|
Shapash (Canaanite Goddess)
Shapash (Ugaritic: 𐎌𐎔𐎌 ''špš'', "sun"), alternatively written as Shapshu or Shapsh, was a Canaanite sun goddess. She also served as the royal messenger of the high god El, her probable father. Her most common epithets in the Ugaritic corpus are ''nrt 'ilm špš'' ("Shapash, lamp of the gods", also translated as "torch" or "luminary" of the gods by various authors), ''rbt špš'' ("great lady Shapash"), and ''špš 'lm'' ("eternal Shapash"). In the pantheon lists KTU 1.118 and 1.148, Shapash is equated with the Akkadian dšamaš. Cult Unlike Shamash or Utu in Mesopotamia, but like Shams in Arabia, Shapash was a female solar deity. In addition to attestations in Ugaritic texts, Amarna letter EA 323 uses the Sumerogram for the sun deity, dUTU, as a feminine noun (''ša tiram dUTU'', line 19); given the letter's provenance with Yidya of Ashkelon it may refer to Shapash. Similarly, the letter EA 155 from Abimilki of Tyre to the Pharaoh includes a feminine dUTU (''LUGAL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugaritic
Ugaritic () is an extinct Northwest Semitic language, classified by some as a dialect of the Amorite language and so the only known Amorite dialect preserved in writing. It is known through the Ugaritic texts discovered by French archaeologists in 1929 at Ugarit, including several major literary texts, notably the Baal cycle. It has been used by scholars of the Hebrew Bible to clarify Biblical Hebrew texts and has revealed ways in which the cultures of ancient Israel and Judah found parallels in the neighboring cultures. Ugaritic has been called "the greatest literary discovery from antiquity since the deciphering of the Egyptian hieroglyphs and Mesopotamian cuneiform". Corpus The Ugaritic language is attested in texts from the 14th through the 12th century BC. The city of Ugarit was destroyed roughly 1190 BC. Literary texts discovered at Ugarit include the ''Legend of Keret'', the legends of Danel, the ''Myth of Baal-Aliyan'', and the ''Death of Baal''. The latter two are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophoric Names
A theophoric name (from Greek: , ''theophoros'', literally "bearing or carrying a god") embeds the word equivalent of 'god' or God's name in a person's name, reflecting something about the character of the person so named in relation to that deity. For example, names embedding Apollo, such as ''Apollonios'' or ''Apollodorus'', existed in Greek antiquity. Theophoric personal names, containing the name of a god in whose care the individual is entrusted (or a generic word for ''god''), were also exceedingly common in the ancient Near East and Mesopotamia. Some names of theophoric origin remain common today, such as Theodore (''theo-'', "god"; ''-dore'', origin of word compound in Greek: ''doron'', "gift"; hence "God's gift"; in Greek: ''Theodoros'') or less recognisably as Jonathan (from Hebrew ''Yonatan/Yehonatan'', meaning "Yahweh has given"). Classical Greek and Roman theophoric names * Demetrius and its derivatives mean "follower of Demeter." * Dennis, in Latin ''Dionysius' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestrina
Palestrina (ancient ''Praeneste''; grc, Πραίνεστος, ''Prainestos'') is a modern Italian city and ''comune'' (municipality) with a population of about 22,000, in Lazio, about east of Rome. It is connected to the latter by the Via Prenestina. It is built upon the ruins of the ancient city of Praeneste. Palestrina is the birthplace of composer Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina. Geography Palestrina is sited on a spur of the Monti Prenestini, a mountain range in the central Apennines. Modern Palestrina borders the following municipalities: Artena, Castel San Pietro Romano, Cave, Gallicano nel Lazio, Labico, Rocca di Cave, Rocca Priora, Rome, San Cesareo, Valmontone, Zagarolo. History Ancient Praeneste Ancient mythology connected the origin of Praeneste to Ulysses, or to other fabled characters such as Caeculus, Telegonus, Erulus or ''Praenestus''. The name probably derives from the word ''Praenesteus'', referring to its overlooking location. Early burials show that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Civilization
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region. Etruscan civilization endured until it was assimilated into Roman society. Assimilation began in the late 4thcenturyBC as a result of the Roman–Etruscan Wars; it accelerated with the grant of Roman citizenship in 90 BC, and became complete in 27 BC, when the Etr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Language
Phoenician ( ) is an extinct language, extinct Canaanite languages, Canaanite Semitic languages, Semitic language originally spoken in the region surrounding the cities of Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre and Sidon. Extensive Tyro-Sidonian trade and commercial dominance led to Phoenician becoming a lingua franca of the maritime Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean during the Iron Age. The Phoenician alphabet History of the Greek alphabet, spread to Greece during this period, where it became the source of all modern Alphabet#European_alphabets, European scripts. The area in which Phoenician was spoken includes the northern Levant and, at least as a prestige language, Anatolia, specifically the areas now including Syria, Lebanon, parts of Cyprus and some adjacent areas of Turkey. It was also spoken in the area of Phoenician colonies, Phoenician colonization along the coasts of the southwestern Mediterranean Sea, including those of modern Tunisia, Morocco, Libya and Algeria as well as Malta, the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
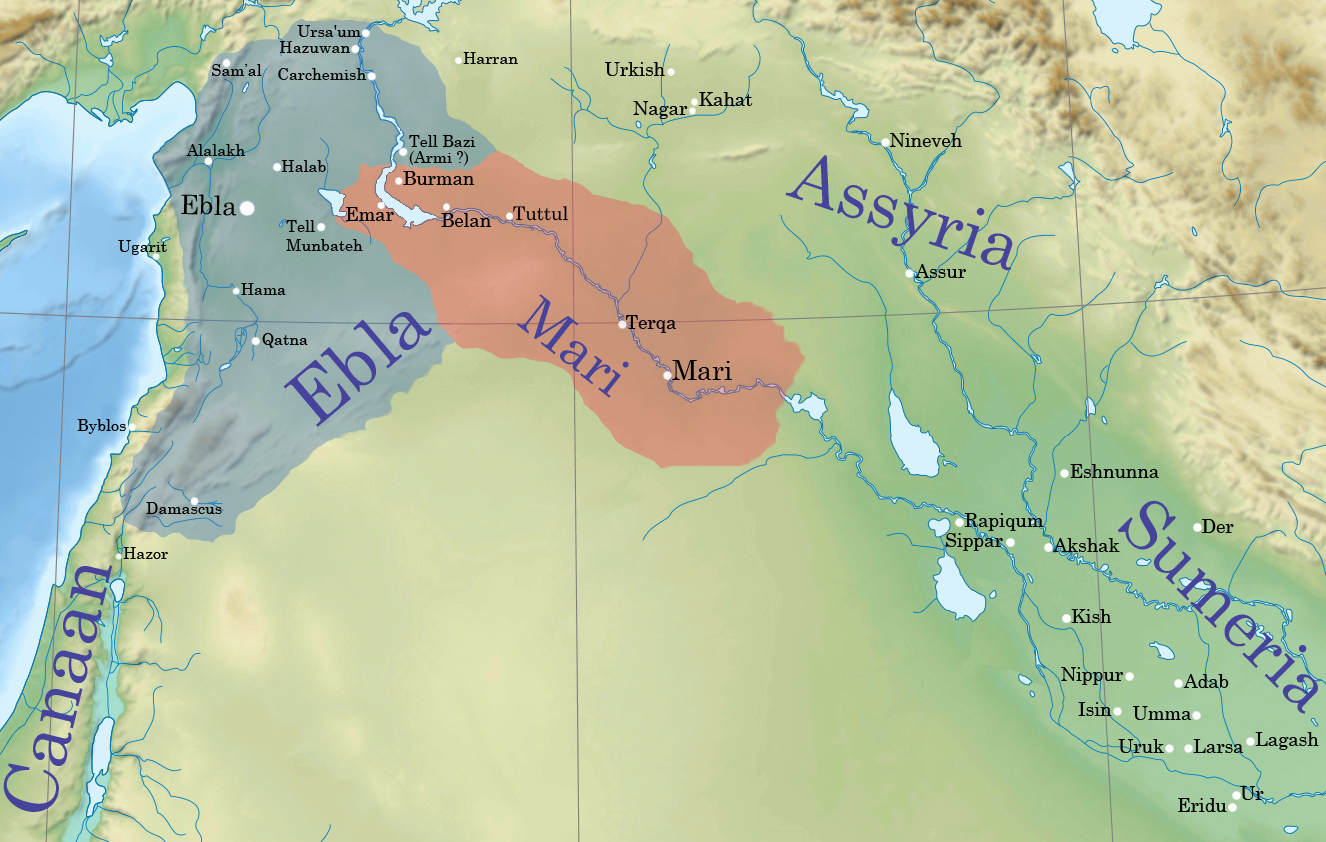
Emar
) , image = View_from_the_Byzantine_Tower_at_Meskene,_ancient_Barbalissos.jpg , alt = , caption = View from the Byzantine Tower at Meskene, ancient Barbalissos , map_type = Syria , map_alt = , map_size = 200 , location = Near Maskanah, Aleppo Governorate, Syria , region = Lake Assad shoreline , coordinates = , type = settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = 1187 BC , epochs = , cultures = Amorite , dependency_of = Ebla, Yamhad, Carchemish , occupants = , event = , excavations = 1972–19761996–2002 , archaeologists = Jean-Claude Margueron , condition = , ownership = Public , public_access = Yes , website = , notes = Emar (modern Tell Meskene) is an archaeological site in Aleppo Governorate, northern Syria. It sits in the great bend of the mid-Euphrates, now on the shoreline of the man-made Lake Assad near the town of Mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibbi-Sipish
Ibbi-Sipish or Ibbi-Zikir (ca. 23rd century BC) was the vizier of Ebla for king Ishar-Damu for 17 years. He was the son of his predecessor, Ibrium, who had been Ishar-Damu's vizier for 15 years. Ibbi-Sipish visited cities abroad, such as Kish. He also concluded a treaty with Armi It is further known from one tablet that Ibbi-Sipish vanquished king Hida'ar of Mari, Ebla's main rival in the region, in the 32nd year of Ishar-Damu's reign. However, Ebla's destruction was to come only three years later, presumably at the hands of the Akkadian ruler Sargon the Great Sargon of Akkad (; akk, ''Šarrugi''), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highl .... Until 1985, the consensus of scholars had been that Ibbi-Sipish, Ibrium, and Ibrium's predecessor Ar-ennum, had all been reigning monarchs in Ebla; consequently, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefire Steles
The Sfire or Sefire steles are three 8th-century BCE basalt ''stelae'' containing Aramaic inscriptions discovered near Al-Safirah ("Sfire") near Aleppo, Syria. The Sefire treaty inscriptions are the three inscriptions on the steles; they are known as KAI 222-224. A fourth stele, possibly from Sfire, is known as KAI 227 (the "Starcky Tablet", at the Louvre). Discovery of the inscriptions Sefire I Discovered in 1930, it is held in the National Museum of Damascus. This is a basalt slab broken in two horizontally. The first two steles each have three faces bearing writing. Sefire II Discovered in 1930, it is held in the National Museum of Damascus. As with Sefire I stele, Sefire II had three faces bearing writing. While most of the text of Sefire II A and B permit coherent translation only with comparison with Sefire I and III, the concluding portion of Sefire II A and B is quite clear. Sefire III Discovered in 1956, Sefire III is made up of nine fragments of the reverse of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in the ancient region of Syria. For over three thousand years, It is a sub-group of the Semitic languages. Aramaic varieties served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires and also as a language of divine worship and religious study. Several modern varieties, namely the Neo-Aramaic languages, are still spoken in the present-day. The Aramaic languages belong to the Northwest group of the Semitic language family, which also includes the Canaanite languages such as Hebrew, Edomite, Moabite, and Phoenician, as well as Amorite and Ugaritic. Aramaic languages are written in the Aramaic alphabet, a descendant of the Phoenician alphabet, and the most prominent alphabet variant is the Syriac alphabet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jebel Aqra
Jebel Aqra ( ar, جبل الأقرع, translit=Jabal al-ʾAqraʿ, ; tr, Kel Dağı) is a limestone mountain located on the Syrian– Turkish border near the mouth of the Orontes River on the Mediterranean Sea. Rising from a narrow coastal plain, Jebel Aqra is a mariners' landmark which gathers thunderstorms. The mountain was a cult site in ancient Canaanite religion and continuing through classical antiquity. A mound of ash and debris remains; an archaeological investigation was broken off because of military restrictions imposed due to the mountain's border location. Names The ancient Semitic name of the mountain, Ṣapōn, is recorded in Akkadian as (), Ugaritic as (), Egyptian as (), Aramaic as (), Phoenician as (), and Hebrew as (). The Hurrians and the Hittites respectively called the mountain () and (), which was a name also used for it in early Akkadian texts. The Hurro-Hittite name gave rise to the mountain's Ancient Greek name of (). History Jebel Aqra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_2008.jpg)