|
Shahab-4
The Shahab-4 ( fa, شهاب ۴, meaning "Meteor-4") (a.k.a. IRIS) was an unbuilt Iranian rocket, derived from the Shahab-3 medium-range ballistic missile. According to Iran it was intended to be a space launch vehicle, after a slip by the Defense Minister in which he acknowledged it as a "more capable ballistic missile than the Shahab-3". According to Western observers, it was intended to be part of a nuclear-capable ballistic missile. History The IRIS/''Shahab-4'' project was initiated in 1988 but according to some sources, it never went beyond the drawing board. The design heritage of the IRIS was later incorporated into the Safir (rocket), Safir. b14643.de In 1997, an American satellite captured evidence of a Shahab-4 test facility in Parchin. In 1999, it was suspected that the Shahab-4 was largely derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahab-3
The Shahab-3 ( fa, شهاب ۳, Šahâb 3; meaning "meteor-3") is a liquid-propelled medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) developed by Iran and based on the North Korean Nodong-1. The Shahab-3 has a range of ; a MRBM variant can now reach (can hit targets as far as Israel, Egypt, Romania, Bulgaria and Greece). It was tested from 1998 to 2003 and added to the military arsenal on 7 July 2003, with an official unveiling by Ayatollah Khamenei on July 20. With an accuracy of 140 m CEP, the Shahab-3 missile is primarily effective against large, soft targets (like military airfields). Given the Shahab-3’s payload capacity, it would likely be capable of delivering nuclear warheads. According to the IAEA, Iran in the early 2000s may have explored various fuzing, arming and firing systems to make the Shahab-3 more capable of reliably delivering a nuclear warhead. The forerunners to this missile include the Shahab-1 and Shahab-2. In 2007, the then- Iranian Defence Minister Admiral Sham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-12 Dvina
The R-12 Dvina was a theatre ballistic missile developed and deployed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. Its GRAU designation was 8K63 (8K63U or 8K63У in Cyrillic for silo-launched version), and it was given the NATO reporting name of SS-4 Sandal. The R-12 rocket provided the Soviet Union with the capability to attack targets at medium ranges with a megaton-class thermonuclear warhead and constituted the bulk of the Soviet offensive missile threat to Western Europe. Deployments of the R-12 missile in Cuba caused the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962. A total of 2335 missiles were produced; all were destroyed in 1993 under the START II treaty. As well as the single-stage ballistic technology, the R-12 Dvina had a two-stage capability that allowed payloads to be placed into low Earth orbit. The Iranian Shahab-4 missile is likely an offshoot of the R-12 Dvina. History Beginning OKB-586 formed from a spin-off of portions of Sergei Korolev's OKB-1 production infrastructure und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within the Earth's atmosphere, while intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are launched on a sub-orbital flight. These weapons are in a distinct category from cruise missiles, which are aerodynamically guided in powered flight. Unlike cruise missiles, which are restricted to the atmosphere, it is advantageous for ballistic missiles to avoid the denser parts of the atmosphere and they may travel above the atmosphere into outer space. History The earliest form of ballistic missile dates from the 13th century with its use derived from the history of rockets. In the 14th century, the Ming Chinese navy used an early form of a ballistic missile weapon called the Huolongchushui in naval battles against enemy ships.Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Launch Vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to large operating costs. An orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles are multistage rockets which use chemical propellants such as solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid oxygen, or Hypergolic propellants. Launch vehicles are classified by their orbital payload capacity, ranging from small-, medium-, heavy- to super-heavy lift. Mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safir (rocket)
The Safir ( fa, سفیر, meaning "ambassador") was the first Iranian expendable launch vehicle able to place a satellite in orbit. The first successful orbital launch using the Safir launch system took place on 2 February 2009 when a Safir carrier rocket placed the Omid satellite into an orbit with a apogee. Making Iran the ninth nation capable of producing and launching a satellite. The Simorgh is a larger orbital launcher based on Safir technology which has since replaced the Safir, and is sometimes called the Safir-2. Design and specifications The Safir measures 1.25 meters in diameter, 22 meters in height and has a launching mass of 26 tons. The rocket consists of two stages; The first stage utilizes an upgraded Nodong/Shahab-3 type engine which burns a hypergolic combination of UDMH as fuel and nitrogen tetroxide as oxidant, producing 37 tons (363 kN; 82,500 lbf) of thrust. The second stage utilizes a pair of smaller engines (originally the Vernier engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parchin
Parchin ( fa, پارچین) is an Iranian military complex, located about southeast of Tehran. It is closely linked with the Khojir missile production complex. Geography Parchin is located on the bank of the Jajrud (river). History Missile engines To the northwest of Parchin in the Barjamali Hills, a test range for liquid-propellant missile engines is part of the Shahid Hemmat Industrial Group (SHIG) Khojir research facility where signature of engine test stand firing, probably including technology from the Russian SS-4 Sandal missile, was confirmed by an American spy satellite in August 1997. On December 15, 1997, SHIG conducted at least a sixth 1997 test of an engine needed for an ballistic missile. The test was either the sixth or the eighth during 1997 according to available intelligence. 1997 wind tunnel It is reported the Russian Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute TsAGI contracted in early 1997 to build a wind tunnel at SHIG, for both Iranian and Russian mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuzhnoye Design Office
Pivdenne Design Office ( uk, Державне конструкторське бюро «Південне» ім. М. К. Янгеля , lit=State design bureau "Southern", named after M. K. Yangel, translit=Derzhavne konstruktorske biuro "Pivdenne" im. M. K. Yanhelia), located in Dnipro, Ukraine, is a designer of satellites and rockets, and formerly of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), established by Mikhail Yangel. During Soviet times the bureau's OKB designation was OKB-586. The company is in close co-operation with the PA Pivdenmash multi-product machine-building company, also situated in Dnipro. Pivdenmash is the main manufacturer of the models developed by Pivdenne Design Office. Directors * 1954–1971 Mikhail Yangel * 1971–1991 Vladimir Utkin * 1991–2010 * 2010–2020 Products Current Ballistic missiles *Hrim-2 Orbital launch vehicles *Zenit rocket family **Zenit-2 **Zenit-2M **Zenit-3F **Zenit-3SL **Zenit-3SLB *Antares fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
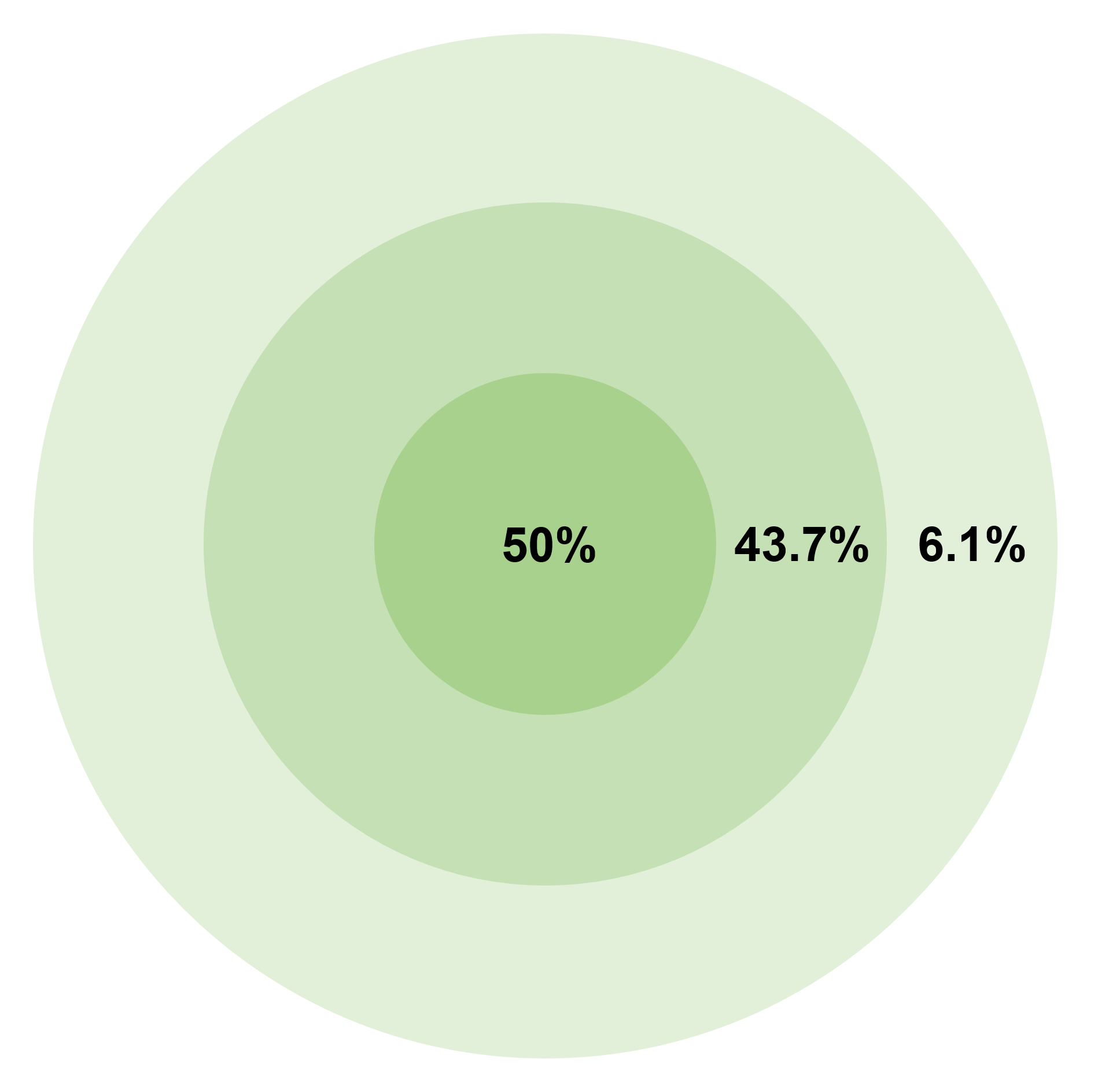
Circle Of Equal Probability
In the military science of ballistics, circular error probable (CEP) (also circular error probability or circle of equal probability) is a measure of a weapon system's precision. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the mean, whose perimeter is expected to include the landing points of 50% of the rounds; said otherwise, it is the median error radius. That is, if a given munitions design has a CEP of 100 m, when 100 munitions are targeted at the same point, 50 will fall within a circle with a radius of 100 m around their average impact point. (The distance between the target point and the average impact point is referred to as bias.) There are associated concepts, such as the DRMS (distance root mean square), which is the square root of the average squared distance error, and R95, which is the radius of the circle where 95% of the values would fall in. The concept of CEP also plays a role when measuring the accuracy of a position obtained by a navigati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Launch Vehicles Of Iran
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as spacetime. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. Debates concerning the nature, essence and the mode of existence of space date back to antiquity; namely, to treatises like the ''Timaeus'' of Plato, or Socrates in his reflections on what the Greeks called ''khôra'' (i.e. "space"), or in the ''Physics'' of Aristotle (Book IV, Delta) in the definition of ''topos'' (i.e. place), or in the later "geometrical conception of place" as "spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Missiles Of Iran
Ballistics may refer to: Science * Ballistics, the science that deals with the motion, behavior, and effects of projectiles ** Forensic ballistics, the science of analyzing firearm usage in crimes ** Internal ballistics, the study of the processes accelerating a projectile ** Transition ballistics, the study of the projectile's behavior when it leaves the barrel ** External ballistics, the study of the passage of the projectile through space or the air ** Terminal ballistics, the study of the interaction of a projectile with its target * Ballistic conduction, conduction of electricity with negligible charge scattering * Ballistic movement of muscles in an animal Combat * Ballistic missile, a missile that follows a sub-orbital flightpath * Ballistic knife, a specialized combat knife with a detachable, self-propelled blade * Ballistic shield, a shield meant to protect the user from bullets Arts and media Comics * Ballistic (Image Comics), a comic character of Top Cow Product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-surface Missiles Of Iran
A surface-to-surface missile (SSM) or ground-to-ground missile (GGM) is a missile designed to be launched from the ground or the sea and strike targets on land or at sea. They may be fired from hand-held or vehicle mounted devices, from fixed installations, or from a ship. They are often powered by a rocket engine or sometimes fired by an explosive charge, since the launching platform is typically stationary or moving slowly. They usually have fins and/or wings for lift and stability, although hyper-velocity or short-ranged missiles may use body lift or fly a ballistic trajectory. The V-1 flying bomb was the first operational surface-to-surface missile. Contemporary surface-to-surface missiles are usually guided. An unguided surface-to-surface missile is usually referred to as a rocket (for example, an RPG-7 or M72 LAW is an anti-tank rocket whereas a BGM-71 TOW or AT-2 Swatter is an anti-tank guided missile). Examples of surface-to-surface missile include the MGM-140 ATACMS, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |