|
Septimal Diesis
In music, septimal diesis (or slendro diesis) is an Interval (music), interval with the ratio of 49:48 , which is the difference between the septimal whole tone and the septimal minor third. It is about 35.7 cents wide, which is narrower than a quarter-tone but wider than the septimal comma. It may also be the ratio 36:35, or 48.77 cents. In equal temperament In 12 equal temperament this interval is not tempered out; the 7-limit, septimal whole tone and septimal minor third are replaced by the normal whole tone and minor third. This makes the diesis a semitone, about twice its "correct" size. The septimal diesis is musical temperament, tempered out by a number of equally tempered tuning systems, including 19 equal temperament, 19-ET, quarter tone, 24-ET and 29 equal temperament, 29-ET; these tunings do not distinguish between the septimal whole tone and septimal minor third. It is not tempered out however by 22 equal temperament, 22-ET or 31 equal temperament, 31-ET (or indeed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
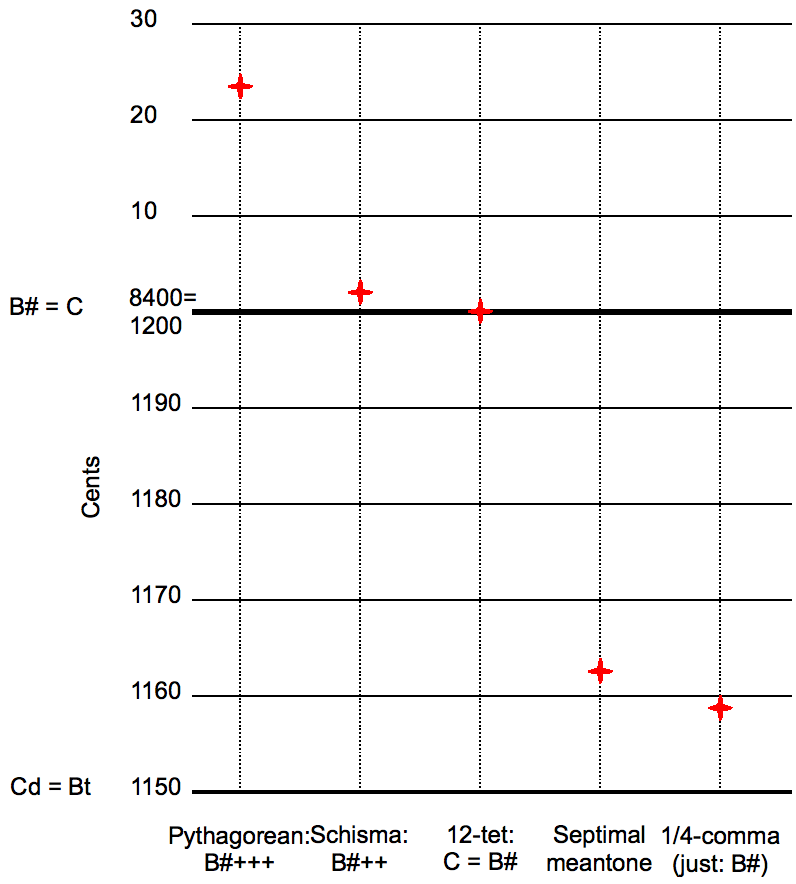
Septimal Diesis On C
Septimal may refer to: *Septimal chromatic semitone, the interval 21:20, about 84.47 cents *Septimal comma, a small musical interval in just intonation divisible by 7 *Septimal diatonic semitone, the interval 15:14, about 119.44 cents *Septimal diesis, an interval with the ratio of 49:48, about 38.71 cents *Septimal kleisma, an interval of approximately 7.7 cents *Septimal major third, the musical interval with a 9:7 ratio of frequencies *Septimal meantone temperament, the tempering of 7-limit musical intervals by a meantone temperament tuning *Septimal minor third, the musical interval exactly or approximately equal to a 7/6 ratio of frequencies *Septimal quarter tone, an interval with the ratio of 36:35, about 48.77 cents *Septimal semicomma, an interval with the ratio 126/125, about 13.79 cents *Septimal sixth-tone (or jubilisma), an interval with the ratio of 50:49, about 34.98 cents *Septimal tritone, the interval 7:5, about 582.51 cents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Temperament
In musical tuning, a temperament is a tuning system that slightly compromises the pure intervals of just intonation to meet other requirements. Most modern Western musical instruments are tuned in the equal temperament system. Tempering is the process of altering the size of an interval by making it narrower or wider than pure. "Any plan that describes the adjustments to the sizes of some or all of the twelve fifth intervals in the circle of fifths so that they accommodate pure octaves and produce certain sizes of major thirds is called a ''temperament''." Temperament is especially important for keyboard instruments, which typically allow a player to play only the pitches assigned to the various keys, and lack any way to alter pitch of a note in performance. Historically, the use of just intonation, Pythagorean tuning and meantone temperament meant that such instruments could sound "in tune" in one key, or some keys, but would then have more dissonance in other keys. In the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commas (music)
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. Some typefaces render it as a small line, slightly curved or straight, but inclined from the vertical; others give it the appearance of a miniature filled-in figure placed on the baseline. In many typefaces it is the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark . The comma is used in many contexts and languages, mainly to separate parts of a sentence such as clauses, and items in lists mainly when there are three or more items listed. The word ''comma'' comes from the Greek (), which originally meant a cut-off piece, specifically in grammar, a short clause. A comma-shaped mark is used as a diacritic in several writing systems and is considered distinct from the cedilla. In Byzantine and modern copies of Ancient Greek, the " rough" and "smooth breathings" () appear above the letter. In Latvian, Romanian, and Livonian, the comma diacritic appears below the letter, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesis
In classical music from Western culture, a diesis ( or enharmonic diesis, plural dieses ( , or "difference"; Greek: "leak" or "escape" is either an accidental (see sharp), or a very small musical interval, usually defined as the difference between an octave (in the ratio 2:1) and three justly tuned major thirds (tuned in the ratio 5:4), equal to 128:125 or about 41.06 cents. In 12-tone equal temperament (on a piano for example) three major thirds in a row equal an octave, but three justly-tuned major thirds fall quite a bit narrow of an octave, and the diesis describes the amount by which they are short. For instance, an octave (2:1) spans from C to C′, and three justly tuned major thirds (5:4) span from C to B (namely, from C, to E, to G, to B). The difference between C-C′ (2:1) and C-B (125:64) is the diesis (128:125). Notice that this coincides with the interval between B and C′, also called a diminished second. As a comma, the above-mentioned 128:125 r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
31 Equal Temperament
In music, 31 equal temperament, which can also be abbreviated (31 tone ) or (equal division of the octave), also known as tricesimoprimal, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into 31 equally-proportioned steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or 38.71 cents (). is a very good approximation of quarter-comma meantone temperament. More generally, it is a regular diatonic tuning in which the tempered perfect fifth is equal to 696.77 cents, as shown in Figure 1. On an isomorphic keyboard, the fingering of music composed in is precisely the same as it is in any other syntonic tuning (such as so long as the notes are spelled properly—that is, with no assumption of enharmonicity. History and use Division of the octave into 31 steps arose naturally out of Renaissance music theory; the lesser diesis – the ratio of an octave to three major thirds, 128:125 or 41.06 cents – was app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
22 Equal Temperament
In music, 22 equal temperament, called 22-TET, 22- EDO, or 22-ET, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into 22 equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or 54.55 cents (). When composing with 22-ET, one needs to take into account a variety of considerations. Considering the 5-limit, there is a difference between 3 fifths and the sum of 1 fourth and 1 major third. It means that, starting from C, there are two A's—one 16 steps and one 17 steps away. There is also a difference between a major tone and a minor tone. In C major, the second note (D) will be 4 steps away. However, in A minor, where A is 6 steps below C, the fourth note (D) will be 9 steps above A, so 3 steps above C. So when switching from C major to A minor, one needs to slightly change the D note. These discrepancies arise because, unlike 12-ET, 22-ET does not temper out the syntonic comma of 81/80, but instead exaggerates its size by mapping it to one ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
29 Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system that approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same. This system yields pitch steps perceived as equal in size, due to the logarithmic changes in pitch frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been 12 equal temperament (also known as ''12 tone equal temperament'', ' or ', informally abbreviated as ''12 equal''), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the 12th root of 2, (\sqrt 2/math> ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western countries the term ''equal temperament'', without qualification, generally means '. In modern times, is usually tuned relative to a stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Tone
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide (orally, or logarithmically) as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, and have 24 different pitches. Quarter tones have their roots in the music of the Middle East and more specifically in Persian traditional music. However, the first evidenced proposal of the equally-tempered quarter tone scale, or 24 equal temperament, was made by 19th-century music theorists Heinrich Richter in 1823 Julian Rushton, "Quarter-Tone", ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie and John Tyrrell (London: Macmillan, 2001). and Mikhail Mishaqa about 1840. Composers who have written music using this scale include: Pierre Boulez, Julián Carrillo, Mildred Couper, George Enescu, Alberto Ginastera, Gérard Grisey, Alois Hába, Ljubica Marić, Charles Ives, Tristan Murail, Kr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19 Equal Temperament
In music, 19 equal temperament, called 19 TET, 19 EDO ("Equal Division of the Octave"), 19-ED2 ("Equal Division of 2:1) or 19 Equal temperament, ET, is the musical temperament, tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into 19 equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or 63.16 cent (music), cents (). The fact that traditional western music maps unambiguously onto this scale (unless it presupposes 12-EDO enharmonic equivalences) makes it easier to perform such music in this tuning than in many other tunings. 19 EDO is the tuning of the syntonic temperament in which the tempered perfect fifth is equal to 694.737 cents, as shown in Figure 1 (look for the label "19 TET"). On an isomorphic keyboard, the fingering of music composed in 19 EDO is precisely the same as it is in any other syntonic tuning (such as 12-TET, 12 EDO), so long as the notes are "spelled properly" – that is, with no assumption t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7-limit
7-limit or septimal tunings and intervals are musical instrument tunings that have a limit of seven: the largest prime factor contained in the interval ratios between pitches is seven. Thus, for example, 50:49 is a 7-limit interval, but 14:11 is not. For example, the greater just minor seventh, 9:5 () is a 5-limit ratio, the harmonic seventh has the ratio 7:4 and is thus a septimal interval. Similarly, the septimal chromatic semitone, 21:20, is a septimal interval as 21÷7=3. The harmonic seventh is used in the barbershop seventh chord and music. () Compositions with septimal tunings include La Monte Young's ''The Well-Tuned Piano'', Ben Johnston's String Quartet No. 4, Lou Harrison's ''Incidental Music for Corneille's Cinna'', and Michael Harrison's ''Revelation: Music in Pure Intonation''. The Great Highland bagpipe is tuned to a ten-note seven-limit scale: 1:1, 9:8, 5:4, 4:3, 27:20, 3:2, 5:3, 7:4, 16:9, 9:5. In the 2nd century Ptolemy described the septima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all human societies. Definitions of music vary widely in substance and approach. While scholars agree that music is defined by a small number of elements of music, specific elements, there is no consensus as to what these necessary elements are. Music is often characterized as a highly versatile medium for expressing human creativity. Diverse activities are involved in the creation of music, and are often divided into categories of musical composition, composition, musical improvisation, improvisation, and performance. Music may be performed using a wide variety of musical instruments, including the human voice. It can also be composed, sequenced, or otherwise produced to be indirectly played mechanically or electronically, such as via a music box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12 Equal Temperament
12 equal temperament (12-ET) is the musical system that divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are Equal temperament, equally tempered (equally spaced) on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the Twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2 (\sqrt[12] ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. Twelve-tone equal temperament is the most widespread system in music today. It has been the predominant tuning system of Western music, starting with classical music, since the 18th century, and Europe almost exclusively used approximations of it for millennia before that. It has also been used in other cultures. In modern times, 12-ET is usually tuned relative to a standard pitch of 440 Hz, called A440 (pitch standard), A440, meaning one note, A (musical note), A4 (the A in the 4th octave of a typical 88-key piano), is tuned to 440 hertz and all other notes are defined as some multiple of semitones apart from it, ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |