|
Sergey Volkov (astronaut)
Sergey Aleksandrovich Volkov (russian: Сергей Александрович Волков; born April 1, 1973, in Chuhuiv, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union) is a retired Russian cosmonaut and engineer. He was a member of three missions to the International Space Station, spending more than a year in total in space. During his missions he did four spacewalks lasting more than 23 hours in total. Volkov retired from the Cosmonaut group in February 2017. Personal Volkov is the first second-generation cosmonaut (and space walker), the son of cosmonaut Aleksandr Volkov (cosmonaut), Aleksandr Volkov. He was born on April 1, 1973 in Chuguyev, Kharkov Region, Ukraine. Volkov and his wife Natalia have a son who was born in 2001. His recreational activities include tennis, windsurfing, reading, and visiting museums. Education Volkov graduated from Star City high school in 1990 and entered the Tambov Air Force Academy for Pilots. He graduated in 1995 with a degree of pilot/engineer. Awar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federal Space Agency
The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" (russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос»), commonly known simply as Roscosmos (russian: Роскосмос), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency, which was established on 25 February 1992russian: Российское космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (russian: РКА). and restructured in 1999 and 2004, as the Russian Aviation and Space Agencyrussian: Российское авиационно-космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISS Expedition 45 Patch
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian ''Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to be i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expedition 7
Expedition 7 was the seventh expedition to the International Space Station. Crew Planned crew before ''Columbia'' disaster Mission parameters *Perigee: 384 km *Apogee: 396 km *Inclination: 51.6° *Period: 92 min Mission objectives The seventh crew of the International Space Station lifted off in Soyuz TMA-2 from the Russian Space Agency's Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on 25 April 2003, at 05:56:20 UTC. The Soyuz docked on 28 April 2003 and took over command of the ISS. The ''Space Shuttle'' fleet had been grounded due to the ''Columbia'' disaster, so the crew size was reduced to two, as opposed to the three that could be carried by the shuttle. The Expedition Seven crew—along with European Space Agency Astronaut Pedro Duque—landed back on Earth on 27 October 2003 at Kazakhstan at 02:41:20 UTC, after undocking from the International Space Station in their Soyuz spacecraft at 23:17 UTC. Due to the reduced crew size, the scientific work had to be scaled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Volkov Expedition17
Sergius is a male given name of Ancient Roman origin after the name of the Latin ''gens'' Sergia or Sergii of regal and republican ages. It is a common Christian name, in honor of Saint Sergius, or in Russia, of Saint Sergius of Radonezh, and has been the name of four popes. It has given rise to numerous variants, present today mainly in the Romance (Serge, Sergio, Sergi) and Slavic languages (Serhii, Sergey, Serguei). It is not common in English, although the Anglo-French name Sergeant is possibly related to it. Etymology The name originates from the Roman ''nomen'' (patrician family name) ''Sergius'', after the name of the Roman ''gens'' of Latin origins Sergia or Sergii from Alba Longa, Old Latium, counted by Theodor Mommsen as one of the oldest Roman families, one of the original 100 ''gentes originarie''. It has been speculated to derive from a more ancient Etruscan name but the etymology of the nomen Sergius is problematic. Chase hesitantly suggests a connection with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-134
The Tupolev Tu-134 (NATO reporting name: Crusty) is a twin-engined, narrow-body jet airliner built in the Soviet Union for short and medium-haul routes from 1966 to 1989. The original version featured a glazed-nose design and, like certain other Russian airliners (including its sister model the Tu-154), it can operate from unpaved airfields. One of the most widely used aircraft in former Comecon countries, the number in active service is decreasing because of operational safety concerns and noise restrictions. The model has seen long-term service with some 42 countries, with some European airlines having scheduled as many as 12 daily takeoffs and landings per plane. In addition to regular passenger service, it has also been used in various air force, army and navy support roles; for pilot and navigator training; and for aviation research and test projects. In recent years, a number of Tu-134s have been converted for use as VIP transports and business jets. A total of 854 Tu-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
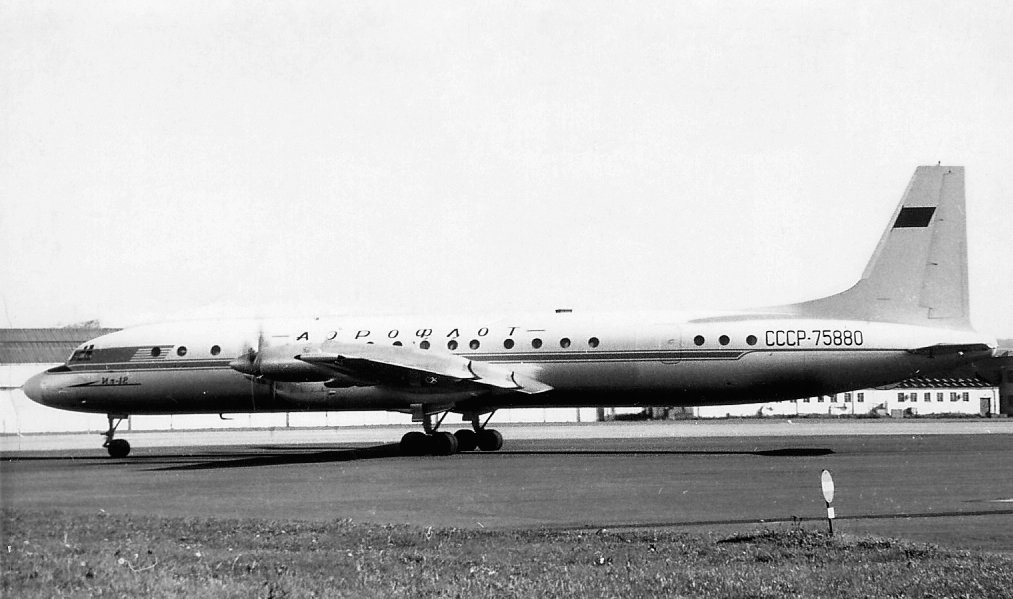
Ilyushin Il-18
The Ilyushin Il-18 (russian: Илью́шин Ил-18; NATO reporting name: Coot) is a large turboprop airliner that first flew in 1957 and became one of the best known and most durable Soviet aircraft of its era. The Il-18 was one of the world's principal airliners for several decades and was widely exported. Due to the aircraft's airframe durability, many examples achieved over 45,000 flight hours and the type remains operational in both military and (to a lesser extent) civilian capacities. The Il-18's successor was the long range Il-62 jet airliner. Design and development Two Soviet aircraft shared the designation Ilyushin Il-18. The first Il-18 was a propeller-driven airliner of 1946 but after a year of test flights that programme was abandoned. In the early 1950s with a need to replace older designs and increase the size of the Soviet civil transport fleet, a Soviet Council of Ministers directive was issued on 30 December 1955 to the chief designers Kuznetsov and Ivchenko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
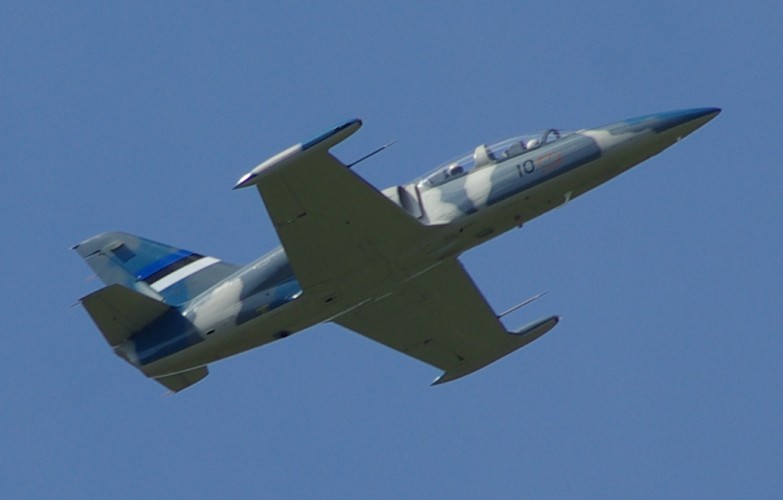
Aero L-39 Albatros
The Aero L-39 Albatros is a high-performance jet trainer designed and produced in Czechoslovakia by Aero Vodochody. It is the most widely used jet trainer in the world; in addition to performing basic and advanced pilot training, it has also flown combat missions in a light-attack role. Unusually, the aircraft never received a NATO reporting name. The L-39 Albatros was designed during the 1960s as a successor to the Aero L-29 Delfín, an early jet-powered principal training aircraft. Performing its maiden flight on 4 November 1968, it became the first trainer aircraft in the world to be equipped with a turbofan powerplant. Quantity production of the L-39 Albatros proceeded in 1971; one year later, it was formally recognized by the majority of the Warsaw Pact countries as their preferred primary trainer. Accordingly, thousands of L39s would be produced for various military customers in Eastern Europe. Additionally, it was exported to a range of countries across the world both as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aero L-29 Delfín
The Aero L-29 Delfín ( en, Dolphin, NATO reporting name: Maya) is a military jet trainer developed and manufactured by Czechoslovakian aviation manufacturer Aero Vodochody. It is the country's first locally designed and constructed jet aircraft, as well as likely being the biggest aircraft industrial programme to take place in any of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (COMECON) countries except the Soviet Union."Selling to Eastern Europe." ''Flight International'', 13 June 1974. p. 174. In response to a sizable requirement for a common jet-propelled trainer to be adopted across the diverse nations of the , Aero decided to embark upon their own desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksandr Volkov (cosmonaut)
Aleksandr Aleksandrovich Volkov (russian: Алекса́ндр Алекса́ндрович Во́лков; born 27 May 1948) is a retired Russian cosmonaut. He is a veteran of 3 space flights, including twice to the Mir Soviet space station, and is the father of cosmonaut Sergey Volkov. Biography and career Volkov was born in Ukrainian SSR in a family of Russian ethnicity. At the age of 13, Volkov witnessed Yuri Gagarin become the first man in space and this inspired him to become a cosmonaut. He joined the Soviet space programme and became a test pilot before realising his dream. He flew into space three times. His first spaceflight was a trip to Salyut 7 in 1985 (64 days in space), followed by two flights to the Mir space station, in 1988–1989 (151 days) and again in 1991–1992 (175 days) as commander of flight Soyuz TM-13. On board the Mir space station, he controlled the docking procedures among other things. The Soviet Union broke up in 1991 during his second stay on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmonaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and tourists. "Astronaut" technically applies to all human space travelers regardless of nationality. However, astronauts fielded by Russia or the Soviet Union are typically known instead as cosmonauts (from the Russian "kosmos" (космос), meaning "space", also borrowed from Greek). Comparatively recent developments in crewed spaceflight made by China have led to the rise of the term taikonaut (from the Mandarin "tàikōng" (), meaning "space"), although its use is somewhat informal and its origin is unclear. In China, the People's Liberation Army Astronaut Corps astronauts and thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenta , a coastal village in Crete
{{disambiguation ...
Lenta can refer to: * Lenta (retail), a Russian hyper- and supermarket chain * Lenta, Piedmont, a municipality in Italy * Lenta.ru, a Russian online newspaper * ''Lenta'' (лента), ribbon or tape in the Russian language ** Especially the ribbon of Saint George * a barley cultivar See also * Lentas Lentas (Greek Λέντας), Lentas is a coastal village 75 km south of Heraklion, on the south coast of Crete in Greece. It belongs to the community of Miamou within the municipality of Gortyna. Origins of the name The name of Lentas possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)