|
Sertorian War
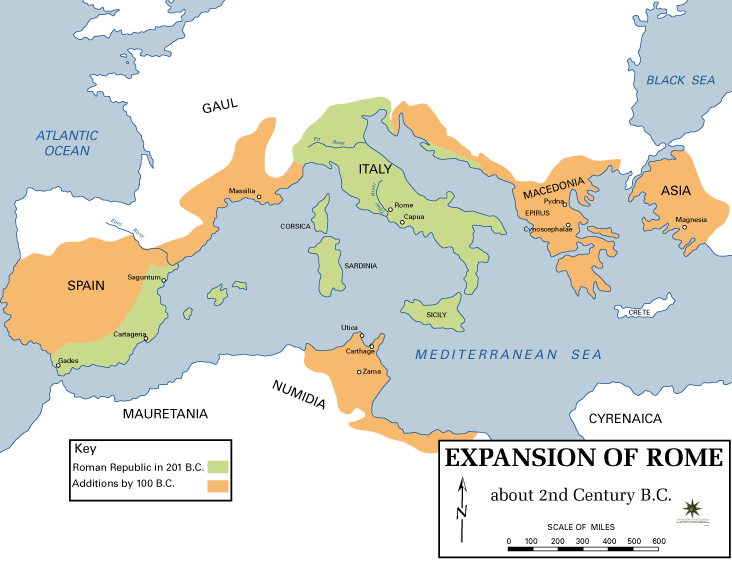
The Sertorian War was a civil war fought from 80 to 72 BC between a faction of Roman rebels ( Sertorians) and the government in Rome (Sullans). The war was fought on the Iberian Peninsula (called ''Hispania'' by the Romans) and was one of the Roman civil wars of the first century BC. The Sertorians, a coalition of Celts, Aquitanians, Iberians and Roman and Italic rebels, fought against the representatives of the regime established by Sulla. The war takes its name from Quintus Sertorius, the leader of the opposition. It was notable for Sertorius' successful use of guerrilla warfare. The war ended after Sertorius was assassinated by Marcus Perperna, who was then promptly defeated by Pompey. Origin of the war During Sulla's civil war, Quintus Sertorius fought for the Marian- Cinna faction against Sulla. In 83 BC, Sertorius, after falling out with his faction's leadership, was sent to the Iberian Peninsula as its governor. Unfortunately for Sertorius his faction lost the war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Of The Roman Republic
The crisis of the Roman Republic refers to an extended period of political instability and social unrest from about 134 BC to 44 BC that culminated in the demise of the Roman Republic and the advent of the Roman Empire. The causes and attributes of the crisis changed throughout the decades, including the forms of slavery, brigandage, wars internal and external, overwhelming corruption, land reform, the invention of excruciating new punishments, the expansion of Roman citizenship, and even the changing composition of the Roman army. Modern scholars also disagree about the nature of the crisis. Traditionally, the expansion of citizenship (with all its rights, privileges, and duties) was looked upon negatively by Sallust, The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, Gibbon, and others of their schools, because it caused internal dissension, disputes with Rome's Italian allies, slave revolts, and riots.Fields, p. 41, citing Sallust, ''Iugurthinum'' 86.2. However, other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
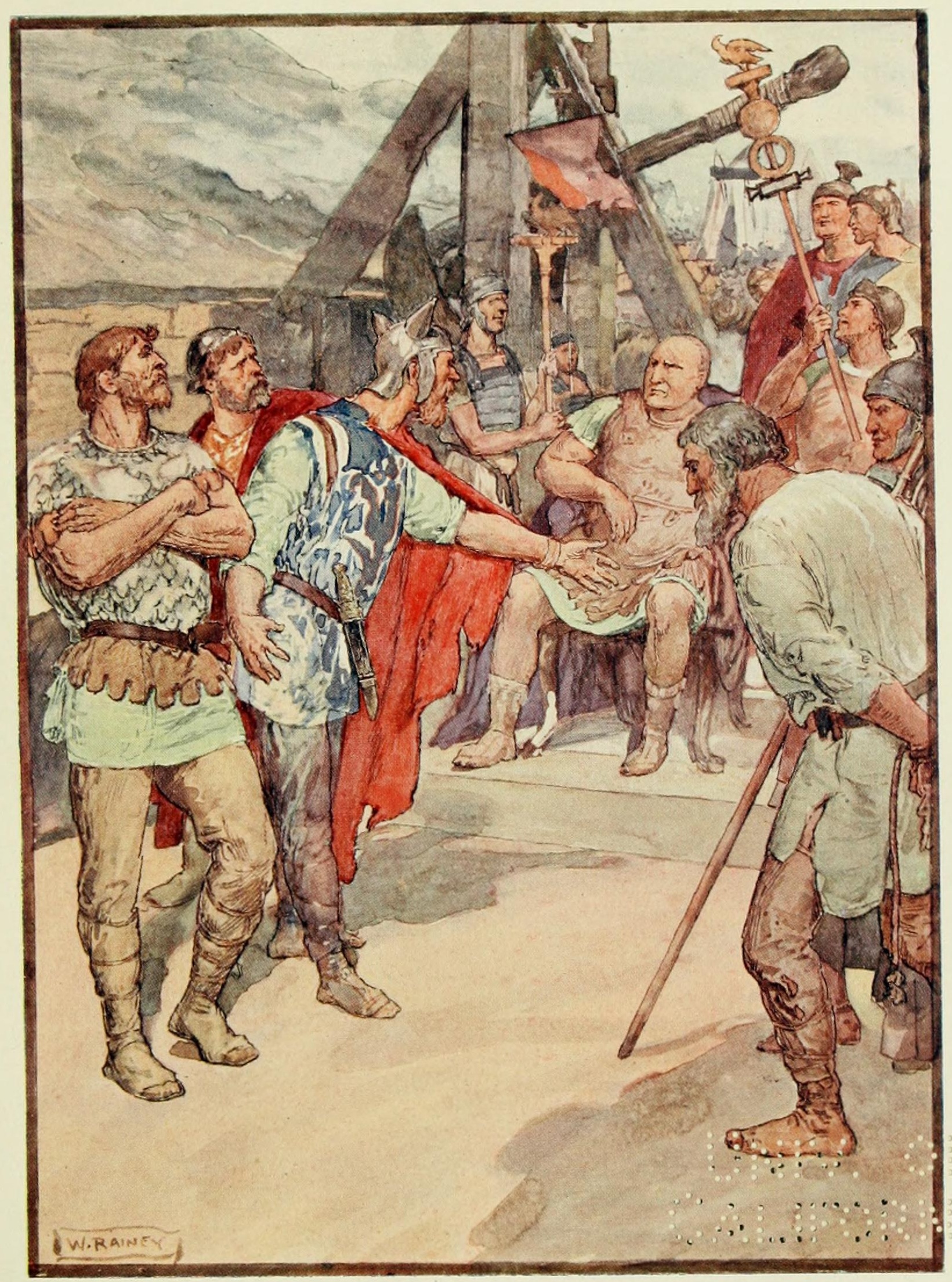
Sertorius
Quintus Sertorius (c. 126 – 73 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who led a large-scale rebellion against the Roman Senate on the Iberian peninsula. He had been a prominent member of the populist faction of Cinna and Marius. During the later years of the civil war of 83–81 BC, he was sent to recover the Iberian Peninsula. When his faction lost the war he was proscribed (outlawed) by the dictator Sulla. Supported by a majority of the native Iberian tribes, Sertorius skillfully used irregular warfare to repeatedly defeat various commanders sent by Rome to subdue him. He was never decisively beaten on the battlefield and remained a thorn in the Senate's side until his murder in 73 BC. The famous Greek biographer Plutarch dedicated one of his Parallel Lives to Sertorius; in it he pairs Sertorius with Eumenes. Like Eumenes, Sertorius was betrayed by his own men. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pillars Of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank the entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar. The northern Pillar, Calpe Mons, is the Rock of Gibraltar. A corresponding North African peak not being predominant, the identity of the southern Pillar, Abila Mons, has been disputed throughout history, with the two most likely candidates being Monte Hacho in Ceuta and Jebel Musa in Morocco. History According to Greek mythology adopted by the Etruscans and Romans, when Hercules had to perform twelve labours, one of them (the tenth) was to fetch the Cattle of Geryon of the far West and bring them to Eurystheus; this marked the westward extent of his travels. A lost passage of Pindar quoted by Strabo was the earliest traceable reference in this context: "the pillars which Pindar calls the 'gates of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lusitani
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania. History Origins Frontinus mentions Lusitanian leader Viriathus as the leader of the Celtiberians, in their war against the Romans. The Greco-Roman historian Diodorus Siculus attributed them a name of another Celtic tribe: "Those who are called Lusitanians are the bravest of all Cimbri", often thought of as Germanic. The Lusitanians were also called Belitanians, according to the diviner Artemidorus. . .l. Real Academia de la Historia, 2000. 33 p. vol. 6 of Bibliotheca archaeologica hispana, v. 6 of Publicaciones del Gabinete de Antigüedades. Strabo differentiated the Lusitanians from the Iberian tribes and called them Celts who had been known as Oestriminis in ancient times. On the other hand, Pliny the Elder and Pomponiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania. History Origins Frontinus mentions Lusitanian leader Viriathus as the leader of the Celtiberians, in their war against the Romans. The Greco-Roman historian Diodorus Siculus attributed them a name of another Celtic tribe: "Those who are called Lusitanians are the bravest of all Cimbri", often thought of as Germanic. The Lusitanians were also called Belitanians, according to the diviner Artemidorus. . .l. Real Academia de la Historia, 2000. 33 p. vol. 6 of Bibliotheca archaeologica hispana, v. 6 of Publicaciones del Gabinete de Antigüedades. Strabo differentiated the Lusitanians from the Iberian tribes and called them Celts who had been known as Oestriminis in ancient times. On the other hand, Pliny the Elder and Pompon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tingis
Tingis (Latin; grc-gre, Τίγγις ''Tíngis'') or Tingi ( Ancient Berber:), the ancient name of Tangier in Morocco, was an important Carthaginian, Moor, and Roman port on the Atlantic Ocean. It was eventually granted the status of a Roman colony and made the capital of the province of Mauretania Tingitana and, after Diocletian's reforms, the diocese of Hispania. Legends The Greeks claimed that Tingis had been named for a daughter of the titan Atlas, who was supposed to support the vault of heaven nearby. They claimed that the Berber legends comported with the stories of Hercules's labors, which carried him to North Africa and the North Atlantic to retrieve the golden apples of the Hesperides. Having killed her husband Antaeus and again condemned her father to eternally supporting the firmament, Hercules slept with Tinja and fathered the Berber hero Syphax. Syphax supposedly founded the port of Tingis and named it his mother's honor after her death.. The gigan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Cornelius Cinna
Lucius Cornelius Cinna (died 84 BC) was a four-time consul of the Roman Republic, serving four consecutive terms from 87 to 84 BC, and a member of the ancient Roman Cinna family of the Cornelia gens. Cinna's influence in Rome exacerbated the tensions which existed between Gaius Marius and Lucius Cornelius Sulla. After the death of Marius, he became the leading power in Rome until his own death. His main impact upon Roman politics was his ability to veil his tyranny and make it appear that he was working under a constitutional government. His policies also impinged on Julius Caesar, who married his daughter. Rise to power Little is known about Cinna before his bid for the consulship of 87 BC. He had praetorian rank in the Social War (91–88 BC), and had most likely also been praetor previous to this time. Cinna was elected as Roman consul in 87 BC, but historians disagree about who supported his election and what his original political goals and causes were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
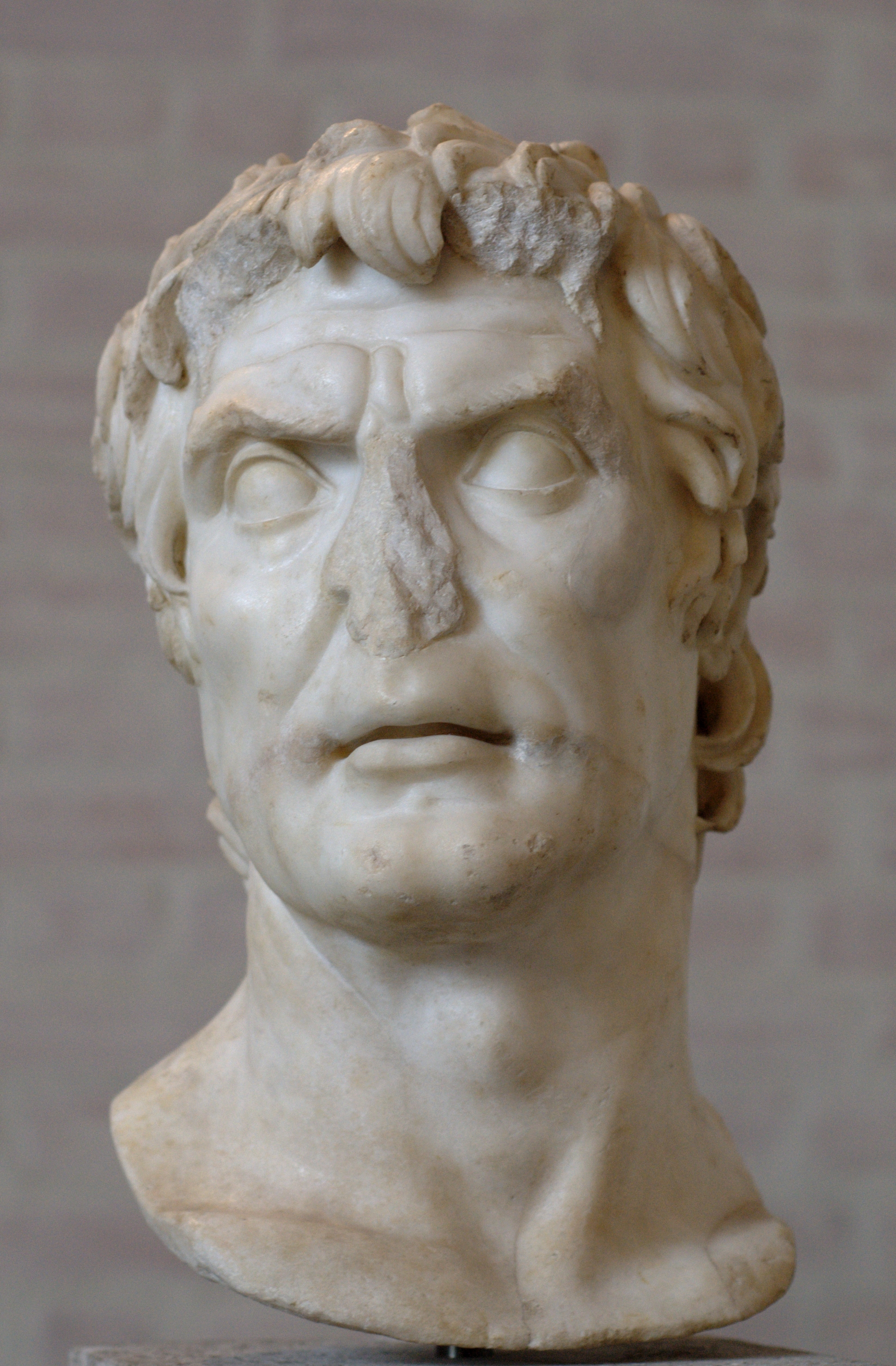
Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important reforms of Roman armies. He set the precedent for the shift from the militia levies of the middle Republic to the professional soldiery of the late Republic; he also improved the ''pilum'', a javelin, and made large-scale changes to the logistical structure of the Roman army. Rising from a well-off provincial Italian family in Arpinum, Marius acquired his initial military experience serving with Scipio Aemilianus at the Siege of Numantia in 134 BC. He won election as tribune of the plebs in 119 BC and passed a law limiting aristocratic interference in elections. Barely elected praetor in 115 BC, he next became the governor of Further Spain where he campaigned against bandits. On his return from Spain he married Julia, the aunt o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulla's Civil War
Sulla's civil war was fought between the Roman general Lucius Cornelius Sulla and his opponents, the Cinna-Marius faction (usually called the Marians or the Cinnans after their former leaders Gaius Marius and Lucius Cornelius Cinna), in the years 83–81 BC. The war ended with a decisive battle just outside Rome itself. After the war the victorious Sulla made himself dictator of the republic. Prelude Sulla had achieved temporary control of Rome and Marius's exile to Africa following his first march on Rome, but departed soon afterwards to lead the First Mithridatic War. This departure allowed Gaius Marius and his son Gaius Marius the younger to return to Rome with an army and, with Lucius Cornelius Cinna, to wrest control of Rome back from Sulla's supporter Gnaeus Octavius during Sulla's absence. Based on the orders of Marius, some of his soldiers went through Rome killing the leading supporters of Sulla, including Octavius. Their heads were exhibited in the Forum. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guerrilla Warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics, and mobility, to fight a larger and less-mobile traditional military. Although the term "guerrilla warfare" was coined in the context of the Peninsular War in the 19th century, the tactical methods of guerrilla warfare have long been in use. In the 6th century BC, Sun Tzu proposed the use of guerrilla-style tactics in '' The Art of War''. The 3rd century BC Roman general Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus is also credited with inventing many of the tactics of guerrilla warfare through what is today called the Fabian strategy. Guerrilla warfare has been used by various factions throughout history and is particularly associated with revolutionary movements and popular resistance against invading or occupying armies. Guerrilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Civil Wars
This is a list of civil wars and organized civil disorder, revolts and rebellions in ancient Rome (Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic, and Roman Empire) until the fall of the Western Roman Empire (753 BCE – 476 CE). For the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantine Empire after the division of the Empire in West and East, see List of Byzantine revolts and civil wars (330–1453). For external conflicts, see List of Roman wars and battles. 3rd century BC * 241 BC: Falisci revolt – revolt suppressed * 216–203 BC: Defection of Rome's Italian allies to the Carthaginians during the Second Punic War 2nd century BC * 135–132 BC: First Servile War in Sicily - revolt suppressed * 125 BC: Fregellae revolt - revolt suppressed * 104–100 BC: Second Servile War in Sicily - revolt suppressed 1st century BC * 91–87 BC: Social War, between Rome and many of its fellow Italian allies - Roman victory. * 88 BC: Sulla's march on Rome, causing his enemy, Gaius Marius, to be outlawed * 87 BC: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman People
grc, Ῥωμαῖοι, , native_name_lang = , image = Pompeii family feast painting Naples.jpg , image_caption = 1st century AD wall painting from Pompeii depicting a multigenerational banquet , languages = , religions = Imperial cult, Roman religion, Hellenistic religion, Christianity , related = Other ancient Italic peoples (including other Latins and the Falisci), other ancient peoples of Italy, other Mediterranean Sea peoples, modern Romance peoples and Greeks The Romans ( la, Rōmānī; grc, Ῥωμαῖοι, Rhōmaîoi) were a cultural group, variously referred to as an ethnicity or a nationality, that in classical antiquity, from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD, came to rule large parts of Europe, the Near East and North Africa through conquests made during the Roman Republic and the later Roman Empire. Originally only referring to the Italic Latin citizens of Rome itself, the meaning of "Roman" underwent conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_01.jpg)





