|
Sermilik
Sermilik ( da, Egede og Rothes Fjord) is a fjord in eastern Greenland. It is part of the Sermersooq municipality. The settlement of Tasiilaq is located about 15 km to the east of the mouth of the fjord. Geography This fjord, whose Greenlandic name 'Sermilik' means 'place with glaciers' is located at the southern end of King Christian IX Land, west of Ammassalik Fjord. It is one of the largest fjords in the southeastern coast of Greenland. Its waters are fed by the Helheim Glacier, Fenris Glacier and Midgard Glacier among others. The fjord stretches inland in a roughly northern direction and splits into two branches at its head —at the southern limit of Schweizerland, the western one being the Helheim Fjord and the right one the Ningerti. Sermilik's mouth is located between Kitak Island and Cape Tycho Brahe in the Denmark Strait area of the Atlantic Ocean. Kangersivartikajik is the next fjord to the east along the coast. Near the fjord's entrance on the wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenris Glacier
Fenris Glacier ( da, Fenrisgletscher) is a glacier in the Sermersooq municipality, Eastern Greenland. This glacier is named after Fenris (Fenrir), the mighty wolf of Norse mythology. Geography The Fenris Glacier is located on the eastern side of the Greenland ice sheet, forming the boundary of the western and southwestern area of Schweizerland.GoogleEarth It flows roughly southwards from the area of Gaule Bjerg, west of the Midgard Glacier and northeast of the Helheim Glacier. Its terminus is at the mouth of the Ningerti, one of the northernmost branches of Sermilik ''(Egede og Rothes Fjord)'', a large fjord system. See also *List of glaciers in Greenland This is a list of glaciers in Greenland. Details on the size and flow of some of the major Greenlandic glaciers are listed by Eric Rignot and Pannir Kanagaratnam (2006) Ice sheets and caps *Greenland Ice Sheet * Christian Erichsen Ice Cap * Fla ... References External links TC - Freshwater flux to Sermilik Fjord, SE Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
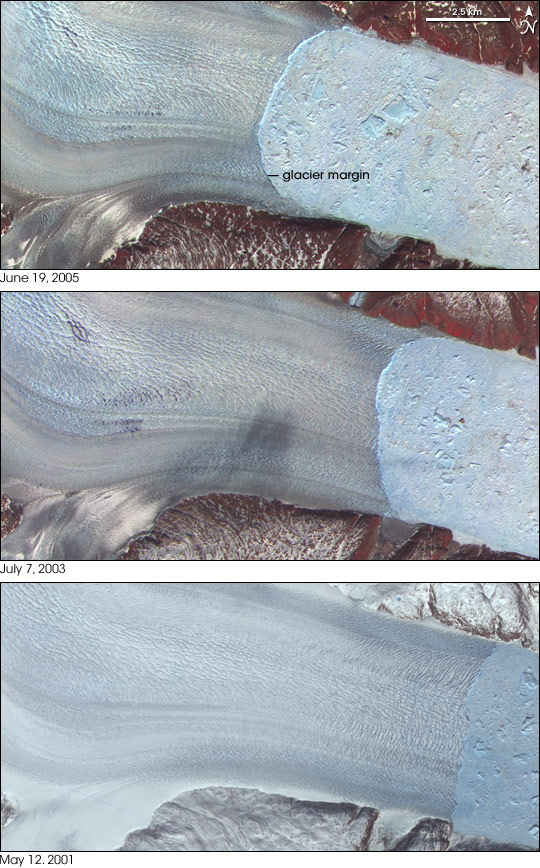
Helheim Glacier
Helheim Glacier is a glacier in the Sermersooq municipality, Eastern Greenland. This glacier is named after Helheim, the world of the dead in Norse Mythology. Geography The Helheim Glacier is located on the eastern side of the Greenland ice sheet. It is one of Greenland's largest outlet glaciers. It flows roughly in an ESE direction and feeds the waters of the Helheim Fjord, a branch at the northern end of the Sermilik (Egede og Rothes Fjord) system, where there are a number of other glaciers calving and discharging at rapid rates such as the Fenris and the Midgard Glacier. Retreat Helheim Glacier accelerated from per year in 2000 to per year in 2005. Like many of Greenland's outlet glaciers, it is a common site where glacial earthquakes are monitored. See also *List of glaciers in Greenland This is a list of glaciers in Greenland. Details on the size and flow of some of the major Greenlandic glaciers are listed by Eric Rignot and Pannir Kanagaratnam (2006) Ice sheets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fridtjof Nansen
Fridtjof Wedel-Jarlsberg Nansen (; 10 October 186113 May 1930) was a Norwegian polymath and Nobel Peace Prize laureate. He gained prominence at various points in his life as an explorer, scientist, diplomat, and humanitarian. He led the team that made the first crossing of the Greenland interior in 1888, traversing the island on cross-country skis. He won international fame after reaching a record northern latitude of 86°14′ during his ''Fram'' expedition of 1893–1896. Although he retired from exploration after his return to Norway, his techniques of polar travel and his innovations in equipment and clothing influenced a generation of subsequent Arctic and Antarctic expeditions. Nansen studied zoology at the Royal Frederick University in Christiania and later worked as a curator at the University Museum of Bergen where his research on the central nervous system of lower marine creatures earned him a doctorate and helped establish neuron doctrine. Later, neuroscientist Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nansen Greenland Crossing Map Af
Fridtjof Wedel-Jarlsberg Nansen (; 10 October 186113 May 1930) was a Norwegian polymath and Nobel Peace Prize laureate. He gained prominence at various points in his life as an explorer, scientist, diplomat, and humanitarian. He led the team that made the first crossing of the Greenland interior in 1888, traversing the island on cross-country skis. He won international fame after reaching a record northern latitude of 86°14′ during his ''Fram'' expedition of 1893–1896. Although he retired from exploration after his return to Norway, his techniques of polar travel and his innovations in equipment and clothing influenced a generation of subsequent Arctic and Antarctic expeditions. Nansen studied zoology at the Royal Frederick University in Christiania and later worked as a curator at the University Museum of Bergen where his research on the central nervous system of lower marine creatures earned him a doctorate and helped establish neuron doctrine. Later, neuroscientist S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midgard Glacier
Midgard Glacier ( da, Midgårdsgletscher) is a glacier in the Sermersooq municipality, Eastern Greenland. This glacier is named after Midgard, one of the Nine Worlds in Norse mythology. Geography The Midgard Glacier is located on the eastern side of the Greenland ice sheet, at the southern limit of Schweizerland. It flows from the Femstjernen in the NE, just east of the Fenris Glacier. Its terminus is in the Ningerti, one of the northernmost branches of Sermilik ''(Egede og Rothes Fjord)'', a large fjord system where there are a number of other glaciers discharging such as the Helheim Glacier. See also *List of glaciers in Greenland This is a list of glaciers in Greenland. Details on the size and flow of some of the major Greenlandic glaciers are listed by Eric Rignot and Pannir Kanagaratnam (2006) Ice sheets and caps *Greenland Ice Sheet * Christian Erichsen Ice Cap *Flad ... References External links Glaciers Not On Simple, Upward Trend Of Meltingsciencedaily.com, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schweizerland
Schweizerland, also known as Schweizerland Alps, is a mountain range in King Christian IX Land, eastern Greenland. Administratively this range is part of the Sermersooq Municipality.Google Earth Its highest point is one of the highest peaks in Greenland. Owing to its high peaks Schweizerland is a popular climbing destination, together with the Watkins Range to the northeast and the Stauning Alps further north. Tasiilaq Heliport is located near the area of the range. History The range was formerly a remote unknown area. It was named 'Schweizerland' in 1912 by Swiss geophysicist and Arctic explorer Alfred de Quervain following the Second Swiss Expedition in which he crossed the Greenland ice cap from Godhavn (Qeqertarsuaq) on the west, to Sermilik Fjord on the eastern side. De Quervain also identified the position and approximate height of Mont Forel, highest point of Schweizerland. Mont Forel was then thought to be the highest mountain in the Arctic Circle area. However, at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angmagssalik Map
Tasiilaq, formerly Ammassalik and Angmagssalik, is a town in the Sermersooq municipality in southeastern Greenland. With 1,985 inhabitants as of 2020, it is the most populous community on the eastern coast, and the seventh-largest town in Greenland. The Sermilik Station, dedicated to the research of the nearby Mittivakkat Glacier, is located near the town. History Prehistory to the fifteenth century The people of Saqqaq culture were the first to reach eastern Greenland, arriving from the north,eastgreenland.com ''History of East Greenland'' through what is now known as and |
Tasiilaq
Tasiilaq, formerly Ammassalik and Angmagssalik, is a town in the Sermersooq municipality in southeastern Greenland. With 1,985 inhabitants as of 2020, it is the most populous community on the eastern coast, and the seventh-largest town in Greenland. The Sermilik Station, dedicated to the research of the nearby Mittivakkat Glacier, is located near the town. History Prehistory to the fifteenth century The people of Saqqaq culture were the first to reach eastern Greenland, arriving from the north,eastgreenland.com ''History of East Greenland'' through what is now known as and |
Umivik Bay
Umivik Bay ( da, Umivik Bugt), also known as ''Umiivik'' and ''Umerik'', is a bay in King Frederick VI Coast, southeastern Greenland. It is part of the Sermersooq municipality. Unlike the jagged and forbidding appearance of most fjord systems in East Greenland, the Umivik area has a relatively gentle shape. Here the massive Greenland ice sheet comes down to the shore in smooth, even undulations and the landscape looks unbroken, with only few glimpses of bare rock.''Prostar Sailing Directions 2005 Greenland and Iceland Enroute'', p. 102 Owing to this smoothness, Umivik Bay was chosen as launching point for westward overland crossings, including the pioneering 1888 Greenland venture by Fridtjof Nansen. Geography Umivik Bay is located between the Fridtjof Nansen Peninsula to the north and the Odinland Peninsula to the south. It includes a sound and a fjord and has a few large islands, the largest of which is Upernattivik (Upernarsuak) lying squarely in the middle of the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Christian IX Land
King Christian IX Land ( da, Kong Christian IX Land) is a coastal area of Southeastern Greenland in Sermersooq Municipality fronting the Denmark Strait and extending through the Arctic Circle from 65°N to 70°N. History This area was named in September 1884 by Gustav Frederik Holm who claimed it for Denmark, naming it after the then-reigning Danish King Christian IX. Geography King Christian IX Land is bordered by King Frederick VI Coast on the south, King Christian X Land and the Scoresby Sound to the north, and the Greenland Ice Sheet to the west. Greenland's highest mountain range, the Watkins Range, as well as the nearly as high Schweizerland are located in this region. The shore area of King Christian IX Land includes the Blosseville Coast to the east. There are many fjords, the largest of which are Sermilik, Kangerlussuaq and Kangertittivatsiaq, as well as numerous coastal islands, including Ammassalik which is the site of the most populous town in Eastern Greenland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammassalik Fjord
Ammassalik Fjord (old spelling: ''Angmagssalik Fjord'') is a long fjord in the Sermersooq municipality in southeastern Greenland. Geography The head of the fjord at is formed by the confluence of two narrow, tributary fjords: ''Qingertivaq Fjord'' and ''Tasiilaq Fjord'' (one of two fjords of that name). The fjord has a north-to-south orientation in its northern part, to then turn midway to the south-west-south at approximately . While the shores of the northern part separate peninsulas of the mainland of Greenland, the southern, progressively wider half of the fjord separates the large Ammassalik Island in the west from islands of the eponymous Ammassalik Archipelago in the east and southeast, including the largest, Apusiaajik Island.''Tasiilaq'', Saga Map, Tage Schjøtt, 1992 The fjord is joined by narrow waterways with other waterbodies in the region: the Ikaasartivaq Strait separating Ammassalik Island from the mainland connects the fjord to the wider Sermilik Fjord in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jason (ship)
''Jason'' was a Norwegian whaling vessel laid down in 1881 by Rødsverven in Sandefjord, Norway, the same shipyard which later built Ernest Shackleton's ship ''Endurance''. The ship, financed by Christen Christensen, an entrepreneur from Sandefjord, was noted for his participation in an 1892-1893 Antarctic expedition led by Carl Anton Larsen. The vessel reached 68°10'S, and set a new record for distance travelled south along the eastern Antarctic Peninsula. The ship's first mate during the expedition was Søren Andersen, also of Sandefjord. ''Jason'' was sold to an Italian company in 1899 and rechristened ''Stella Polare''. Usage as ''Jason'' In 1888, Fridtjof Nansen captained ''Jason'' to Greenland in order to attempt the first documented crossing of the island. From 1892 to 1894, the ship was used on scientific whaling expeditions to the Antarctic, funded by A/S Oceana. The purpose of these expeditions were to map the presence of whales and seals in the area. During th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

