|
Shahi Qila, Jaunpur
Shahi Qila (English: Royal Fort), also known as Karar Fort or Jaunpur Fort, is a fort built during the 14th century in Jaunpur, Uttar Pradesh, India. The fort is located close to the Shahi Bridge on the Gomti river. Background A tourist attraction of the Jaunpur city, it is located near Shahi Bridge of the Gomti river, from Jaunpur. Constructed by Ibrahim Naib Barbak, a chieftain of Firoz Shah Tughlaq, it was built using the material owned by temples and palaces of the Rathore kings of Kannauj. The fort was destroyed multiple times by rulers, including the Lodhis and the British Empire. It went through extensive renovations and repairs during the rule of the Mughal Empire. History The ''Kerar Kot'' fort once stood on the same site on the left (north) bank of the Gomti river. It contained a mosque and a spacious and stylish set of baths (hammam) installed by Barbak, the brother of Tughlaq. The fort's layout is an irregular quadrangle enclosed in stone walls. The walls surr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forts In India
The existence of the earliest forts in India have been substantiated by documentation and excavation. In the medieval times, the architecture of the forts had both Hindu and Muslim influence. The forts constructed by the British Raj, British initially opted for simple designs. The existing castles are continually modified and many of them are privately owned. Etymology Most of the forts in India are actually castles or fortresses. But when the British Government in India were cataloging them in the 17th–19th century they used the word forts as it was common in Britain then. All fortifications whether European or Indian were termed forts. Thereafter this became the common usage in India. In local languages, the fort names are suffixed by local word for fort thus usage of the Sanskrit word ''durga'', or Urdu word ''qila'' or the Hindi word ''garh'' or ''gad'' in Rajasthan, and Maharashtra is common. For example, Suvarnadurg, Mehrangarh, Sudhagad etc. Indian Forts in ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gomti River
The Gomti, Gumti or Gomati River is a tributary of the Ganges. According to beliefs, the river is the son of Rishi Vashishtha and bathing in the Gomti on Ekadashi (the 11th day of the two lunar phases of the Hindu calendar month) can wash away sins. According to the ''Bhagavata Purana,'' one of Hinduism's major religious works, Gomti is one of the five transcendental rivers of India. The rare Gomti Chakra is found there. Course The Gomti, a monsoon- and groundwater-fed river, originates from Gomat Taal (formally known as Fulhaar jheel) in fulhar village of tehsil kalinagar, Pilibhit, India. It extends through Uttar Pradesh and meets the Ganges near Saidpur (Ghazipur district), Kaithi, from Varanasi district. It meets a small river, the Gaihaaee, from its origin. The Gomti is a narrow stream until it reaches Mohammadi Kheri, a tehsil of Lakhimpur Kheri district (about from its origin), where it is joined by tributaries such as the Sukheta, Choha and Andhra Choha. The rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Forts In Uttar Pradesh
This is a list of forts in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 .... Gallery {{DEFAULTSORT:Forts in Uttar Pradesh U F F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BIMSTEC
The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is an international organisation of seven South Asian and Southeast Asian nations, housing 1.73 billion people and having a combined gross domestic product of US$4.4 trillion (2022). The BIMSTEC member states – Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Thailand – are among the countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal. Fourteen priority sectors of cooperation have been identified and several BIMSTEC centres have been established to focus on those sectors. A BIMSTEC free trade agreement is under negotiation (c. 2018), also referred Similar to SAARC. Leadership is rotated in alphabetical order of country names. The permanent secretariat is in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Background On 6 June 1997, a new sub-regional grouping was formed in Bangkok under the name BIST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation). Following the inclusion of Myanmar on 22 D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAARC
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. SAARC comprises 3% of the world's land area, 21% of the world's population and 5.21% (USD 4.47 trillion) of the global economy, as of 2021. SAARC was founded in Dhaka on 8 December 1985. Its secretariat is based in Kathmandu, Nepal. The organization promotes economic development and regional integration. It launched the South Asian Free Trade Area in 2006. SAARC maintains permanent diplomatic relations at the United Nations as an observer and has developed links with multilateral entities, including the European Union. Historical background The idea of co-operation among South Asian Countries was discussed in three conferences: the Asian Relations Conference held in New Delhi in April 1947; the Baguio Conference in the Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
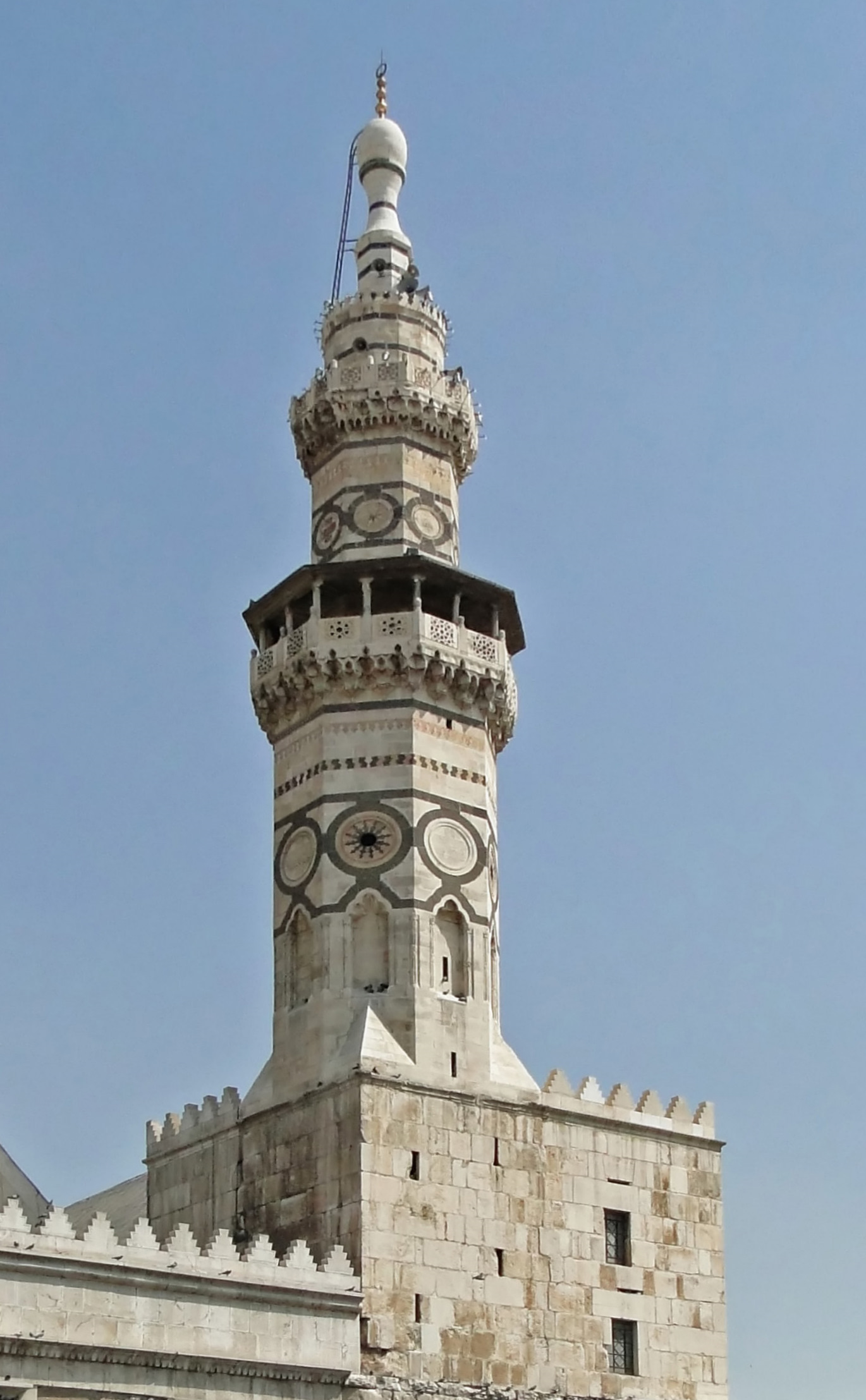
Minar
A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer (''adhan''), but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can have a variety of forms, from thick, squat towers to soaring, pencil-thin spires. Etymology Two Arabic words are used to denote the minaret tower: ''manāra'' and ''manār''. The English word "minaret" originates from the former, via the Turkish version (). The Arabic word ''manāra'' (plural: ''manārāt'') originally meant a "lamp stand", a cognate of Hebrew '' menorah''. It is assumed to be a derivation of an older reconstructed form, ''manwara''. The other word, ''manār'' (plural: ''manā'ir'' or ''manāyir''), means "a place of light". Both words derive from the Arabic root ''n-w-r'', which has a mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Of Bengal
The architecture of Bengal, which comprises the modern country of Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak Valley, has a long and rich history, blending indigenous elements from the Indian subcontinent, with influences from different parts of the world. Bengali architecture includes ancient urban architecture, religious architecture, rural vernacular architecture, colonial townhouses and country houses and modern urban styles. The bungalow style is a notable architectural export of Bengal. The corner towers of Bengali religious buildings were replicated in medieval Southeast Asia. Bengali curved roofs, suitable for the very heavy rains, were adopted into a distinct local style of Indo-Islamic architecture, and used decoratively elsewhere in north India in Mughal architecture. Bengal is not rich in good stone for building, and traditional Bengali architecture mostly uses brick and wood, often reflecting the styles of the wood, bamboo and thatch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcade (architecture)
An arcade is a succession of contiguous arches, with each arch supported by a colonnade of columns or piers. Exterior arcades are designed to provide a sheltered walkway for pedestrians. The walkway may be lined with retail stores. An arcade may feature arches on both sides of the walkway. Alternatively, a blind arcade superimposes arcading against a solid wall. Blind arcades are a feature of Romanesque architecture that influenced Gothic architecture. In the Gothic architectural tradition, the arcade can be located in the interior, in the lowest part of the wall of the nave, supporting the triforium and the clerestory in a cathedral, or on the exterior, in which they are usually part of the walkways that surround the courtyard and cloisters. Many medieval arcades housed shops or stalls, either in the arcaded space itself, or set into the main wall behind. From this, "arcade" has become a general word for a group of shops in a single building, regardless of the architectural f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verandah
A veranda or verandah is a roofed, open-air gallery or porch, attached to the outside of a building. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure. Although the form ''verandah'' is correct and very common, some authorities prefer the version without an "h" (the ''Concise Oxford English Dictionary'' gives the "h" version as a variant and '' The Guardian Style Guide'' says "veranda not verandah"). Australia's ''Macquarie Dictionary'' prefers ''verandah''. Architecture styles notable for verandas Australia The veranda has featured quite prominently in Australian vernacular architecture and first became widespread in colonial buildings during the 1850s. The Victorian Filigree architecture style is used by residential (particularly terraced houses in Australia and New Zealand) and commercial buildings (particularly hotels) across Australia and features decorative screens of wrought iron, cast iron "lace" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niche (architecture)
A niche (CanE, or ) in Classical architecture is an exedra or an apse that has been reduced in size, retaining the half-dome heading usual for an apse. Nero's Domus Aurea (AD 64–69) was the first semi-private dwelling that possessed rooms that were given richly varied floor plans, shaped with niches and exedrae; sheathed in dazzling polished white marble, such curved surfaces concentrated or dispersed the daylight. A is a very shallow niche, usually too shallow to contain statues, and may resemble a blind window (a window without openings) or sealed door. (Compare: blind arcade) The word derives from the Latin (), via the French . The Italian '' nicchio'' () may also be involved,OED, "Niche" as the traditional decoration for the top of a niche is a scallop shell, as in the illustration, hence also the alternative term of "conch" for a semi-dome, usually reserved for larger exedra. In Gothic architecture, a niche may be set within a tabernacle framing, like a richly de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spandrels
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the flanks being able to protect the curtain wall and the adjacent bastions. Compared with the medieval fortified towers they replaced, bastion fortifications offered a greater degree of passive resistance and more scope for ranged defence in the age of gunpowder artillery. As military architecture, the bastion is one element in the style of fortification dominant from the mid 16th to mid 19th centuries. Evolution By the middle of the 15th century, artillery pieces had become powerful enough to make the traditional medieval round tower and curtain wall obsolete. This was exemplified by the campaigns of Charles VII of France who reduced the towns and castles held by the English during the latter stages of the Hundred Years War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)