|
Shapurdukhtak
Shapurdukhtak (Middle Persian: ''Šābuhrduxtag'', literally "daughter of Shapur") was a 3rd-century Sasanian queen ('' banbishn''). She was the wife of her cousin, king Bahram II (r. 274–293). Biography She was the only daughter of Shapur Meshanshah, a Sasanian prince who governed Meshan, and was the son of the Sasanian shah Shapur I. Her mother was a queen named Denag. Shapurdukhtak had many brothers: Hormizdag, Odabakht, Bahram, Shapur, Peroz, and Hormizd. She was probably raised in Meshan, which was then governed by her father. In 260, her father died and was probably succeeded by Denag as the governor of Meshan. In 274, her cousin Bahram II ascended the throne, and she was married shortly married to the latter, and was given the title of '' bānbishnān bānbishn'', meaning "queen of queens". In c. 281, her brother Hormizd revolted against Bahram II, and was supported by the inhabitants of Eastern Iran, including the inhabitants of Gilan. Hormizd's revolt was finally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahram II
Bahram II (also spelled Wahram II or Warahran II; pal, 𐭥𐭫𐭧𐭫𐭠𐭭) was the fifth Sasanian King of Kings (''shahanshah'') of Iran, from 274 to 293. He was the son and successor of Bahram I (). Bahram II, while still in his teens, ascended the throne with the aid of the powerful Zoroastrian priest Kartir, just like his father had done. He was met with considerable challenges during his reign, facing a rebellion in the east led by his brother, the Kushano-Sasanian dynast Hormizd I Kushanshah, who also assumed the title of King of Kings and possibly laid claims to the Sasanian throne. Another rebellion, led by Bahram II's cousin Hormizd of Sakastan in Sakastan, also occurred around this period. In Khuzestan, a Zoroastrian factional revolt led by a high-priest (''mowbed'') occurred. The Roman emperor Carus exploited the turbulent situation of Iran by launching a campaign into its holdings in Mesopotamia in 283. Bahram II, who was in the east, was unable to mount an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narseh
Narseh (also spelled Narses or Narseus; pal, 𐭭𐭥𐭮𐭧𐭩, New Persian: , ''Narsē'') was the seventh Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 293 to 303. The youngest son of Shapur I (), Narseh served as the governor of Sakastan, Hind and Turan under his father. Shapur I was eventually succeeded by his son Hormizd I (), who died after a reign of one year. Shapur I's eldest son Bahram I, who had never been considered as a candidate for succession to the throne by his father, ascended the throne with the aid of the powerful Zoroastrian priest Kartir. He then made a settlement with Narseh to give up his entitlement to the throne in return for the governorship of the important frontier province of Armenia, which was a persistent cause for war between the Roman and Sasanian Empires. Narseh held the title of ''Vazurg Šāh Arminān'' ("Great King of Armenia"), which was used by the heir to the throne in the early Sasanian times. Nevertheless, Narseh most likely still viewed Bahram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banbishn
''Bānbishn'' was a Middle Persian title meaning "queen", and was held by royal women in Sasanian Iran who were the king's daughters and sisters, and also by the consorts of the Sasanian princes that ruled parts of the country as governors. The full version of the title was ''bānbishnān bānbishn'' ("Queen of Queens"). Etymology Although the Old Persian form of ''bānbishn'' is not found in any source, it was most likely spelled ''māna-pashnī'', matching the Avestan ''dəmąnō.paθnī'' ("mistress"), which is from Old Iranian ''dmāna-paθnī''. The word was later absorbed into the Armenian language, where it was spelled ''bambishn''. The Sogdian version of the word is ''bāmbusht''. History In the Sasanian inscriptions, ''banbishn'' is the female equivalent of ''shah'' (king). The title is first attested in 262/3 in Shapur I's inscription at the Ka'ba-ye Zartosht, being held by a certain Denak. Shapur I's daughter Adur-Anahid held the title of ''bānbishnān bānbishn'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩, Šābuhr ) was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the Arab city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire , and seized its cities of Nisibis and Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III (), he was the following year able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman Emperor Philip the Arab () to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most shameful t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormizd Of Sakastan
Hormizd of Sakastan was a Sasanian prince who was the leader of a revolt in Sakastan and its surrounding regions. He was the son of Shapur Mishanshah, a Sasanian prince who governed Maishan, and was the son of the Sassanian shah Shapur I. Hormizd's mother was a certain queen named Denag. Hormizd had many other siblings named Hormizdag, Odabakht, Bahram, Shapur, Peroz, and Shapurdukhtak. In 260, his father died and was probably succeeded by Denag as the governor of Maishan. In 274, he was appointed as the governor of Sakastan and its surrounding regions. Three years later, when his cousin Bahram II Bahram II (also spelled Wahram II or Warahran II; pal, 𐭥𐭫𐭧𐭫𐭠𐭭) was the fifth Sasanian King of Kings (''shahanshah'') of Iran, from 274 to 293. He was the son and successor of Bahram I (). Bahram II, while still in his teens, ... ascended the throne, Hormizd's sister Shapurdukhtak married the latter. In ca. 281, Hormizd revolted against Bahram II, and was supporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur Meshanshah
Shapur Meshanshah ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 𐭱𐭠𐭤𐭬𐭩𐭱𐭠𐭭), was a 3rd-century Sasanian prince. He was the second son of the Sassanian shah Shapur I, and was married to a certain queen named Denag, who bore him several children named Hormizd, Hormizdag, Odabakht, Bahram, Shapur, Peroz, and Shapurdukhtak. Shapur was during an unknown date appointed as the governor of Meshan Meshan (Middle Persian: 𐭬𐭩𐭱𐭠𐭭) was a province of the Sasanian Empire. It consisted of the Parthian vassal kingdom of Characene and reached north along the Shatt al-Arab river and then the lower Tigris river, Tigris to Madhar and po ... by his father, and sometime later he gave his wife the honorific title of Dastgerd-Shapur. He died in 260, and was probably succeeded by his wife as the governor of Meshan. Sources * * * {{s-end 3rd-century Iranian people Sasanian princes 260 deaths 3rd-century births Sasanian governors of Meshan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
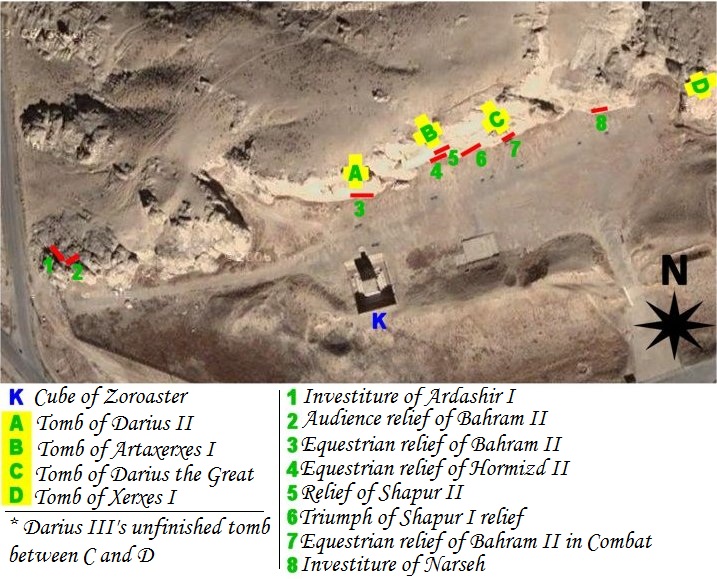
Naqsh-e Rostam
Naqsh-e Rostam ( lit. mural of Rostam, fa, نقش رستم ) is an ancient archeological site and necropolis located about 12 km northwest of Persepolis, in Fars Province, Iran. A collection of ancient Iranian rock reliefs are cut into the face of the mountain and the mountain contains the final resting place of four Achaemenid kings, notably king Darius the Great and his son, Xerxes. This site is of great significance to the history of Iran and to Iranians, as it contains various archeological sites carved into the rock wall through time for more than a millennium from the Elamites and Achaemenids to Sassanians. It lies a few hundred meters from Naqsh-e Rajab, with a further four Sassanid rock reliefs, three celebrating kings and one a high priest. Naqsh-e Rostam is the necropolis of the Achaemenid dynasty ( 550–330 BC), with four large tombs cut high into the cliff face. These have mainly architectural decoration, but the facades include large panels over the doorway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odabakht
Odabakht was a 3rd-century Sasanian prince. He was the son of Shapur Mishanshah, a Sasanian prince who governed Maishan, and was the son of the Sassanian shah Shapur I. Odabakht's mother was a certain queen named Denag. Odabakht had many other siblings named Hormizdag, Hormizd, Bahram, Shapur, Peroz, and Shapurdukhtak. In 260, his father died and was probably succeeded by Denag as the governor of Maishan. Odabakht probably later died before the ascension of his uncle Narseh Narseh (also spelled Narses or Narseus; pal, 𐭭𐭥𐭮𐭧𐭩, New Persian: , ''Narsē'') was the seventh Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 293 to 303. The youngest son of Shapur I (), Narseh served as the governor of Sakastan, Hind and T ... in 293. Sources * * 3rd-century Iranian people Sasanian princes 3rd-century deaths 3rd-century births {{Sasanian-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahram III
Bahram III (also spelled Wahram III or Warahran III; pal, 𐭥𐭫𐭧𐭫𐭠𐭭, New Persian: ), was the sixth king (shah) of the Sasanian Empire. He was son and successor of Bahram II.Touraj Daryaee, ''Sasanian Persia'', (I.B.Tauris Ltd, 2010), 11. He was appointed viceroy to the province of Sakastan after Bahram II's re-conquest of it sometime in the 280s. Bahram III ascended to the throne vacated by his father following his death in 293. Bahram III was considered too weak to rule the kingdom by much of the nobility and many nobles challenged his succession, instead pledging allegiance to his grand-uncle Narseh. After reigning for a period of only four months, Bahram III was either captured or more likely killed during a campaign by Narseh who then ascended to the throne in Bahram's place. Name His theophoric name "Bahram" is the New Persian form of the Middle Persian ''Warahrān'' (also spelled ''Wahrām''), which is derived from the Old Iranian ''Vṛθragna''. The Aves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle Persian continued to function as a prestige language. It descended from Old Persian, the language of the Achaemenid Empire and is the linguistic ancestor of Modern Persian, an official language of Iran, Afghanistan (Dari) and Tajikistan ( Tajik). Name "Middle Iranian" is the name given to the middle stage of development of the numerous Iranian languages and dialects. The middle stage of the Iranian languages begins around 450 BCE and ends around 650 CE. One of those Middle Iranian languages is Middle Persian, i.e. the middle stage of the language of the Persians, an Iranian people of Persia proper, which lies in the south-western highlands on the border with Babylonia. The Persians called their language ''Parsik'', meaning "Persian". Anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sar Mashhad
Sar Mashhad ( fa, سرمشهد; also known as Sar Meshad) is a village in Dadin Rural District, Jereh and Baladeh District, Kazerun County, Fars Province, Iran. At the 2012 census, its population was 3,047, in 623 families. The place is notable for being the site of a Sasanian rock relief made during the reign of king (shah) Bahram II (). The relief portrays him as a hunter who has slayed a lion whilst throwing his sword at another. His wife is holding his right hand in a signal of safeguard, whilst the high priest Kartir and another figure, most likely a prince, are watching. The scenery has been the subject of several symbolic and metaphorical meanings, thought it is most likely supposed to portray a simple royal display of braveness during a real-life hunt. An inscription of Kartir is underneath the relief. Population This village is located in Dadin district and according to the census of the Statistics Center of Iran in 2016, its population was 2818 people (748 families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Queens
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the Sasanian dynasty, House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived List of monarchs of Persia, Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |