|
Set Shifting
Cognitive flexibility is an intrinsic property of a cognitive system often associated with the mental ability to adjust its activity and content, switch between different task rules and corresponding behavioral responses, maintain multiple concepts simultaneously and shift internal attention between them. The term ''cognitive flexibility'' is traditionally used to refer to one of the executive functions. In this sense, it can be seen as neural underpinnings of adaptive and flexible behavior. Most flexibility tests were developed under this assumption several decades ago. Nowadays, cognitive flexibility can also be referred to as a set of properties of the brain that facilitate flexible yet relevant switching between functional brain states. Cognitive flexibility varies during the lifespan of an individual. In addition, certain conditions such as obsessive–compulsive disorder are associated with reduced cognitive flexibility. Since cognitive flexibility is a vital component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Shifting
Cognitive shifting is the mental process of ''consciously'' redirecting one's attention from one fixation to another. In contrast, if this process happened ''unconsciously'', then it is referred to as task switching. Both are forms of cognitive flexibility. In the general framework of cognitive therapy and awareness management, cognitive shifting refers to the conscious choice to take charge of one's mental habits—and redirect one's focus of attention in helpful, more successful directions. In the term's specific usage in corporate awareness methodology, cognitive shifting is a performance-oriented technique for refocusing attention in more alert, innovative, charismatic and empathic directions. Origins in cognitive therapy In cognitive therapy, as developed by its founder Aaron T. Beck and others, a client is taught to shift his or her cognitive focus from one thought or mental fixation to a more positive, realistic focus—thus the descriptive origins of the term "cognitive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Psychology (journal)
''Cognitive Psychology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering cognitive psychology. It was established in 1970 and is published eight times per year by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is Caren Rotello (University of Massachusetts Amherst). Gordon Logan (Vanderbilt University) was the editor-in-chief from 1999 through 2021. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2015 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 4.537. References External links * Elsevier academic journals Cognitive science journals Publications established in 1970 English-language journals {{psychology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Experimental Child Psychology
The ''Journal of Experimental Child Psychology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal covering experimental child psychology. It was established in 1964 and is published by Elsevier (formerly Academic Press). The editor-in-chief is David F. Bjorklund (Florida Atlantic University). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 2.424. References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Journal of Experimental Child Psychology Experimental psychology journals Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1964 Monthly journals English-language journals Developmental psychology journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Science
''Developmental Science'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering developmental psychology and developmental cognitive neuroscience that was established in 1998. The current editors are Charles A. Nelson, Michelle de Haan, and Paul C. Quinn. Topics covered include: * Clinical, computational, and comparative approaches to development * Cognitive and social development * Functional neuroimaging of the developing brain * Developmental disorders According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 3.808. References External links * {{Official website, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/10.1111/(ISSN)1467-7687 Publications established in 1998 Wiley-Blackwell academic journals En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Directions In Psychological Science
''Current Directions in Psychological Science '' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal from the Association for Psychological Science (APS) that is published by SAGE Publications. Publication Scope ''Current Directions in Psychological Science'' publishes concise reviews by leading experts spanning all of scientific psychology and its applications. The reviews published in this journal cover diverse topics such as language, memory and cognition, development, the neural basis of behavior and emotions, various aspects of psychopathology, and theory of mind. These articles allow readers to stay apprised of important developments across subfields beyond their areas of expertise and bodies of research they might not otherwise be aware of. The articles in ''Current Directions'' are also written to be accessible to non-experts, making them suitable for use in the classroom as teaching supplements. The current editor of the journal is Robert Goldstone at Indiana University Bloo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychonomic Bulletin & Review
The Psychonomic Society is an international scientific society of over 4,500 scientists in the field of experimental psychology. The mission of the Psychonomic Society is to foster the science of cognition through the advancement and communication of basic research in experimental psychology and allied sciences. It is open to international researchers, and almost 40% of members are based outside of North America. Although open to all areas of experimental and cognitive psychology, its members typically study areas such as learning, memory, attention, motivation, perception, categorization, decision making, and psycholinguistics. Its name is taken from the word psychonomics, meaning "the science of the laws of the mind". History The Psychonomic Society was founded by a group of experimental psychologists during a meeting in Chicago, Illinois, USA in December 1959. The main goal was to create a society that would support open communication about psychological science with minimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension is the ability to process text, understand its meaning, and to integrate with what the reader already knows. Fundamental skills required in efficient reading comprehension are knowing meaning of words, ability to understand meaning of a word from discourse context, ability to follow organization of passage and to identify antecedents and references in it, ability to draw inferences from a passage about its contents, ability to identify the main thought of a passage, ability to answer questions answered in a passage, ability to recognize the literary devices or propositional structures used in a passage and determine its tone, to understand the situational mood (agents, objects, temporal and spatial reference points, casual and intentional inflections, etc.) conveyed for assertions, questioning, commanding, refraining etc. and finally ability to determine writer's purpose, intent and point of view, and draw inferences about the writer (discourse-semantics). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluency
Fluency (also called volubility and eloquency) is the property of a person or of a system that delivers information quickly and with expertise. Language use Language fluency is one of a variety of terms used to characterize or measure a person's language ability, often used in conjunction with accuracy and complexity. Although there are no widely agreed-upon definitions or measures of language fluency, someone is typically said to be fluent if their use of the language appears ''fluid'', or natural, coherent, and easy as opposed to slow, halting use. In other words, fluency is often described as the ability to produce language on demand and be understood. Varying definitions of fluency characterize it by the language user’s automaticity, their speed and coherency of language use, or the length and rate of their speech output. Theories of automaticity postulate that more fluent language users can manage all of the components of language use without paying attention to each in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Intelligence
The concepts of fluid intelligence (''g''f) and crystallized intelligence (''g''c) were introduced in 1963 by the psychologist Raymond Cattell. According to Cattell's psychometrically-based theory, general intelligence (''g'') is subdivided into ''g''f and ''g''c. Fluid intelligence is the ability to solve novel reasoning problems and is correlated with a number of important skills such as comprehension, problem-solving, and learning. Crystallized intelligence, on the other hand, involves the ability to deduce secondary relational abstractions by applying previously learned primary relational abstractions. History Fluid and crystallized intelligence are constructs originally conceptualized by Raymond Cattell. The concepts of fluid and crystallized intelligence were further developed by Cattell and his former student John L. Horn. Fluid versus crystallized intelligence Fluid intelligence (''g''f) refers to basic processes of reasoning and other mental activities that depend on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Educational Psychology
The ''Journal of Educational Psychology'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that was established in 1910 and covers educational psychology. It is published by the American Psychological Association. The current editor-in-chief is Steve Graham (Arizona State University). The journal publishes original psychological research on education at all ages and educational levels, as well as occasional theoretical and review articles deemed of particular importance. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 5.805. The journal has implemented the Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines. The TOP Guidelines provide structure to research planning and reporting and aim to make research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Piaget
Jean William Fritz Piaget (, , ; 9 August 1896 – 16 September 1980) was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. Piaget's theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called " genetic epistemology". Piaget placed great importance on the education of children. As the Director of the International Bureau of Education, he declared in 1934 that "only education is capable of saving our societies from possible collapse, whether violent, or gradual". His theory of child development is studied in pre-service education programs. Educators continue to incorporate constructivist-based strategies. Piaget created the International Center for Genetic Epistemology in Geneva in 1955 while on the faculty of the University of Geneva, and directed the center until his death in 1980. The number of collaborations that its founding made possible, and their impact, ultimately led to the Center being referred to in the scholarly literature as "Piaget's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
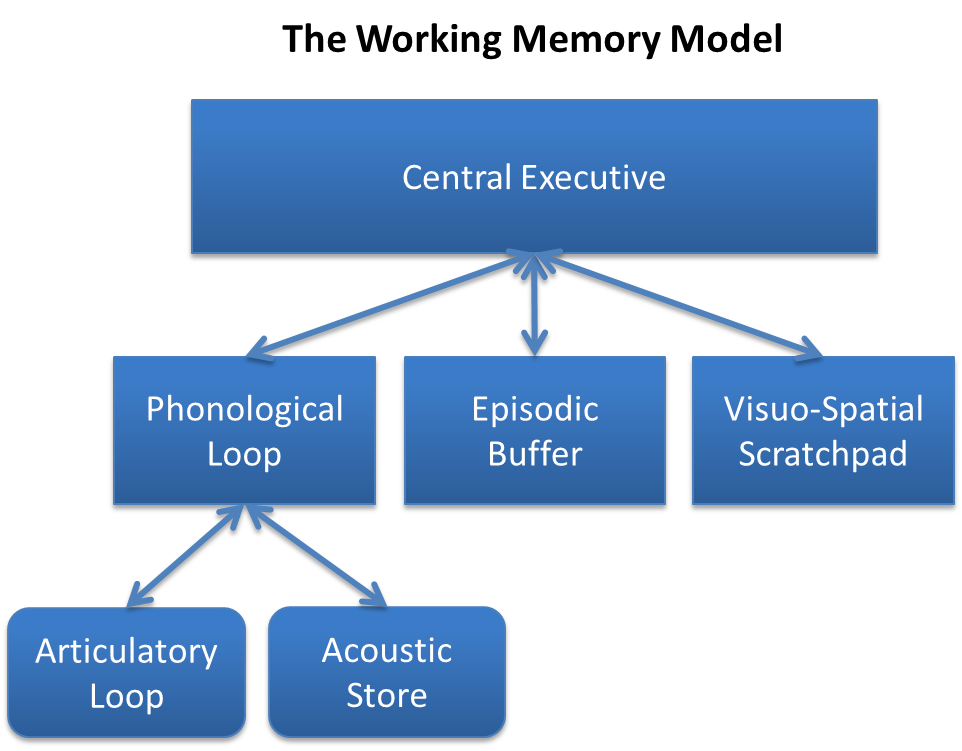
Working Memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience. History The term "working memory" was coined by Miller, Galanter, and Pribram, and was used in the 1960s in the context of theories that likened the mind to a computer. In 1968, Atkinson and Shiffrin used the term to describe their "short-term store". What we now call working memory was formerly referred to variously as a "short-term store" or short-term memory, primary memory, immediate memory, operant memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |