|
Sentence Extraction
Sentence extraction is a technique used for automatic summarization of a text. In this shallow approach, statistical heuristics are used to identify the most salient sentences of a text. Sentence extraction is a low-cost approach compared to more knowledge-intensive deeper approaches which require additional knowledge bases such as ontologies or linguistic knowledge. In short, sentence extraction works as a filter that allows only meaningful sentences to pass. The major downside of applying sentence-extraction techniques to the task of summarization is the loss of coherence in the resulting summary. Nevertheless, sentence extraction summaries can give valuable clues to the main points of a document and are frequently sufficiently intelligible to human readers. Procedure Usually, a combination of heuristics is used to determine the most important sentences within the document. Each heuristic assigns a (positive or negative) score to the sentence. After all heuristics have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Summarization
Automatic summarization is the process of shortening a set of data computationally, to create a subset (a summary) that represents the most important or relevant information within the original content. Artificial intelligence algorithms are commonly developed and employed to achieve this, specialized for different types of data. Text summarization is usually implemented by natural language processing methods, designed to locate the most informative sentences in a given document. On the other hand, visual content can be summarized using computer vision algorithms. Image summarization is the subject of ongoing research; existing approaches typically attempt to display the most representative images from a given image collection, or generate a video that only includes the most important content from the entire collection. Video summarization algorithms identify and extract from the original video content the most important frames (''key-frames''), and/or the most important video seg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heuristic (computer Science)
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', ''Heuristic (psychology), mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a Pragmatism, pragmatic method that is not fully Mathematical optimisation, optimized, perfected, or Rationality, rationalized, but is nevertheless "good enough" as an approximation or attribute substitution. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of Decision-making, making a decision. Context Gigerenzer & Gaissmaier (2011) state that Set (mathematics), sub-sets of ''strategy'' include heuristics, regression analysis, and Bayesian inference. Heuristics are strategies based on rules to generate optimal decisions, like the anchoring effect and utility maximization problem. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontology (computer Science)
In information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definitions of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, or entities that pertain to one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of terms and relational expressions that represent the entities in that subject area. The field which studies ontologies so conceived is sometimes referred to as ''applied ontology''. Every academic discipline or field, in creating its terminology, thereby lays the groundwork for an ontology. Each uses ontological assumptions to frame explicit theories, research and applications. Improved ontologies may improve problem solving within that domain, interoperability of data systems, and discoverability of data. Translating research papers within every field is a problem made easier when experts from different countries mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence (linguistics)
Coherence in linguistics is what makes a text semantically meaningful. It is especially dealt with in text linguistics. Coherence is achieved through syntactic features such as the use of deictic, anaphoric and cataphoric elements or a logical tense structure, and semantic features such as presuppositions and implications connected to general world knowledge. Robert De Beaugrande and Wolfgang U. Dressler define coherence as a "continuity of senses" and "the mutual access and relevance within a configuration of concepts and relations". Thereby a textual world is created that does not have to comply to the real world. But within this textual world the arguments also have to be connected logically so that the reader/hearer can produce coherence. "Continuity of senses" implies a link between cohesion and the theory of Schemata initially proposed by F. C. Bartlett in 1932 which creates further implications for the notion of a "text". Schemata, subsequently distinguished into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Peter Luhn
Hans Peter Luhn (July 1, 1896 – August 19, 1964) was a German-American researcher in the field of computer science and Library & Information Science for IBM, and creator of the Luhn algorithm, KWIC (Key Words In Context) indexing, and selective dissemination of information ("SDI"). His inventions have found applications in diverse areas like computer science, the textile industry, linguistics, and information science. He was awarded over 80 patents. He created one of the earliest practical hash functions in the 1950s. Early life and education Luhn was born in Barmen, Germany (now part of Wuppertal) on July 1, 1896. After he completed secondary school, Luhn moved to Switzerland to learn the printing trade so he could join the family business. His career in printing was halted by his service as a communications officer in the German Army during World War I. Career After the war, Luhn entered the textile field, which eventually led him to the United States, where he inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Journal
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is a publicly traded company and one of the 30 companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. IBM is the largest industrial research organization in the world, with 19 research facilities across a dozen countries; for 29 consecutive years, from 1993 to 2021, it held the record for most annual U.S. patents generated by a business. IBM was founded in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR), a holding company of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems. It was renamed "International Business Machines" in 1924 and soon became the leading manufacturer of punch-card tabulating systems. During the 1960s and 1970s, the IBM mainframe, exemplified by the System/360 and its successors, was the world's dominant computing platform, with the company p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The ACM
The ''Journal of the ACM'' (''JACM'') is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering computer science in general, especially theoretical aspects. It is an official journal of the Association for Computing Machinery. Its current editor-in-chief is Venkatesan Guruswami. The journal was established in 1954 and "computer scientists universally hold the ''Journal of the ACM'' in high esteem". See also * ''Communications of the ACM ''Communications of the ACM'' (''CACM'') is the monthly journal of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). History It was established in 1958, with Saul Rosen as its first managing editor. It is sent to all ACM members. Articles are i ...'' References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Journal Of The Acm Academic journals established in 1954 Computer science journals Association for Computing Machinery academic journals Bimonthly journals English-language journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
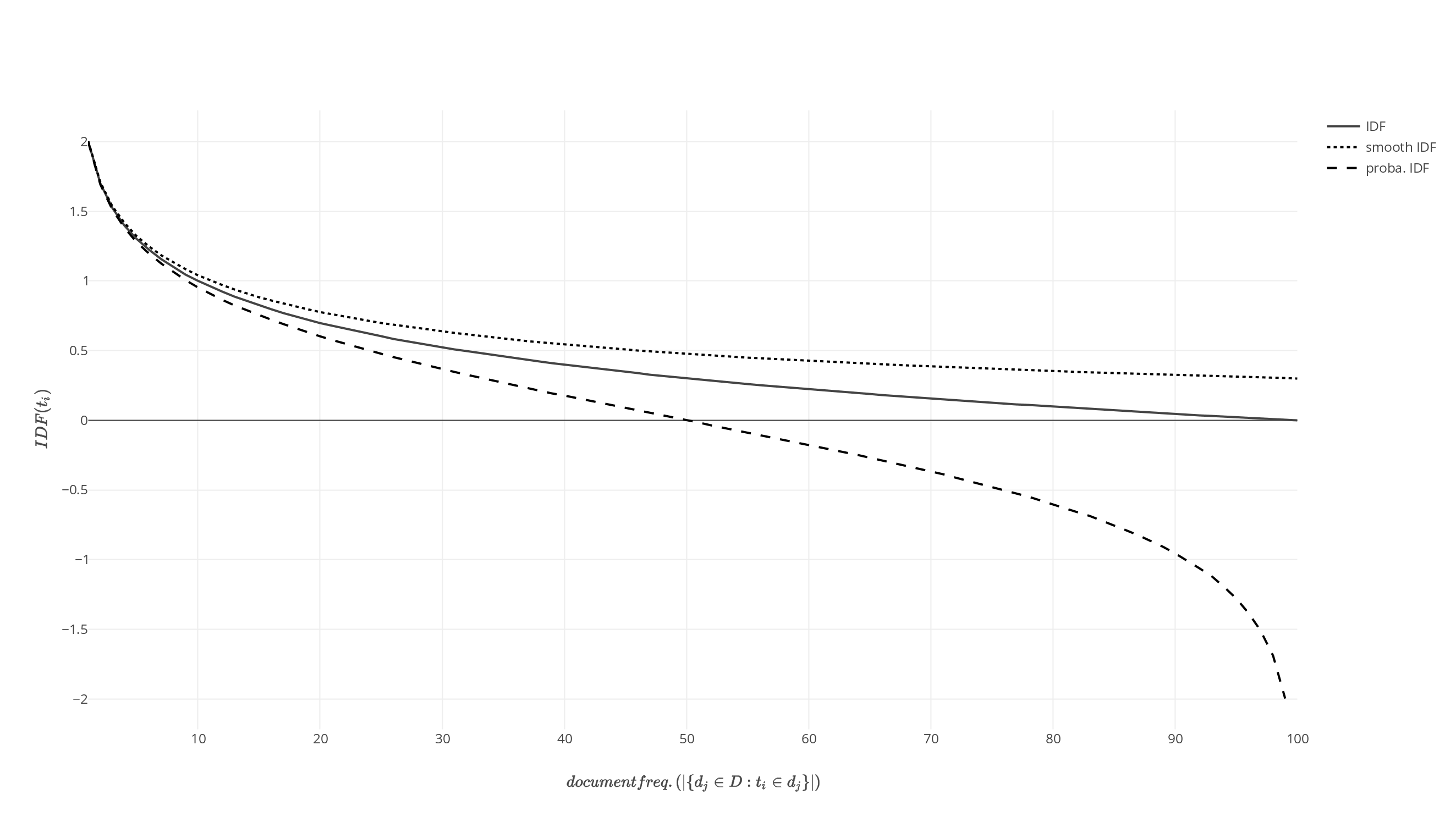
Tf–idf
In information retrieval, tf–idf (term frequency–inverse document frequency, TF*IDF, TFIDF, TF–IDF, or Tf–idf) is a measure of importance of a word to a document in a collection or Text corpus, corpus, adjusted for the fact that some words appear more frequently in general. Like the bag-of-words model, it models a document as a multiset of words, without word order. It is a refinement over the simple bag-of-words model, by allowing the weight of words to depend on the rest of the corpus. It was often used as a weighting factor in searches of information retrieval, text mining, and user modeling. A survey conducted in 2015 showed that 83% of text-based recommender systems in digital libraries used tf–idf. Variations of the tf–idf weighting scheme were often used by search engines as a central tool in scoring and ranking a document's Relevance (information retrieval), relevance given a user Information retrieval, query. One of the simplest ranking functions is computed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the task of identifying and retrieving information system resources that are relevant to an Information needs, information need. The information need can be specified in the form of a search query. In the case of document retrieval, queries can be based on full-text search, full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Automated information retrieval systems are used to reduce what has been called information overload. An IR system is a software system that provides access to books, journals and other documents; it also stores and manages those documents. Web search engines are the most visible IR applications. Overview An information retrieval process begins when a user enters a query into the sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentence Boundary Disambiguation
Sentence boundary disambiguation (SBD), also known as sentence breaking, sentence boundary detection, and sentence segmentation, is the problem in natural language processing of deciding where sentences begin and end. Natural language processing tools often require their input to be divided into sentences; however, sentence boundary identification can be challenging due to the potential ambiguity of punctuation marks. In written English, a period may indicate the end of a sentence, or may denote an abbreviation, a decimal point, an ellipsis, or an email address, among other possibilities. About 47% of the periods in ''The Wall Street Journal'' corpus denote abbreviations. Question marks and exclamation marks can be similarly ambiguous due to use in emoticons, source code, and slang. Some languages including Japanese and Chinese have unambiguous sentence-ending markers. Strategies The standard 'vanilla' approach to locate the end of a sentence: :(a) If it is a period, it ends a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Segmentation
Text segmentation is the process of dividing written text into meaningful units, such as words, sentences, or topics. The term applies both to mental processes used by humans when reading text, and to artificial processes implemented in computers, which are the subject of natural language processing. The problem is non-trivial, because while some written languages have explicit word boundary markers, such as the word spaces of written English and the distinctive initial, medial and final letter shapes of Arabic, such signals are sometimes ambiguous and not present in all written languages. Compare speech segmentation, the process of dividing speech into linguistically meaningful portions. Segmentation problems Word segmentation Word segmentation is the problem of dividing a string of written language into its component words. In English and many other languages using some form of the Latin alphabet, the space is a good approximation of a word divider (word delimiter), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |