|
Shams Al-Din Muhammad (Mihrabanid Malik)
Shams al-Din Muhammad was the Mihrabanid malik of Sistan from 1480 until around the end of the 15th century. He was the eldest son of Nizam al-Din Yahya. Biography In the last years of Nizam al-Din's reign, the Mihrabanids had lost control of the greater part of Sistan to the Timurids under Badi' al-Zaman. The Mihrabanids were confined to the remote northern lands of Makran bordering Sistan, where Nizam al-Din died in 1480. Following this, his military commanders met and agreed to recognize Shams al-Din as his successor. In 1481 Shams al-Din received a request from the people of Zirih to come to attempt to take control of Sistan. Deciding not to go personally, he instead sent an army under the command of his brothers Sultan Mahmud Shah 'Ali. Badi' al-Zaman, however, was able to raise a numerically superior force which crushed the Mihrabanid army. Shams al-Din's authority thus continued to be restricted to the northern fringes of Makran, although his ineffectiveness as a ruler qui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihrabanid
The Mihrabanid dynasty was a Muslim dynasty that ruled Sistan (or Nimruz) from 1236 until the mid-16th century. It was the third indigenous Muslim dynasty of Sistan, having been preceded by the Saffarid and Nasrid dynasties. Overview Most of what is known about the Mihrabanids comes from two sources. The first, the ''Tarikh-i Sistan'', was completed in the mid-14th century by an unknown chronologist and covers the first hundred years of the dynasty's history. The other, the ''Ihya' al-muluk'', was written by the 17th century author Malik Shah Husayn ibn Malik Ghiyath al-Din Muhammad and covers the entire history of the Mihrabanids' rule of Sistan. The Mihrabanids used the title of malik during their rule of Sistan. A malik could inherit the throne or be appointed by the nobles and military commanders. Their capital was generally the city of Shahr-i Sistan. Outside of the capital, the Mihrabanids frequently had problems asserting their authority over the outer towns of the provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malik
Malik, Mallik, Melik, Malka, Malek, Maleek, Malick, Mallick, or Melekh ( phn, 𐤌𐤋𐤊; ar, ملك; he, מֶלֶךְ) is the Semitic term translating to "king", recorded in East Semitic and Arabic, and as mlk in Northwest Semitic during the Late Bronze Age (e.g. Aramaic, Canaanite, Hebrew). Although the early forms of the name were to be found among the pre-Arab and pre-Islamic Semites of the Levant, Canaan, and Mesopotamia, it has since been adopted in various other, mainly but not exclusively Islamized or Arabized non-Semitic Asian languages for their ruling princes and to render kings elsewhere. It is also sometimes used in derived meanings. The female version of Malik is Malikah ( ar, ملكة; or its various spellings such as Malekeh or Melike), meaning "queen". The name Malik was originally found among various pre-Arab and non-Muslim Semitic peoples such as the indigenous ethnic Assyrians of Iraq, Amorites, Jews, Arameans, Mandeans, Syriacs, and pre-Islami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
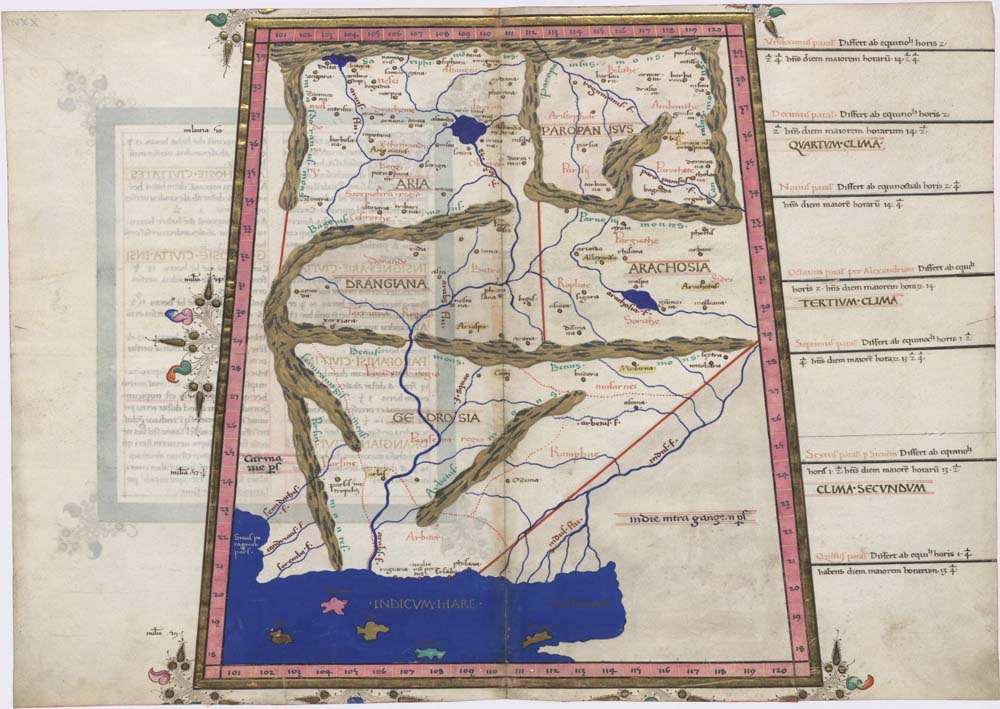
Sistan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan (Nimruz, Helmand, Kandahar). Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, the largest river in Afghanistan, which empties into the Hamun Lake that forms part of the border between the two countries. Etymology Sistan derives its name from ''Sakastan'' ("the land of the Saka"). The Sakas were a Scythians, Scythian tribe which from the 2nd century BC to the 1st century migrated to the Iranian Plateau and Indus valley, where they carved a kingdom known as the Indo-Scythians, Indo-Scythian Kingdom. In the Bundahishn, a Zoroastrian scripture written in Middle Persian, Pahlavi, the province is called "Seyansih". After the Muslim conquest of Persia, Arab conquest of Iran, the province became known as Sijistan/Sistan. The more ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizam Al-Din Yahya
Nizam al-Din Yahya (c. 1417 – October 1480) was the Mihrabanid malik of Sistan from 1438/1439 until his death. He was the son of Shams al-Din 'Ali ibn Qutb al-Din, Shams al-Din 'Ali. Biography Nizam al-Din gained the throne of Sistan after his father's death in 1438 or 1439. During his reign he spent a significant amount of time at the court of the Timurids at Herat. Some time after Abu Sa'id (Timurid dynasty), Abu Sa'id's capture of Greater Khorasan, Khurasan in 1458, Nizam al-Din was summoned by the Timurid to Herat. There he was given one of Abu Sa'id's sisters in marriage. In 1468 Abu Sa'id undertook a military campaign against the Aq Qoyunlu Turkmen of Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan. Nizam al-Din participated in this operation, leading a part of the army of Sistan. Ultimately the campaign ended in disaster; both Abu Sa'id and Nizam al-Din captured by the Aq Qoyunlu, who went on to briefly occupy Herat. The Turkmen leader Uzun Hasan imprisoned Nizam al-Din for six months. He ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timurids
The Timurid Empire ( chg, , fa, ), self-designated as Gurkani ( Chagatai: کورگن, ''Küregen''; fa, , ''Gūrkāniyān''), was a PersianateB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition, 2006 Turco-Mongol empire that dominated Greater Iran in the early 15th century, comprising modern-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, much of Central Asia, the South Caucasus, as well as most of contemporary Pakistan and parts of contemporary North India and Turkey. The empire was founded by Timur (also known as Tamerlane), a warlord of Turco-Mongol lineage, who established the empire between 1370 and his death in 1405. He envisioned himself as the great restorer of the Mongol Empire of Genghis Khan, regarded himself as Genghis's heir, and associated much with the Borjigin. Timur continued vigorous trade relations with Ming China and the Golden Horde, with Chinese diplomats like Ma Huan and Chen Cheng regularly traveling west to Samarkand to buy and sell goods. The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makran
Makran ( fa, مكران), mentioned in some sources as Mecran and Mokrān, is the coastal region of Baluchistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in Balochistan, in Pakistan and Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. It extends westwards, from the Sonmiani Bay to the northwest of Karachi in the east, to the fringes of the region of Bashkardia/Bāšgerd in the southern part of the Sistān and Balučestān province of modern Iran. Makrān is thus bisected by the modern political boundary between Pakistan and Iran. Etymology The southern part of Balochistan is called ''Kech Makran'' on Pakistani side and Makran on the Iranian side which is also the name of a former Iranian province. The location corresponds to that of the Maka satrapy in Achaemenid times. The Sumerian trading partners of Magan are identified with Makran. In Varahamihira's Brihat Samhita, there is a mention of a tribe called ''Makara'' inhabiting the lands west of India. Arrian used the term '' Ichthyophagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan Mahmud Ibn Nizam Al-Din Yahya
Sultan Mahmud (c. 1464 – c. 1543) was the last Mihrabanid malik of Sistan, from c. 1495 until c. 1537. Biography Sultan Mahmud was the son of Nizam al-Din Yahya and the sister of the Timurid Sultan Abu Sa'id. Nizam al-Din Yahya had died in 1480, having lost most of Sistan to the Timurids; his territories were restricted to the mountainous region bordering Baluchistan. The inheritance fell to Sultan Mahmud's half-brother Shams al-Din Muhammad, but the latter quickly proved himself incapable of ruling; as a result Sultan Mahmud ended up assuming effective control of the government. He planned to recapture Sistan and marched on the capital Shahr-i Sistan, but was defeated by the Timurid army and nearly drowned while crossing the Helmand River. A change in the Timurid leadership of Sistan, combined with local appeals for the Mihrabanids to return, prompted Sultan Mahmud and Shams al-Din Muhammad to try again to reconquer the province. This time they were successful, and the bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husayn Bayqarah
Sultan Husayn Bayqara Mirza ( fa, حسین بایقرا / ''Husayn Bāyqarā''; June/July 1438 – 4 May 1506) was the Timurid dynasty, Timurid ruler of Herat from 1469 until May 4, 1506, with a brief interruption in 1470. A skilled statesman, Sultan Husayn Bayqara was best known for his interest in the arts and was renowned as a benefactor and patron of learning in his kingdom, with his reign being heralded as the second Timurid Renaissance. He has been described as "the quintessential Timurid ruler of the later period in Transoxiana" and his sophisticated court and generous artistic patronage was a source of admiration, particularly from his cousin, the Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor Babur. Sultan Husayn Bayqara was the last Timurid ruler of consequence in Greater Khorasan, Khorasan. Early life and lineage Husayn Bayqara was born as Sultan Husayn in Herat in June/July 1438. His parents were Ghiyas ud-din Mansur Mirza of the Barlas tribe and his wife, Firuza Sultan Begum. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safēd Kōh'') in the fertile valley of the Hari River in the western part of the country. An ancient civilization on the Silk Road between the Middle East, Central and South Asia, it serves as a regional hub in the country's west. Herat dates back to Avestan times and was traditionally known for its wine. The city has a number of historic sites, including the Herat Citadel and the Musalla Complex. During the Middle Ages Herat became one of the important cities of Khorasan, as it was known as the ''Pearl of Khorasan''. After the conquest of Tamerlane, the city became an important center of intellectual and artistic life in the Islamic world. Under the rule of Shah Rukh the city served as the focal point of the Timurid Renaissance, whose glor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaranj
Zaranj or Zarang (Persian/Pashto/ bal, زرنج) is a city in southwestern Afghanistan, near the border with Iran, which has a population of 160,902 people as of 2015. It is the capital of Nimruz Province and is linked by highways with Lashkargah and Kandahar to the east, Farah to the north and the Iranian city of Zabol to the west. Zaranj is a major border crossing between Afghanistan and Iran, which is of significant importance to the trade-route between Central Asia and South Asia with the Middle East. The history of Zaranj dates back over 2500 years and Ya'qub ibn al-Layth al-Saffar, founder of the Saffarid dynasty, was born in this old civilization. History Modern Zaranj bears the name of an ancient city whose name is also attested in Old Persian as ''Zranka''. In Greek, this word became Drangiana. Other historical names for Zaranj include Zirra, Zarangia, Zarani etc. Ultimately, the word Zaranj is derived from the ancient Old Persian word ''zaranka'' ("waterland"). Acha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quhistan
Quhistan ( fa, قهستان) or Kohistan (, "mountainous land") was a region of medieval Persia, essentially the southern part of Khurasan. Its boundaries appear to have been south of Khorasan to north, Yazd to West, Sistan to South, Afghanistan to East. Quhistan was a province in old days with a rich history in Persian literature, art and science. Notable historical towns include Tun (modern-day Ferdows), Qa'in, Gunabad, Tabas, Birjand, Turshez (modern-day Kashmar), Khwaf, Taybad, and Zawah (modern-day Torbat-e Heydarieh). It is home to famous castles. Safron, berberies (Zereshk) and jujube (Annab) are among the famous agricultural products that are exclusively produced in Ghohestan. Hakim Nezari Ghohestani, Sima Bina and Professor Reza Ghohestani are among famous people who are originally from Ghohestan. Dagestan in the North Caucasus was previously and originally named ''"Quhistan"'', which has the same meaning as ''Dagestan'': ''dağ'' and ''kuh'' are the Turkic and Persian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)