|
Serotonin–dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor
A serotonin–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SDRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine by blocking the actions of the serotonin transporter (SERT) and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of serotonin and dopamine, and, therefore, an increase in serotonergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission. A closely related type of drug is a serotonin–dopamine releasing agent (SDRA). Comparison to SNDRIs Relative to serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors (SNDRIs), which also inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine in addition to serotonin and dopamine, SDRIs might be expected to have a reduced incidence of certain side effects, namely insomnia, appetite loss, anxiety, and heart rate and blood pressure changes. Examples of SDRIs Unlike the case of other combination monoamine reuptake inhibitors such as serotonin–norepinephrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequences of the use of a drug. Developing drugs is a complicated process, because no two people are exactly the same, so even drugs that have virtually no side effects, might be difficult for some people. Also, it is difficult to make a drug that targets one part of the body but that does not affect other parts, the fact that increases the risk of side effects in the untargeted parts. Occasionally, drugs are prescribed or procedures performed specifically for their side effects; in that case, said side effect ceases to be a side effect and is now an intended effect. For instance, X-rays were historically (and are currently) used as an imaging technique; the discovery of their oncolytic capability led to their employ in radiotherapy (ablation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission. DRIs are used in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy for their psychostimulant effects, and in the treatment of obesity and binge eating disorder for their appetite suppressant effects. They are sometimes used as antidepressants in the treatment of mood disorders, but their use as antidepressants is limited given that strong DRIs have a high abuse potential and legal restrictions on their use. Lack of dopamine reuptake and the increase in extracellular levels of dopamine have been lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norepinephrine Transporter
The norepinephrine transporter (NET), also known as noradrenaline transporter (NAT), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the solute carrier family 6 member 2 (SLC6A2) gene. NET is a monoamine transporter and is responsible for the sodium-chloride (Na+/Cl−)-dependent reuptake of extracellular norepinephrine (NE), which is also known as noradrenaline. NET can also reuptake extracellular dopamine (DA). The reuptake of these two neurotransmitters is essential in regulating concentrations in the synaptic cleft. NETs, along with the other monoamine transporters, are the targets of many antidepressants and recreational drugs. In addition, an overabundance of NET is associated with ADHD. There is evidence that single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the NET gene (''SLC6A2'') may be an underlying factor in some of these disorders. Gene The norepinephrine transporter gene, SLC6A2 is located on human chromosome 16 locus 16q12.2. This gene is encoded by 14 exons. Based on the nucleotide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity (pharmacology)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition of liga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biochemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together, and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen), to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a random cluster of atoms and functional groups, but rather had a definite order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
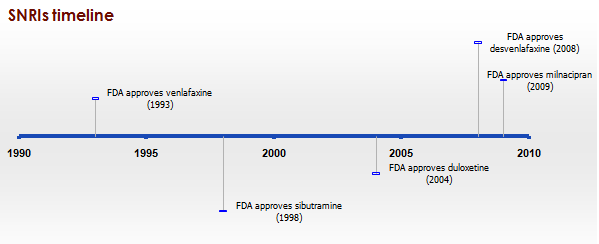
Serotonin–norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant drugs used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), social phobia, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the more widely used selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which act upon serotonin only. The human serotonin transporter (SERT) and noradrenaline transporter (NAT) are membrane transport proteins that are responsible for the reuptake of serotonin and noradrenaline from the synaptic cleft back into the presynaptic nerve terminal. Dual inhibition of serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake can offer advantages over othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental And Clinical Psychopharmacology
''Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Psychological Association. It was established in 1993 and covers research in clinical psychology. The current editor-in-chief is William W. Stoops (University of Kentucky Department of Behavioral Science). The journal has implemented the Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines. The TOP Guidelines provide structure to research planning and reporting and aim to make research more transparent, accessible, and reproducible. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed by MEDLINE/PubMed and the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature—that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the same since 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide, but is also modulated by numerous factors, including, but not limited to, genetics, physical fitness, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness as well as the interaction between and among these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with rates around 40–50 bpm is common and is considered normal. When the heart is not beating in a regular pattern, this is ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |