements, they provide data accompanying the scenarios on national population, urbanization and GDP (per capita). The SSPs can be quantified with various Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs), to explore possible future pathways both with regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Socioeconomic Pathways
Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) are scenarios of projected socioeconomic global changes up to 2100. They are used to derive greenhouse gas emissions scenarios with different climate policies.. The scenarios are: *SSP1: Sustainability (Taking the Green Road) *SSP2: Middle of the Road *SSP3: Regional Rivalry (A Rocky Road) *SSP4: Inequality (A Road divided) *SSP5: Fossil-fueled Development (Taking the Highway) They have been used to help produce the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report on climate change, published on 9 August 2021. The SSPs provide narratives describing alternative socio-economic developments. These storylines are a qualitative description of logic relating elements of the narratives to each other. In terms of quantitative elements, they provide data accompanying the scenarios on national population, urbanization and GDP (per capita). The SSPs can be quantified with various Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs), to explore possible future pathways both with regard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Assessment Modelling
Integrated assessment modelling (IAM) or integrated modelling (IM) is a term used for a type of scientific modelling that tries to link main features of society and economy with the biosphere and atmosphere into one modelling framework. The goal of integrated assessment modelling is to accommodate informed policy-making, usually in the context of climate change though also in other areas of human and social development. While the detail and extent of integrated disciplines varies strongly per model, all climatic integrated assessment modelling includes economic processes as well as processes producing greenhouse gases. Other integrated assessment models also integrate other aspects of human development such as education, health, infrastructure, and governance. These models are integrated because they span multiple academic disciplines, including economics and climate science and for more comprehensive models also energy systems, land-use change, agriculture, infrastructure, confli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change Assessment And Attribution
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude/longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme was the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coupled Model Intercomparison Project
In climatology, the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) is a collaborative framework designed to improve knowledge of climate change. It was organized in 1995 by the Working Group on Coupled Modelling (WGCM) of the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP). It is developed in phases to foster the climate model improvements but also to support national and international assessments of climate change. A related project is the Atmospheric Model Intercomparison Project (AMIP) for global coupled ocean-atmosphere general circulation models (GCMs). Coupled models are computer-based models of the earth's climate, in which different parts (such as atmosphere, oceans, land, ice) are "coupled" together, and interact in simulations. CMIP phases The Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison (PCMDI) at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has been supporting the several CMIP phases by helping WGCM to determine the scope of the project, by maintaining the project's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
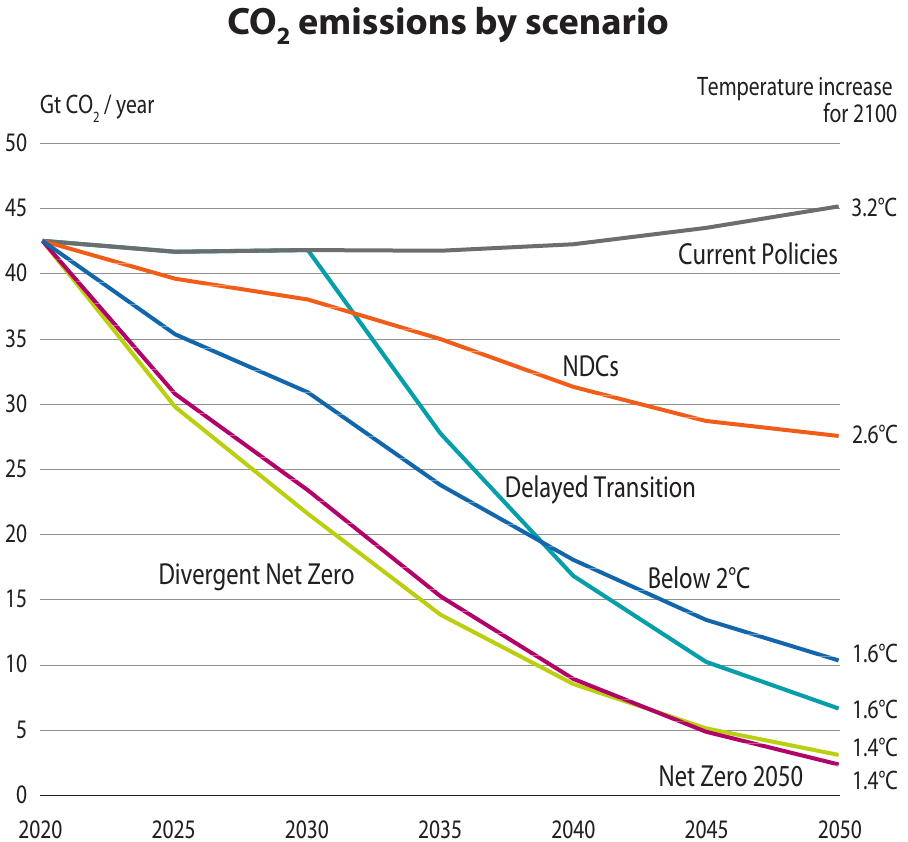
Representative Concentration Pathway
A Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) is a greenhouse gas concentration (not emissions) trajectory adopted by the IPCC. Four pathways were used for climate modeling and research for the IPCC fifth Assessment Report (AR5) in 2014. The pathways describe different climate futures, all of which are considered possible depending on the volume of greenhouse gases (GHG) emitted in the years to come. The RCPs – originally RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP6, and RCP8.5 – are labelled after a possible range of radiative forcing values in the year 2100 (2.6, 4.5, 6, and 8.5 W/m2, respectively). Since AR5 the original pathways are being considered together with Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: as are new RCPs such as RCP1.9, RCP3.4 and RCP7. Concentrations The RCPs are consistent with a wide range of possible changes in future anthropogenic (i.e., human) GHG emissions, and aim to represent their atmospheric concentrations.Collins, M., ''et al.'': Section 12.3.1.3 The New Concentration Driven RC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Report On Emissions Scenarios
The Special Report on Emissions Scenarios (SRES) is a report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) that was published in 2000. The greenhouse gas emissions scenarios described in the Report have been used to make projections of possible future climate change. The SRES scenarios, as they are often called, were used in the IPCC Third Assessment Report (TAR), published in 2001, and in the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (AR4), published in 2007. The SRES scenarios were designed to improve upon some aspects of the IS92 scenarios, which had been used in the earlier IPCC Second Assessment Report of 1995. The SRES scenarios are " baseline" (or "reference") scenarios, which means that they do not take into account any current or future measures to limit greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (e.g., the Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change). Emissions projections of the SRES scenarios are broadly comparable in range to the baseline emis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre2. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external drivers of change to Earth's energy balance. System feedbacks and internal variability are related concepts, encompassing other factors that also influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Positive radiative forcing means Earth receives more incoming energy from sunlight than it radiates to space. This net gain of energy will cause warming. Conversely, negative radiative forcing means that Earth loses more energy to space than it receives from the sun, which produces cooling. A planet in radiative equilibrium with its parent star and the rest of space can be characterized by net zero radiative forcing and by a planetary equilibrium temperature. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission Intensity
An emission intensity (also carbon intensity or C.I.) is the emission rate of a given pollutant relative to the intensity of a specific activity, or an industrial production process; for example grams of carbon dioxide released per megajoule of energy produced, or the ratio of greenhouse gas emissions produced to gross domestic product (GDP). Emission intensities are used to derive estimates of air pollutant or greenhouse gas emissions based on the amount of fuel combusted, the number of animals in animal husbandry, on industrial production levels, distances traveled or similar activity data. Emission intensities may also be used to compare the environmental impact of different fuels or activities. In some case the related terms emission factor and carbon intensity are used interchangeably. The jargon used can be different, for different fields/industrial sectors; normally the term "carbon" excludes other pollutants, such as particulate emissions. One commonly used figure is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
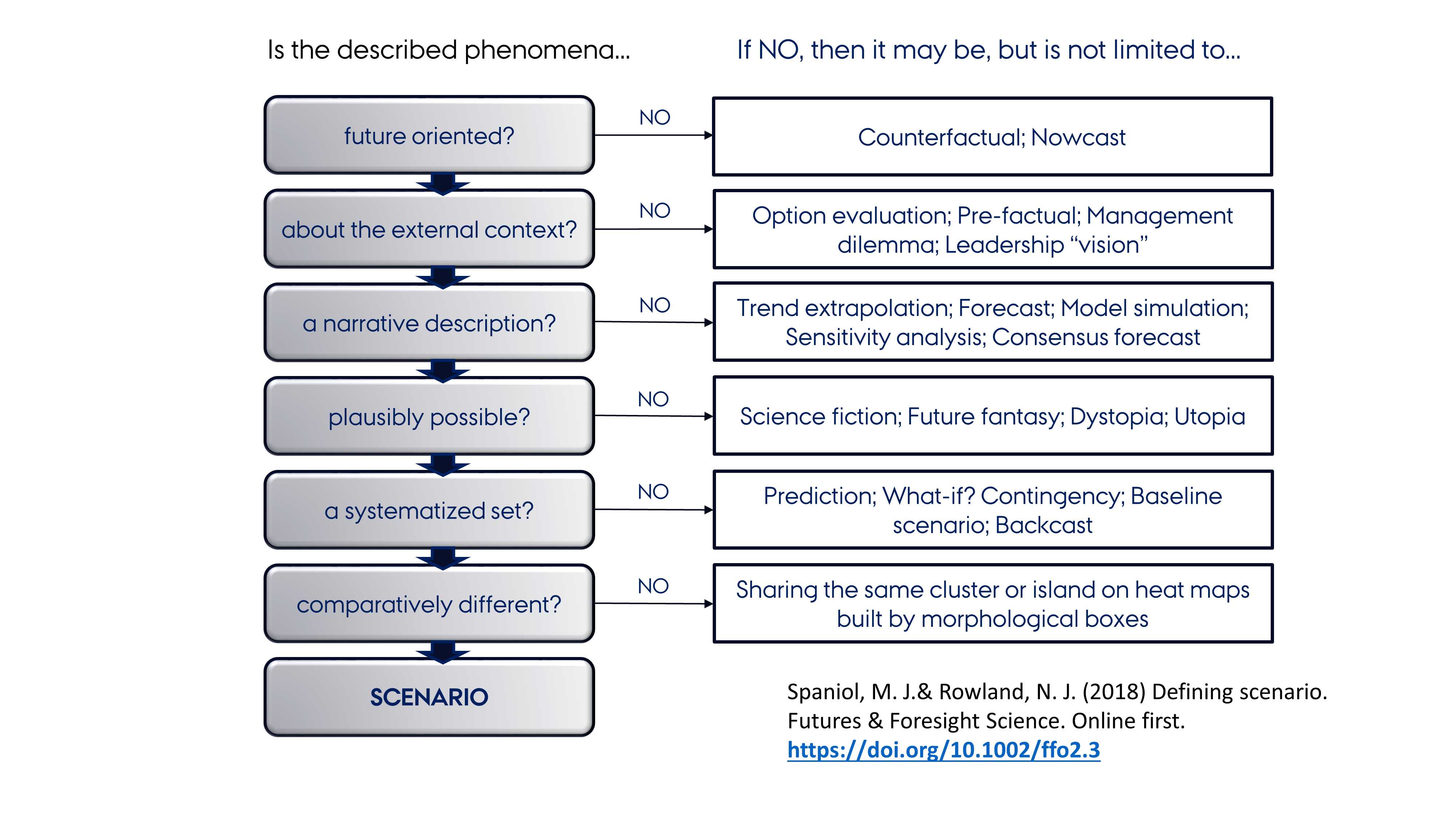
Scenario Planning
Scenario planning, scenario thinking, scenario analysis, scenario prediction and the scenario method all describe a strategic planning method that some organizations use to make flexible long-term plans. It is in large part an adaptation and generalization of classic methods used by military intelligence. In the most common application of the method, analysts generate simulation games for policy makers. The method combines known facts, such as demographics, geography and mineral reserves, with military, political, and industrial information, and key driving forces identified by considering social, technical, economic, environmental, and political ("STEEP") trends. In business applications, the emphasis on understanding the behavior of opponents has been reduced while more attention is now paid to changes in the natural environment. At Royal Dutch Shell for example, scenario planning has been described as changing mindsets about the exogenous part of the world prior to formulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPCC Sixth Assessment Report
The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess scientific, technical, and socio-economic information concerning climate change. Three Working Groups (WGI, II, and III) have been working on the following topics: The Physical Science Basis (WGI); Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (WGII); Mitigation of Climate Change (WGIII). Of these, the first study was published in 2021, the second report February 2022, and the third in April 2022. The final synthesis report is due to be finished by early 2023. The first of the three working groups published its report on 9 August 2021, ''Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis''. A total of 234 scientists from 66 countries contributed to this first working group (WGI) report. The authors built on more than 14,000 scientific papers to produce a 3,949-page report, which was then approved by 195 governments. The Summary for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane Emissions Projections
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it poses technical challenges due to its gaseous state under normal conditions for temperature and pressure. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. The Earth's atmospheric methane concentration has increased by about 150% since 1750, and it accounts for 20% of the total radiative forcing from all of the long-lived and globally mixed greenhouse gases. It has also been detected on other planets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |