|
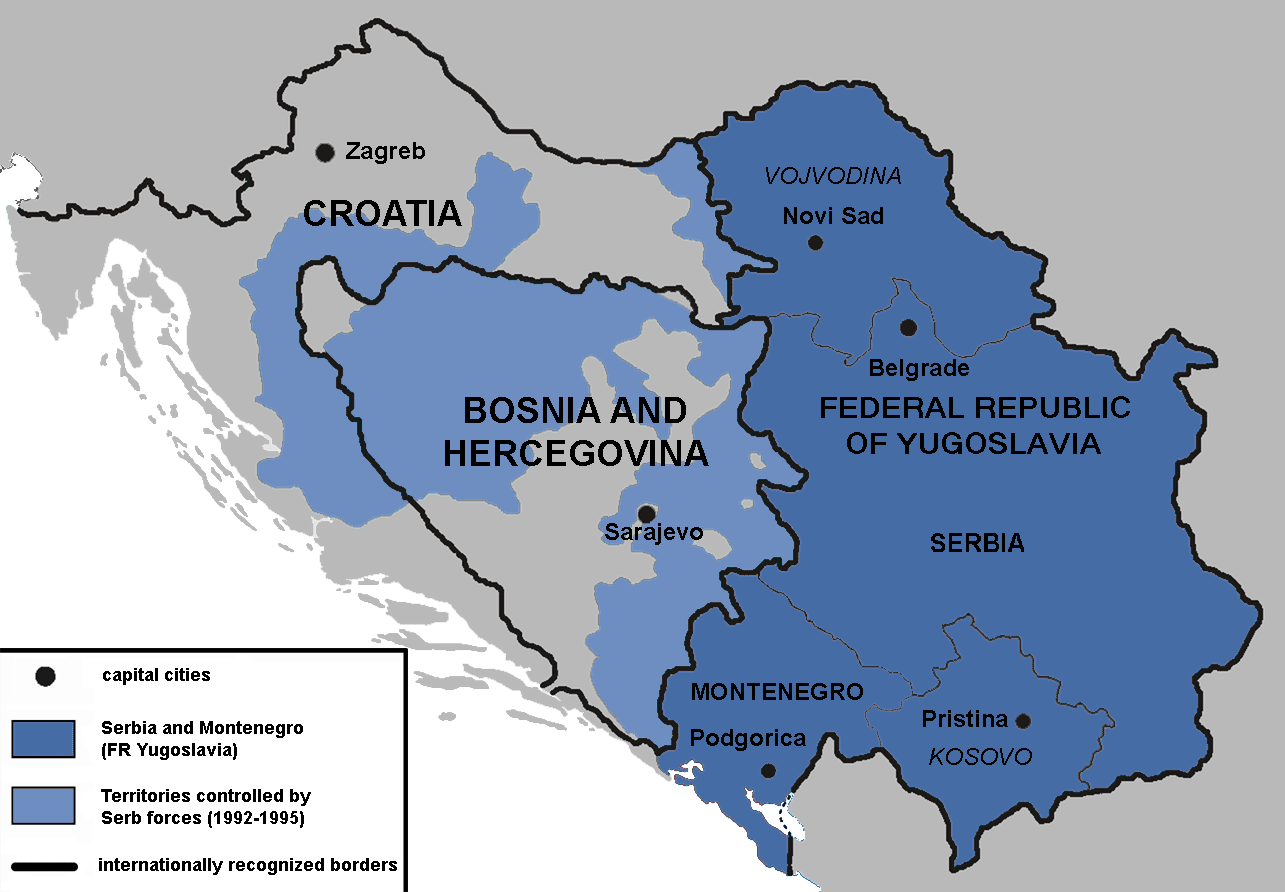
Serbian War Crimes In The Yugoslav Wars
Serbia was involved in the Yugoslav Wars, which took place between 1991 and 1999—the war in Slovenia, the war in Croatia, the war in Bosnia and in Kosovo. From 1991 to 1997, Slobodan Milošević was the President of Serbia. Serbia was part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY). The International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia (ICTY) has established that Milošević was in control of Serb forces in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia during the wars which were fought there from 1991 to 1995. Accused of supporting Serb rebels in Croatia and Bosnia, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was suspended from most international organisations and institutions, and economic and political sanctions were imposed, which resulted in economic disaster and massive emigration from the country. The NATO bombing of Yugoslavia during the Kosovo War significantly damaged the country's infrastructure and economy. After the Yugoslav Wars, Serbia became home to the highest number of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia In The Yugoslav Wars
Serbia was involved in the Yugoslav Wars, which took place between 1991 and 1999—the war in Slovenia, the war in Croatia, the war in Bosnia and in Kosovo. From 1991 to 1997, Slobodan Milošević was the President of Serbia. Serbia was part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY). The International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia (ICTY) has established that Milošević was in control of Serb forces in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia during the wars which were fought there from 1991 to 1995. Accused of supporting Serb rebels in Croatia and Bosnia, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was suspended from most international organisations and institutions, and economic and political sanctions were imposed, which resulted in economic disaster and massive emigration from the country. The NATO bombing of Yugoslavia during the Kosovo War significantly damaged the country's infrastructure and economy. After the Yugoslav Wars, Serbia became home to the highest number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer, it also includes indirect methods aimed at forced migration by coercing the victim group to flee and preventing its return, such as murder, rape, and property destruction. It constitutes a crime against humanity and may also fall under the Genocide Convention, even as ''ethnic cleansing'' has no legal definition under international criminal law. Many instances of ethnic cleansing have occurred throughout history; the term was first used by the perpetrators as a euphemism during the Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s. Since then, the term has gained widespread acceptance due to journalism and the media's heightened use of the term in its generic meaning. Etymology An antecedent to the term is the Greek word (; lit. "enslavement"), which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1997 Serbian General Election
General elections were held in the Republic of Serbia on 21 September 1997 to elect the President and National Assembly. With no presidential candidate receiving over 50% of the vote in the first round, a second round was held on 5 October.Serbian Presidential Elections Since 1990 Balkan Insight, 1 April 2012 Running on a platform of and neoliberal economic reforms, of the |
1996–1997 Protests In Serbia
In the winter of 1996–1997, university students and Serbian opposition parties organized a series of peaceful protests in the Republic of Serbia (then part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia) in response to electoral fraud attempted by the Socialist Party of Serbia of President Slobodan Milošević after the 1996 local elections. During the course of the rallies, students held their protests separately from the citizens' ones, led by opposition then gathered in coalition ''Zajedno'' (Together). The students' protest lasted until 22 March 1997, with additional requests of replacing the management of University of Belgrade and return of the university autonomy. The protests started November 17, 1996 in Niš where thousands of opposition supporters gathered to protest against election fraud. Belgrade University students joined on November 19, 1996 and protests lasted even after February 11, 1997, when Milošević signed the "lex specialis", which accepted the opposition victory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1996 Serbian Local Elections
Local elections were held in Serbia over two rounds on 3 November and 17 November 1996, concurrently with the 1996 Vojvodina provincial election; the first day of voting also coincided with the 1996 Yugoslavian parliamentary election and the 1996 Montenegrin parliamentary election. This was the third local electoral cycle held while Serbia was a member of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the last time that Serbia oversaw local elections throughout Kosovo and Metohija until its parallel elections in 2008. Delegates to city and municipal assemblies were elected in single-member constituencies; if no candidate secured a majority in the first round of voting, the top two candidates would face each other in a runoff vote in the second round. Campaign and aftermath The elections took place during the time of Slobodan Milošević's authoritarian rule as president of Serbia. In most major jurisdictions, Milošević's Socialist Party of Serbia (''Socijalistička partija Srbije'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propaganda During The Yugoslav Wars
During the Yugoslav Wars (1991–2001), propaganda was widely used in the media of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, of Croatia and (to an extent) of Bosnia. Throughout the conflicts, all sides used propaganda as a tool. The media in the former Yugoslavia was divided along ethnic lines, and only a few independent voices countered the nationalist rhetoric. Propaganda was prominently used by Slobodan Milošević and his regime in Serbia. He began his efforts to control the media in the late 1980s, and by 1991, he had successfully consolidated Radio Television of Serbia and the other Serbian media, which largely became a mouthpiece for his regime. Part of the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia's indictment against Milošević charged him with having used the media for propaganda purposes. In Croatia, the media included the state's main public broadcaster, Croatian Radio and Television, and it largely came under the control of Franjo Tuđman and his par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desertion
Desertion is the abandonment of a military duty or post without permission (a pass, liberty or leave) and is done with the intention of not returning. This contrasts with unauthorized absence (UA) or absence without leave (AWOL ), which are temporary forms of absence. Desertion versus absence without leave In the United States Army, United States Air Force, British Armed Forces, Australian Defence Force, New Zealand Defence Force, Singapore Armed Forces and Canadian Armed Forces, military personnel will become AWOL if absent from their post without a valid pass, liberty or leave. The United States Marine Corps, United States Navy, and United States Coast Guard generally refer to this as unauthorized absence. Personnel are dropped from their unit rolls after thirty days and then listed as ''deserters''; however, as a matter of U.S. military law, desertion is not measured by time away from the unit, but rather: * by leaving or remaining absent from their unit, organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-war Movement
An anti-war movement (also ''antiwar'') is a social movement, usually in opposition to a particular nation's decision to start or carry on an armed conflict, unconditional of a maybe-existing just cause. The term anti-war can also refer to pacifism, which is the opposition to all use of military force during conflicts, or to anti-war books, paintings, and other works of art. Some activists distinguish between anti-war movements and peace movements. Anti-war activists work through protest and other grassroots means to attempt to pressure a government (or governments) to put an end to a particular war or conflict or to prevent it in advance. History American Revolutionary War Substantial opposition to British war intervention in America led the British House of Commons on 27 February 1783 to vote against further war in America, paving the way for the Second Rockingham ministry and the Peace of Paris. Antebellum United States Substantial antiwar sentiment developed in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslav People's Army
The Yugoslav People's Army (abbreviated as JNA/; Macedonian and sr-Cyrl-Latn, Југословенска народна армија, Jugoslovenska narodna armija; Croatian and bs, Jugoslavenska narodna armija; sl, Jugoslovanska ljudska armada, JLA), also called the Yugoslav National Army, was the military of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and its antecedents from 1945 to 1992. Origins The origins of the JNA started during the Yugoslav Partisans of World War II. As a predecessor of the JNA, the People's Liberation Army of Yugoslavia (NOVJ) was formed as a part of the anti-fascist People's Liberation War of Yugoslavia in the Bosnian town of Rudo on 22 December 1941. After the Yugoslav Partisans liberated the country from the Axis Powers, that date was officially celebrated as the "Day of the Army" in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFR Yugoslavia). In March 1945, the NOVJ was renamed the "Yugoslav Army" ("''Jugoslavenska/Jugoslovenska Armija' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
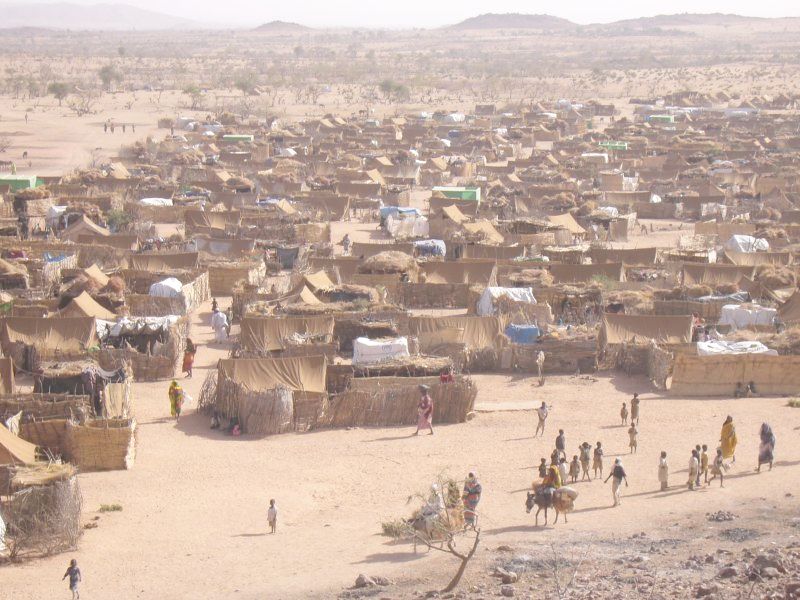
Internally Displaced Person
An internally displaced person (IDP) is someone who is forced to leave their home but who remains within their country's borders. They are often referred to as refugees, although they do not fall within the legal definitions of a refugee. At the end of 2014, it was estimated there were 38.2 million IDPs worldwide, the highest level since 1989, the first year for which global statistics on IDPs are available. As of 3 May 2022 the countries with the largest IDP populations were Ukraine (8 million), Syria (7.6 million), Ethiopia (5.5 million), the Democratic Republic of the Congo (5.2 million), Colombia (4.9 million), Yemen (4.3 million), Afghanistan (3.8 million), Iraq (3.6 million), Sudan (2.2 million), South Sudan (1.9 million), Pakistan (1.4 million), Nigeria (1.2 million) and Somalia (1.1 million). The United Nations and the UNHCR support monitoring and analysis of worldwide IDPs through the Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre. Definition Whereas 'refugee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.FAQ: Who is a refugee? ''www.unhcr.org'', accessed 22 June 2021 Such a person may be called an until granted by the contracting state or the |