|
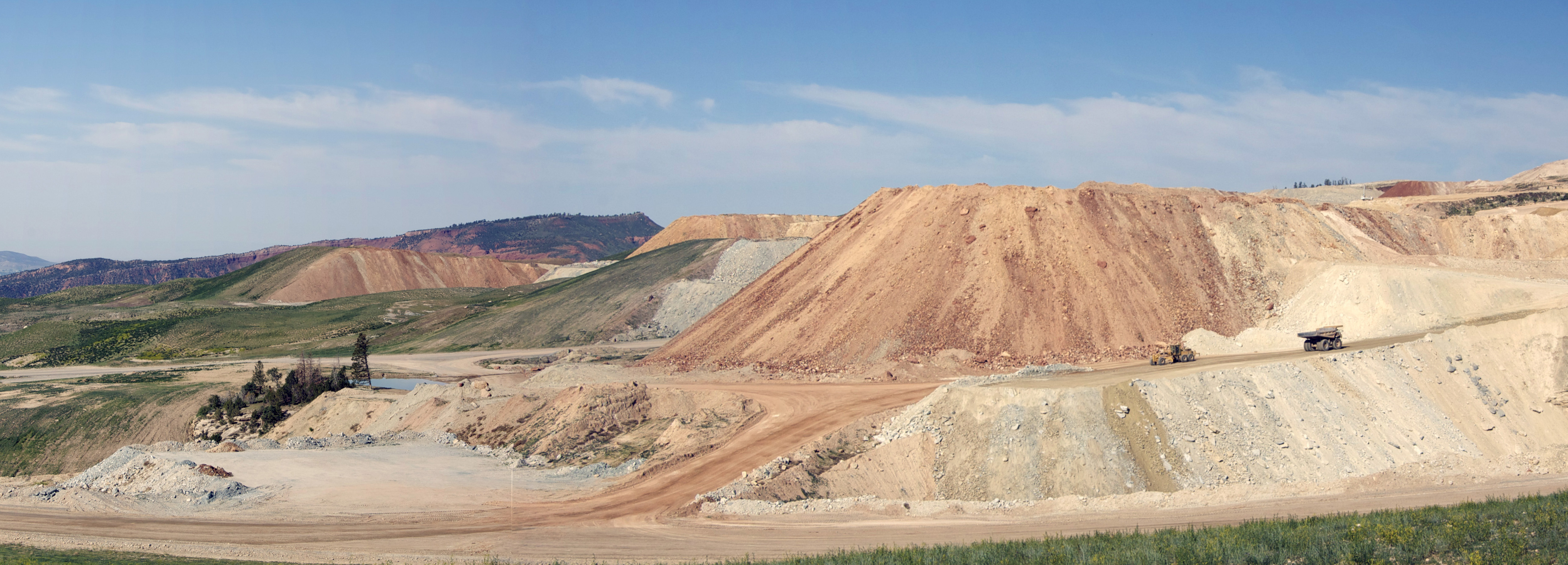
Selwyn, Queensland
Selwyn is a rural town and locality in the Shire of Cloncurry, Queensland, Australia. Selwyn is now an abandoned mining town. In the the locality of Selwyn had a population of 50 people. History Selwyn takes its name from the Selwyn Range, which was named in turn after Alfred Richard Cecil Selwyn, a geologist who was Director of the Geological Survey of Victoria from 1852 to 1869. It was formerly known as Mount Elliott after the prospector James Elliott who discovered copper and gold in the area in 1889. Mount Elliott Provisional School opened on 1908. On 1 January 1909 it became Mount Elliott State School. In 1912 it was renamed Selwyn State School. It closed circa 1936. On 15 December 1910 the Selwyn railway line opened to service the Hampden and Mount Elliott mines. It was a branch of the Great Northern Railway and ran south from Cloncurry to Selwyn. Selwyn's population peaked in 1918 with an estimated population of 1500 people with a hospital and four hotels. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
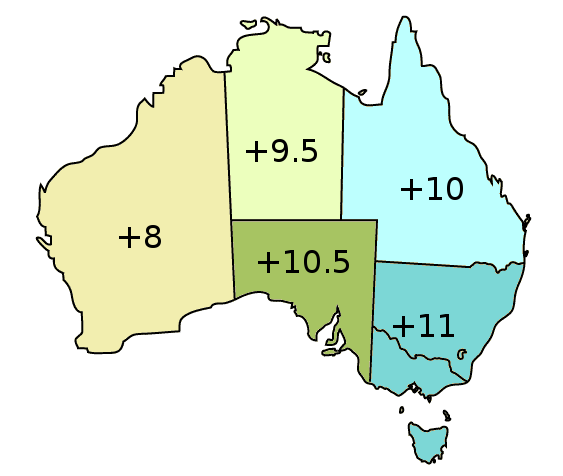
AEST
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Hill Railway Line
The Great Northern Railway is a railway line in Queensland, Australia. The line stretches nearly 1,000 kilometres linking the port city of Townsville, Australia to the mining town of Mount Isa in north-west Queensland. Along with a passenger service called the Inlander, it is a major freight route connecting the Mount Isa Mines to the Port of Townsville. In 2010 the line moved 5.8 million tonnes of cargo, and this is expected to increase significantly in coming years. History Originally approved in 1877, its construction over nearly thirty years along with the building of other lines in Queensland was dictated by the pressing need to transport minerals and wool from isolated inland areas to the coast for shipment. To the goldfields In Townsville’s case it was given impetus by the discovery of gold at Ravenswood, Queensland and Charters Towers, Queensland in 1868 and 1872 respectively. The first section of the railway opened on 20 December 1880 and followe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Hill Railway Station
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Hill Power Station
Phosphate Hill Power Station is located 150 km south of Mount Isa, Queensland, Australia. It is natural gas powered with six Solar Taurus 60 gas turbines and one Siemens steam turbine that generate a combined capacity of approx 30 MW of electricity. Emergency black start capacity is provided from 2 Caterpillar 3516 diesel generators. Phosphate Hill was commissioned in March 2000. See also *List of active power stations in Queensland This is a list of active power stations in Queensland, Australia. Candidates for this list must already be commissioned and capable of generating 1 MW or more of electricity. Queensland has a diverse range of power generating types. Coal fi ... References External linksClough Engineeringpress release on Phosphate Hill Natural gas-fired power stations in Queensland North West Queensland {{Queensland-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incitec Pivot
Incitec Pivot Ltd. () is an Australian multinational corporation that manufactures fertiliser, explosives chemicals, and mining service. Incitec Pivot is the largest supplier of fertilisers in Australia; the largest supplier of explosives products and services in North America; and the second largest supplier of explosives products and services in the world. The company began trading on the ASX on 30 July 2003 having been formed as the result of a merger between Incitec Fertilizers and the Pivot group, and substantially expanded with the acquisition of Southern Cross Fertilisers in 2006 and Dyno Nobel in 2008. Incitec Pivot has approximately 5,000 employees and operates in the United States, Canada, Mexico, and Australia. In 2005, the company struck a deal with the Government of Nauru to re-develop the country's phosphate mining industry, which had fallen into disrepair. The company invested $5 million to facilities and machinery, and phosphate mining resumed in late 2006. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Elliott Mining Complex
Mount Elliott Mining Complex is a heritage-listed copper mine and smelter at Selwyn, Shire of Cloncurry, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by William Henry Corbould and built in 1908. It is also known as Mount Elliott Smelter and Selwyn. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 16 September 2011. History The Mount Elliott Mining Complex is an aggregation of the remnants of copper mining and smelting operations from the early 20th century and the associated former mining township of Selwyn. The earliest copper mining at Mount Elliott was in 1906 with smelting operations commencing shortly after. Significant upgrades to the mining and smelting operations occurred under the management of W.H. Corbould during 1909-1910. Following these upgrades and increases in production, the Selwyn Township grew quickly and had 1500 residents by 1918. The Mount Elliott Company took over other companies on the Cloncurry field in the 1920s, including the Mount Cuthbert and Kuridal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage-listed
This list is of heritage registers, inventories of cultural properties, natural and man-made, tangible and intangible, movable and immovable, that are deemed to be of sufficient heritage value to be separately identified and recorded. In many instances the pages linked below have as their primary focus the registered assets rather than the registers themselves. Where a particular article or set of articles on a foreign-language Wikipedia provides fuller coverage, a link is provided. International *World Heritage Sites (see Lists of World Heritage Sites) – UNESCO, advised by the International Council on Monuments and Sites * Representative list of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity (UNESCO) * Memory of the World Programme (UNESCO) * Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) – Food and Agriculture Organization * UNESCO Biosphere Reserve * European Heritage Label (EHL) are European sites which are considered milestones in the creation of Europe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Family History Society
The Queensland Family History Society (QFHS) is an incorporated association formed in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. History The society was established in 1979 as a non-profit, non-sectarian, non-political organisation. They aim to promote the study of family history local history, genealogy, and heraldry, and encourage the collection and preservation of records relating to the history of Queensland ) , nickname = Sunshine State , image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_ ... families. At the end of 2022, the society relocated from 58 Bellevue Avenue, Gaythorne () to its new QFHS Family History Research Centre at 46 Delaware Street, Chermside (). References External links * Non-profit organisations based in Queensland Historical societies of Australia Libraries in Brisbane Fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern Railway, Queensland
The Great Northern Railway is a railway line in Queensland, Australia. The line stretches nearly 1,000 kilometres linking the port city of Townsville, Australia to the mining town of Mount Isa in north-west Queensland. Along with a passenger service called the Inlander, it is a major freight route connecting the Mount Isa Mines to the Port of Townsville. In 2010 the line moved 5.8 million tonnes of cargo, and this is expected to increase significantly in coming years. History Originally approved in 1877, its construction over nearly thirty years along with the building of other lines in Queensland was dictated by the pressing need to transport minerals and wool from isolated inland areas to the coast for shipment. To the goldfields In Townsville’s case it was given impetus by the discovery of gold at Ravenswood, Queensland and Charters Towers, Queensland in 1868 and 1872 respectively. The first section of the railway opened on 20 December 1880 and follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dajarra And Selwyn Railway Lines
Dajarra and Selwyn Branch Railways were lines in north-west Queensland, Australia. Along with the Mount Cuthbert and Dobbyn Branch Railways, they were essentially built to tap large deposits of copper discovered in the Cloncurry region. History Construction of the Selwyn Branch began in 1909. The line ran about 50 kilometres south from Cloncurry railway station () to Malbon railway station () with sidings built enroute at Dolomite (), Marimo (), Mitakoodi () and Marraba () From there it continued south to the Hampden mine and opened on 11 June 1910. The fledgling township was first named Gulatten, then Hampden, then for a brief time Friezland before finally being renamed in 1916 as Kuridala (an Aboriginal word indicating ''eagle hawk''). An extension further south to the Mount Elliott mine at Selwyn opened on 15 December 1910 (along with the Selwyn Range named after Alfred Selwyn, Director of the Geological Survey of Victoria). Smelted copper was railed east and coking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |