|
Semantic Differential
The semantic differential (SD) is a measurement scale designed to measure a person's subjective perception of, and affective reactions to, the properties of concepts, objects, and events by making use of a set of bipolar scales. The SD is used to assess one's opinions, attitudes, and values regarding these concepts, objects, and events in a controlled and valid way. Respondents are asked to choose where their position lies, on a set of scales with polar adjectives (for example: "sweet - bitter", "fair - unfair", "warm - cold"). Compared to other measurement scaling techniques such as Likert scaling, the SD can be assumed to be relatively reliable, valid, and robust. The SD has been used in both a general and a more specific way. Charles E. Osgood's theory of the semantic differential exemplifies the more general attempt to measure the semantics, or meaning, of words, particularly adjectives, and their referent concepts. In fields such as marketing, psychology, sociology, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opinion
An opinion is a judgement, viewpoint, or statement that is not conclusive, as opposed to facts, which are true statements. Definition A given opinion may deal with subjective matters in which there is no conclusive finding, or it may deal with facts which are sought to be disputed by the logical fallacy that one is entitled to their opinions. Distinguishing fact from opinion is that facts are verifiable, i.e. can be agreed to by the consensus of experts. An example is: "United States of America was involved in the Vietnam War," versus "United States of America was right to get involved in the Vietnam War". An opinion may be supported by facts and principles, in which case it becomes an argument. Different people may draw opposing conclusions (opinions) even if they agree on the same set of facts. Opinions rarely change without new arguments being presented. It can be reasoned that one opinion is better supported by the facts than another, by analyzing the supporting ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Mercurio
(known online as ''El Mercurio On-Line'', ''EMOL'') is a Chilean newspaper with editions in Valparaíso and Santiago. is owned by El Mercurio S.A.P. (''Sociedad Anónima Periodística'' 'joint stock news company'), which operates a network of 19 regional dailies and 32 radio stations across the country. History The Valparaíso edition of was founded by Pedro Félix Vicuña ( Benjamín Vicuña Mackenna's father) on September 12, 1827, and was later acquired by Agustín Edwards Ross in 1880. The Santiago edition was founded by Agustín Edwards Mac Clure, son of Edwards Ross, on June 1, 1900. In 1942 Edwards Mac Clure died and his son Agustín Edwards Budge took over as president. When Edwards Budge died in 1956, his son, Agustín Edwards Eastman, took control of the company. Edwards Eastman died in 2017, leaving the company in hands of his son Cristián Edwards del Río. El Mercurio SAP owns the Chilean afternoon daily newspaper '' La Segunda'', which published news wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Similarity Network
A semantic similarity network (SSN) is a special form of semantic network. designed to represent concepts and their semantic similarity. Its main contribution is reducing the complexity of calculating semantic distances. Bendeck (2004, 2008) introduced the concept of ''semantic similarity networks'' (SSN) as the specialization of a semantic network to measure semantic similarity from ontological representations. Implementations include genetic information handling. The concept is formally defined (Bendeck 2008) as a directed graph, with concepts represented as Vertex (graph theory), nodes and semantic similarity relations as Graph (discrete mathematics), edges. The relationships are grouped into relation types. The concepts and relations contain attribute values to evaluate the semantic similarity between concepts. The semantic similarity relationships of the SSN represent several of the general relationship types of the standard Semantic network, reducing the complexity of the (n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Similarity
Semantic similarity is a metric defined over a set of documents or terms, where the idea of distance between items is based on the likeness of their meaning or semantic content as opposed to lexicographical similarity. These are mathematical tools used to estimate the strength of the semantic relationship between units of language, concepts or instances, through a numerical description obtained according to the comparison of information supporting their meaning or describing their nature. The term semantic similarity is often confused with semantic relatedness. Semantic relatedness includes any relation between two terms, while semantic similarity only includes "is a" relations. For example, "car" is similar to "bus", but is also related to "road" and "driving". Computationally, semantic similarity can be estimated by defining a topological similarity, by using ontologies to define the distance between terms/concepts. For example, a naive metric for the comparison of concepts ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Gap
The semantic gap characterizes the difference between two descriptions of an object by different linguistic representations, for instance languages or symbols. According to Andreas M. Hein, the semantic gap can be defined as "the difference in meaning between constructs formed within different representation systems". In computer science, the concept is relevant whenever ordinary human activities, observations, and tasks are transferred into a computational representation. More precisely the gap means the difference between ambiguous formulation of contextual knowledge in a powerful language (e.g. natural language) and its sound, reproducible and computational representation in a formal language (e.g. programming language). Semantics of an object depends on the context it is regarded within. For practical application this means any formal representation of real world tasks requires the translation of the contextual expert knowledge of an application (high-level) into the elementar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Componential Analysis
Componential analysis (feature analysis or contrast analysis) is the analysis of words through structured sets of semantic features, which are given as "present", "absent" or "indifferent with reference to feature". The method thus departs from the principle of compositionality. Componential analysis is a method typical of structural semantics which analyzes the components of a word's meaning. Thus, it reveals the culturally important features by which speakers of the language distinguish different words in a semantic field or domain (Ottenheimer, 2006, p. 20). Examples ''man'' = MALE MATUREor ''woman'' = �� MALE MATUREor ''boy'' = MALE �� MATUREor ''girl'' = �� MALE �� MATUREor ''child'' = /– MALE �� MATURE In other words, the word ''girl'' can have three basic factors (or semantic properties): human, young, and female. Another example, being edible is an important factor by which plants may be distinguished from one another (Ottenheimer, 2006, p. 20). To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Kahneman
Daniel Kahneman (; ; March 5, 1934 – March 27, 2024) was an Israeli-American psychologist best known for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences together with Vernon L. Smith. Kahneman's published empirical findings challenge the assumption of human rationality prevailing in modern economic theory. Kahneman became known as the "grandfather of behavioral economics." With Amos Tversky and others, Kahneman established a cognitive basis for common human errors that arise from heuristics and biases, and developed prospect theory. In 2011, Kahneman was named by ''Foreign Policy'' magazine in its list of top global thinkers. In the same year, his book '' Thinking, Fast and Slow'', which summarizes much of his research, was published and became a best seller. In 2015, ''The Economist'' listed him as the seventh most influential economist in the world. Kah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed variables mainly reflect the variations in two unobserved (underlying) variables. Factor analysis searches for such joint variations in response to unobserved latent variables. The observed variables are modelled as linear combinations of the potential factors plus "error" terms, hence factor analysis can be thought of as a special case of errors-in-variables models. Simply put, the factor loading of a variable quantifies the extent to which the variable is related to a given factor. A common rationale behind factor analytic methods is that the information gained about the interdependencies between observed variables can be used later to reduce the set of variables in a dataset. Factor analysis is commonly used in psychometrics, pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roget's Thesaurus
''Roget's Thesaurus'' is a widely used English-language thesaurus, created in 1805 by Peter Mark Roget (1779–1869), British physician, natural theologian and lexicographer. History It was released to the public on 29 April 1852. Roget was inspired by the Utilitarian teachings of Jeremy Bentham and wished to help "those who are painfully groping their way and struggling with the difficulties of composition this work processes to hold out a helping hand". The Karpeles Library Museum houses the original manuscript in its collection. Roget's schema of classes and their subdivisions is based on the philosophical work of Leibniz (see ), itself following a long tradition of epistemological work starting with Aristotle. Some of Aristotle's Categories are included in Roget's first class, "abstract relations". Content Roget described his thesaurus in the foreword to the first edition: ''Roget's Thesaurus'' is composed of six primary classes. Each class is composed of mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
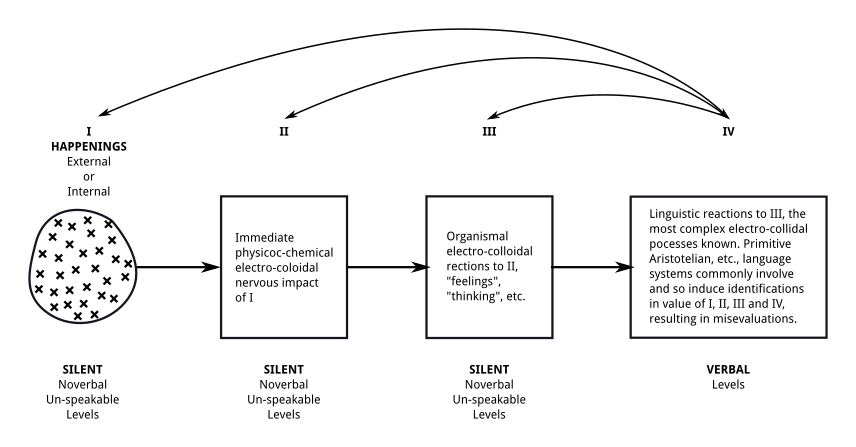
Structural Differential
The structural differential is a physical chart or three-dimensional model illustrating the abstracting processes of the human nervous system. In one form, it appears as a pegboard with tags. Created by Alfred Korzybski, and awarded a U.S. patent on May 26, 1925,US Patent 1,539,194 http://pdfpiw.uspto.gov/.piw?Docid=1539194 it is used as a training device in general semantics. The device is intended to show that human "knowledge" of, or acquaintance with, anything is partial—not total. The model The structural differential consists of three basic objects. The parabola represents a domain beyond our direct observation, the sub-microscopic, dynamic world of molecules, atoms, electrons, protons, quarks, and so on; a world known to us only inferentially from science. Korzybski described it as an 'event' in the sense of "an instantaneous cross-section of a process." Thus the 'event' or parabola represents the sub-microscopic 'stuff' that, at any given moment, constitutes an apple. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korzybski
Alfred Habdank Skarbek Korzybski (; ; July 3, 1879 – March 1, 1950) was a Polish-American philosopher and independent scholar who developed a field called general semantics, which he viewed as both distinct from, and more encompassing than, the field of semantics. He argued that human knowledge of the world is limited both by the human nervous system and the languages humans have developed, and thus no one can have direct access to reality, given that the most we can know is that which is filtered through the brain's responses to reality. His best known dictum is "Map–territory relation, The map is not the territory". Many of his ideas were presented in his book ''Science and Sanity'' (1933). Early life and career Born in Warsaw, Vistula Country, which was then part of the Russian Empire, Korzybski belonged to an aristocratic Polish family whose members had worked as mathematicians, scientists, and engineers for generations. He learned the Polish language at home and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Semantics
General semantics is a school of thought that incorporates philosophy, philosophic and science, scientific aspects. Although it does not stand on its own as a separate list of schools of philosophy, school of philosophy, a separate science, or an academic discipline, it describes itself as a scientifically empiricism, empirical approach to cognition and problem solving. It has been described by nonproponents as a self-help system, and it has been criticized as having pseudoscience, pseudoscientific aspects, but it has also been favorably viewed by various scientists as a useful set of analysis, analytical tools albeit not its own science. General semantics is concerned with how phenomenon, phenomena (observable events) translate to perceptions, how they are further modified by the names and labelling, labels we apply to them, and how we might gain a measure of control over our own cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses. Proponents characterize general semantics as an ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |