|
Semantic Spectrum
The semantic spectrum (sometimes referred to as the ontology spectrum or the smart data continuum or semantic precision) is a series of increasingly precise or rather semantically expressive definitions for data elements in knowledge representations, especially for machine use. At the low end of the spectrum is a simple binding of a single word or phrase and its definition. At the high end is a full ontology that specifies relationships between data elements using precise URIs for relationships and properties. With increased specificity comes increased precision and the ability to use tools to automatically integrate systems but also increased cost to build and maintain a metadata registry. Some steps in the semantic spectrum include the following: # glossary: A simple list of terms and their definitions. A glossary focuses on creating a complete list of the terminology of domain-specific terms and acronyms. It is useful for creating clear and unambiguous definitions for ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy, linguistics and computer science. History In English, the study of meaning in language has been known by many names that involve the Ancient Greek word (''sema'', "sign, mark, token"). In 1690, a Greek rendering of the term ''semiotics'', the interpretation of signs and symbols, finds an early allusion in John Locke's ''An Essay Concerning Human Understanding'': The third Branch may be called [''simeiotikí'', "semiotics"], or the Doctrine of Signs, the most usual whereof being words, it is aptly enough termed also , Logick. In 1831, the term is suggested for the third branch of division of knowledge akin to Locke; the "signs of our knowledge". In 1857, the term '' semasiology'' (borrowed from German ''Semasiologie'') is attested in Josiah W. Gibbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XML Schema (W3C)
XSD (XML Schema Definition), a recommendation of the World Wide Web Consortium ( W3C), specifies how to formally describe the elements in an Extensible Markup Language (XML) document. It can be used by programmers to verify each piece of item content in a document, to assure it adheres to the description of the element it is placed in. Like all XML schema languages, XSD can be used to express a set of rules to which an XML document must conform to be considered "valid" according to that schema. However, unlike most other schema languages, XSD was also designed with the intent that determination of a document's validity would produce a collection of information adhering to specific data types. Such a post-validation '' infoset'' can be useful in the development of XML document processing software. History XML Schema, published as a W3C recommendation in May 2001, is one of several XML schema languages. It was the first separate schema language for XML to achieve Recommendation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Architect
A data architect is a practitioner of data architecture, a data management discipline concerned with designing, creating, deploying and managing an organization's data architecture. Data architects define how the data will be stored, consumed, integrated and managed by different data entities and IT systems, as well as any applications using or processing that data in some way. It is closely allied with business architecture and is considered to be one of the four domains of enterprise architecture. Role According to the Data Management Body of Knowledge, the data architect “provides a standard common business vocabulary, expresses strategic data requirements, outlines high level integrated designs to meet these requirements, and aligns with enterprise strategy and related business architecture.” According to the Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF), a data architect is expected to set data architecture principles, create models of data that enable the implementation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
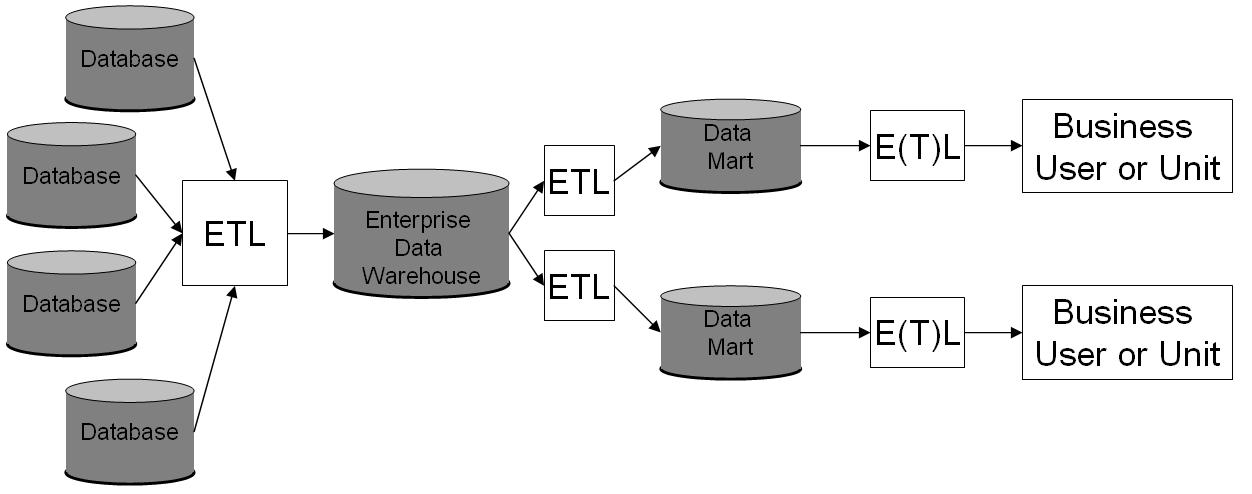
Data Warehousing
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. The data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the operational systems (such as marketing or sales). The data may pass through an operational data store and may require data cleansing for additional operations to ensure data quality before it is used in the DW for reporting. Extract, transform, load (ETL) and extract, load, transform (ELT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse system. ETL-based data warehousing The typical extract, transform, load (ETL)-based data warehouse uses staging, data integration, and access layers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Application Integration
Enterprise application integration (EAI) is the use of software and computer systems' architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications. Overview Enterprise application integration is an integration framework composed of a collection of technologies and services which form a middleware or "middleware framework" to enable integration of systems and applications across an enterprise. Many types of business software such as supply chain management applications, ERP systems, CRM applications for managing customers, business intelligence applications, payroll, and human resources systems typically cannot communicate with one another in order to share data or business rules. For this reason, such applications are sometimes referred to as islands of automation or information silos. This lack of communication leads to inefficiencies, wherein identical data are stored in multiple locations, or straightforward processes are unable to be automated. Enterpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertext Markup Language
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page semantically and originally included cues for the appearance of the document. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, images and other objects such as interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes, and other items. HTML elements are delineated by ''tags'', written using angle brackets. Tags such as and directly introduce content into the page. Other tags such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model-driven Architecture
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001."OMG pursues new strategic direction to build on success of past efforts" Overview Model Driven Architecture® (MDA®) "provides an approach for deriving value from models and architecture in support of the full life cycle of physical, organizational and I.T. systems". A model is a (representation of) an abstraction of a system. MDA® provides value by producing models ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata Publishing
Metadata publishing is the process of making metadata data elements available to external users, both people and machines using a formal review process and a commitment to change control processes. Metadata publishing is the foundation upon which advanced distributed computing functions are being built. But like building foundations, care must be taken in metadata publishing systems to ensure the structural integrity of the systems built on top of them. Definition of metadata publishing Published metadata has the following characteristics: # Metadata structures available to the general public on a public web site or by a download # There is a documented review and approval process for adding or updating data elements to the system # New releases are made available without disturbing prior versions # A publishing organization that makes a commitment to change control process Benefits of metadata publishing When classifying benefits of metadata publishing two groups are usually con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Equivalence
{{about, semantic equivalence of metadata, the concept in mathematical logic, Logical equivalence In computer metadata, semantic equivalence is a declaration that two data elements from different vocabularies contain data that has similar meaning. There are three types of semantic equivalence statements: * Class or concept equivalence. A statement that two high level concepts have similar or equivalent meaning. * Property or attribute equivalence. A statement that two properties, descriptors or attributes of classes have similar meaning. * Instance equivalence. A statement that two instances of data are the same or refer to the same instance. Example Assume that there are two organizations, each having a separate data dictionary. The first organization has a data element entry: PersonFamilyName The name of a person shared with other members of their family. and a second organization has a data dictionary with a data element with the following entry: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocabulary-based Transformation
In metadata, a vocabulary-based transformation (VBT) is a transformation aided by the use of a semantic equivalence statements within a controlled vocabulary. Many organizations today require communication between two or more computers. Although many standards exist to exchange data between computers such as HTML or email, there is still much structured information that needs to be exchanged between computers that is not standardized. The process of mapping one source of data into another is often a slow and labor-intensive process. VBT is a possible way to avoid much of the time and cost of manual data mapping using traditional extract, transform, load technologies. History The term ''vocabulary-based transformation'' was first defined by Roy Shulte of the Gartner Group around May 2003 and appeared in annual "hype-cycle" for integration. Application VBT allows computer systems integrators to more automatically "look up" the definitions of data elements in a centralize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |