|
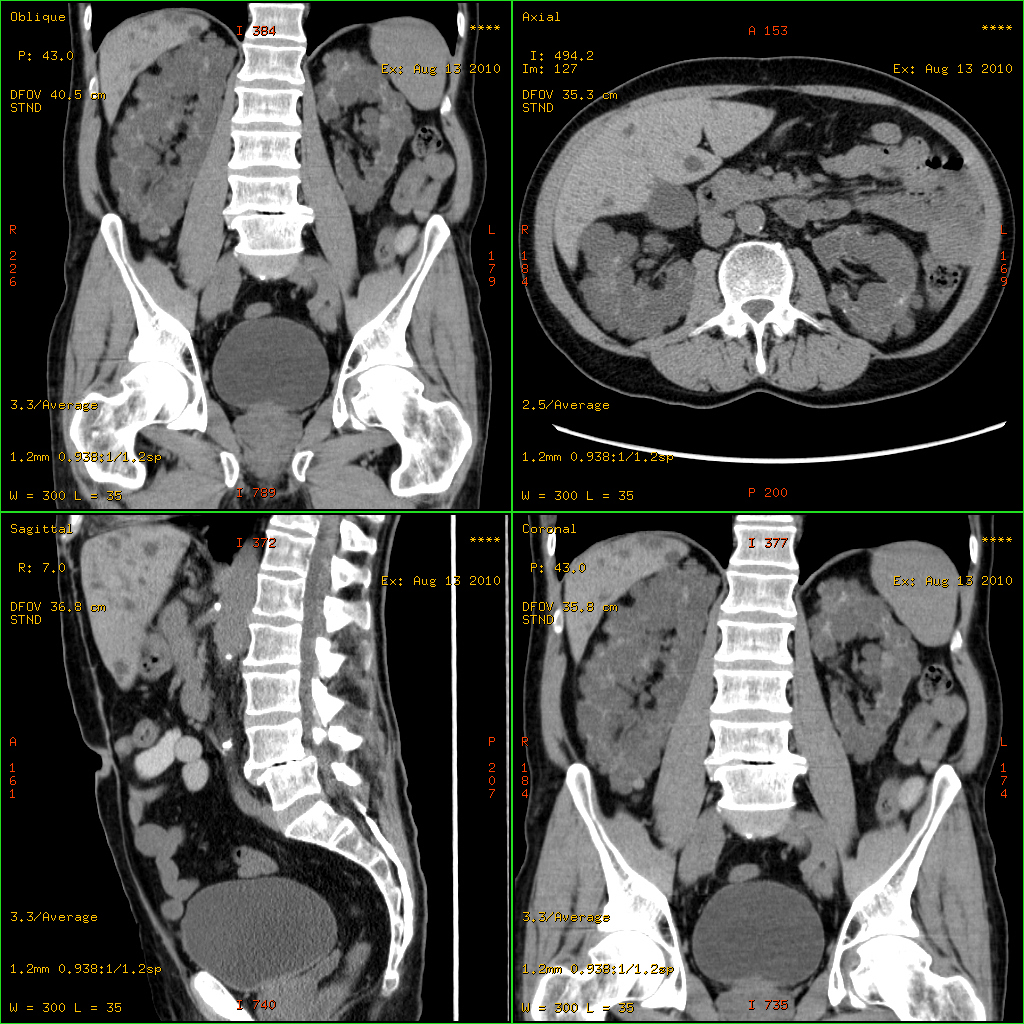
Senior–Løken Syndrome
Senior–Løken syndrome is a congenital eye disorder, first characterized in 1961. It is a rare, ciliopathic, autosomal recessive disorder characterized by juvenile nephronophthis and progressive eye disease.. Genetics Genes involved include: Pathophysiology The cause of Senior–Løken syndrome type 5 has been identified to mutation in the NPHP1 gene which adversely affects the protein formation mechanism of the cilia.. Relation to other rare genetic disorders Recent findings in genetic research have suggested that a large number of genetic disorders, both genetic syndromes and genetic diseases, that were not previously identified in the medical literature as related, may be, in fact, highly related in the genetypical root cause of the widely varying, phenotypically-observed disorders. Such diseases are becoming known as ciliopathies. Known ciliopathies include primary ciliary dyskinesia, Bardet–Biedl syndrome, polycystic kidney and liver disease, nephronopht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Diseases
A rare disease is any disease that affects a small percentage of the population. In some parts of the world, an orphan disease is a rare disease whose rarity means there is a lack of a market large enough to gain support and resources for discovering treatments for it, except by the government granting economically advantageous conditions to creating and selling such treatments. Orphan drugs are ones so created or sold. Most rare diseases are genetic and thus are present throughout the person's entire life, even if symptoms do not immediately appear. Many rare diseases appear early in life, and about 30% of children with rare diseases will die before reaching their fifth birthdays. With only four diagnosed patients in 27 years, ribose-5-phosphate isomerase deficiency is considered the rarest known genetic disease. No single cut-off number has been agreed upon for which a disease is considered rare. A disease may be considered rare in one part of the world, or in a particular gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY, XXY, XXX, XXXX, XXXXX or XXYY, among other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes still contain sexual determination genes even though they are not sex chromosomes. For example, the SRY gene on the Y chromosome e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorders
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinopathy
Retinopathy is any damage to the retina of the eyes, which may cause vision impairment. Retinopathy often refers to retinal vascular disease, or damage to the retina caused by abnormal blood flow. Age-related macular degeneration is technically included under the umbrella term retinopathy but is often discussed as a separate entity. Retinopathy, or retinal vascular disease, can be broadly categorized into proliferative and non-proliferative types. Frequently, retinopathy is an ocular manifestation of systemic disease as seen in diabetes or hypertension. Diabetes is the most common cause of retinopathy in the U.S. as of 2008. Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in working-aged people. It accounts for about 5% of blindness worldwide and is designated a priority eye disease by the World Health Organization. Signs and symptoms Many people often do not have symptoms until very late in their disease course. Patients often become symptomatic when there is irreversible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meckel–Gruber Syndrome
Meckel-Gruber syndrome is a rare, lethal ciliopathic genetic disorder, characterized by renal cystic dysplasia, central nervous system malformations (occipital encephalocele), polydactyly (postaxial), hepatic developmental defects, and pulmonary hypoplasia due to oligohydramnios. Meckel–Gruber syndrome is named for Johann Meckel and Georg Gruber. Pathophysiology Meckel–Gruber syndrome (MKS) is an autosomal recessive lethal malformation. Recently, two MKS genes, MKS1 and MKS3, have been identified. A study done recently has described the cellular, sub-cellular and functional characterization of the novel proteins, MKS1 and meckelin, encoded by these genes. The malfunction of this protein production is mainly responsible for this lethal disorder. Relation to other rare genetic disorders Recent findings in genetic research have suggested that a large number of genetic disorders, both genetic syndromes and genetic diseases, that were not previously identified in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alström Syndrome
Alström syndrome (AS), also called Alström–Hallgren syndrome, is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterised by childhood obesity and multiple organ dysfunction. Symptoms include early-onset type 2 diabetes, cone-rod dystrophy resulting in blindness, sensorineural hearing loss and dilated cardiomyopathy. Endocrine disorders typically also occur, such as hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism and hypothyroidism, as well as acanthosis nigricans resulting from hyperinsulinemia. Developmental delay is seen in almost half of people with Alström syndrome. It is caused by mutations in the gene ''ALMS1'', which is involved in the formation of cellular Cilium, cilia, making Alström syndrome a ciliopathy. At least 239 disease-causing mutations in ''ALMS1'' have been described . Alström syndrome is sometimes confused with Bardet–Biedl syndrome, another ciliopathy which has similar symptoms, but Bardet–Biedl syndrome tends to have later onset in its symptoms, includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystic Liver Disease
Polycystic liver disease (PLD) usually describes the presence of multiple cysts scattered throughout normal liver tissue. PLD is commonly seen in association with autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease, with a prevalence of 1 in 400 to 1000, and accounts for 8–10% of all cases of end-stage renal disease. The much rarer autosomal-dominant polycystic liver disease will progress without any kidney involvement. Presentation Pathophysiology Associations with ''PRKCSH'' and ''SEC63'' have been described. Polycystic liver disease comes in two forms: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (with kidney cysts) and autosomal dominant polycystic liver disease (liver cysts only). Diagnosis Most patients with PLD are asymptomatic with simple cysts found following routine investigations. After confirming the presence of cysts in the liver, laboratory tests may be ordered to check for liver function including bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase, and prothrombin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD or PCKD, also known as polycystic kidney syndrome) is a genetic disorder in which the renal tubules become structurally abnormal, resulting in the development and growth of multiple cysts within the kidney. These cysts may begin to develop in utero, in infancy, in childhood, or in adulthood. Cysts are non-functioning tubules filled with fluid pumped into them, which range in size from microscopic to enormous, crushing adjacent normal tubules and eventually rendering them non-functional as well. PKD is caused by abnormal genes that produce a specific abnormal protein; this protein has an adverse effect on tubule development. PKD is a general term for two types, each having their own pathology and genetic cause: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). The abnormal gene exists in all cells in the body; as a result, cysts may occur in the liver, seminal vesicles, and pancreas. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bardet–Biedl Syndrome
Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a ciliopathic human genetic disorder that produces many effects and affects many body systems. It is characterized by rod/cone dystrophy, polydactyly, central obesity, hypogonadism, and kidney dysfunction in some cases. Historically, slower mental processing has also been considered a principal symptom but is now not regarded as such. Signs and symptoms Bardet–Biedl syndrome is a pleiotropic disorder with variable expressivity and a wide range of clinical variability observed both within and between families. The most common clinical features are rod–cone dystrophy, with childhood-onset night-blindness followed by increasing visual loss; postaxial polydactyly; truncal obesity that manifests during infancy and remains problematic throughout adulthood; varying degrees of learning disabilities; male hypogenitalism and complex female genitourinary malformations; and renal dysfunction, a major cause of morbidity and mortality. There is a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) is a rare, autosomal recessive genetic ciliopathy, that causes defects in the action of cilia lining the upper and lower respiratory tract, sinuses, Eustachian tube, middle ear, Fallopian tube, and flagella of sperm cells. The alternative name of "immotile ciliary syndrome" is no longer favored as the cilia do have movement, but are merely inefficient or unsynchronized. When accompanied by situs inversus the condition is known as Kartagener syndrome. Respiratory epithelial motile cilia, which resemble microscopic "hairs" (although structurally and biologically unrelated to hair), are complex organelles that beat synchronously in the respiratory tract, moving mucus toward the throat. Normally, cilia beat 7 to 22 times per second, and any impairment can result in poor mucociliary clearance, with subsequent upper and lower respiratory infection. Cilia also are involved in other biological processes (such as nitric oxide production), currently th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |