|
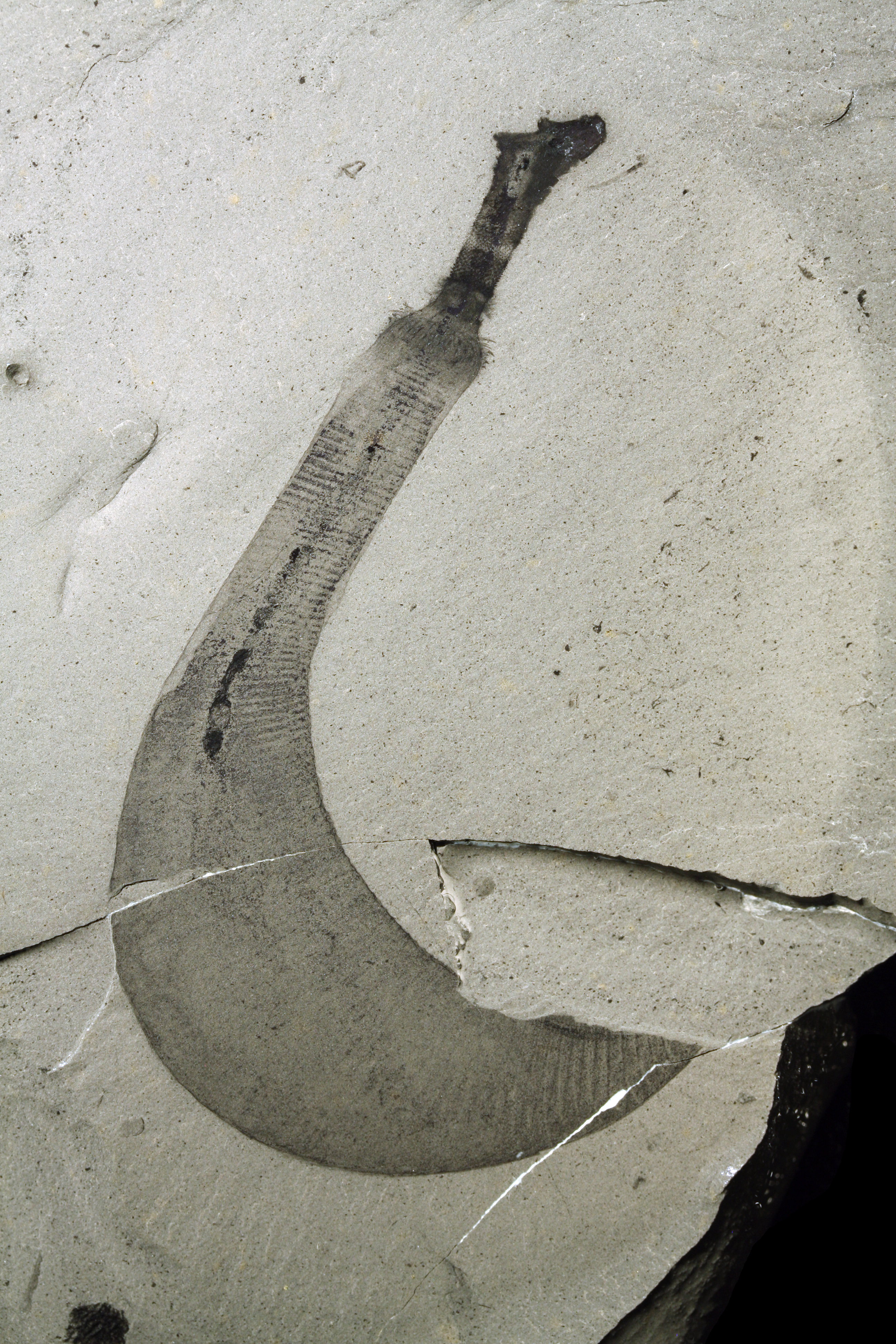
Selkirkia Trianae
''Selkirkia'' is a genus of predatory, tubicolous priapulid worms known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale, Ogygopsis Shale and Puncoviscana Formation. 142 specimens of ''Selkirkia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.27% of the community. In the Burgess Shale, 20% of the tapering, organic-walled tubes are preserved with the worm inside them, whereas the other 80% are empty (or sometimes occupied by one or more small agnostid trilobites). Whilst alive, the tubes were probably vertical, whereas trilobite-occupied tubes are horizontal. Morphology ''Selkirkia'' had a body divisible into a proboscis towards the anterior of a trunk enclosed by a tube. The proboscis would have been partially invertable and was armed with several spinules and spines, decreasing size distally overall. It was controlled by at least two sets of anterior retractor muscles. Immediately behind the proboscis was the trunk, smooth for the most part but lined with papillae tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
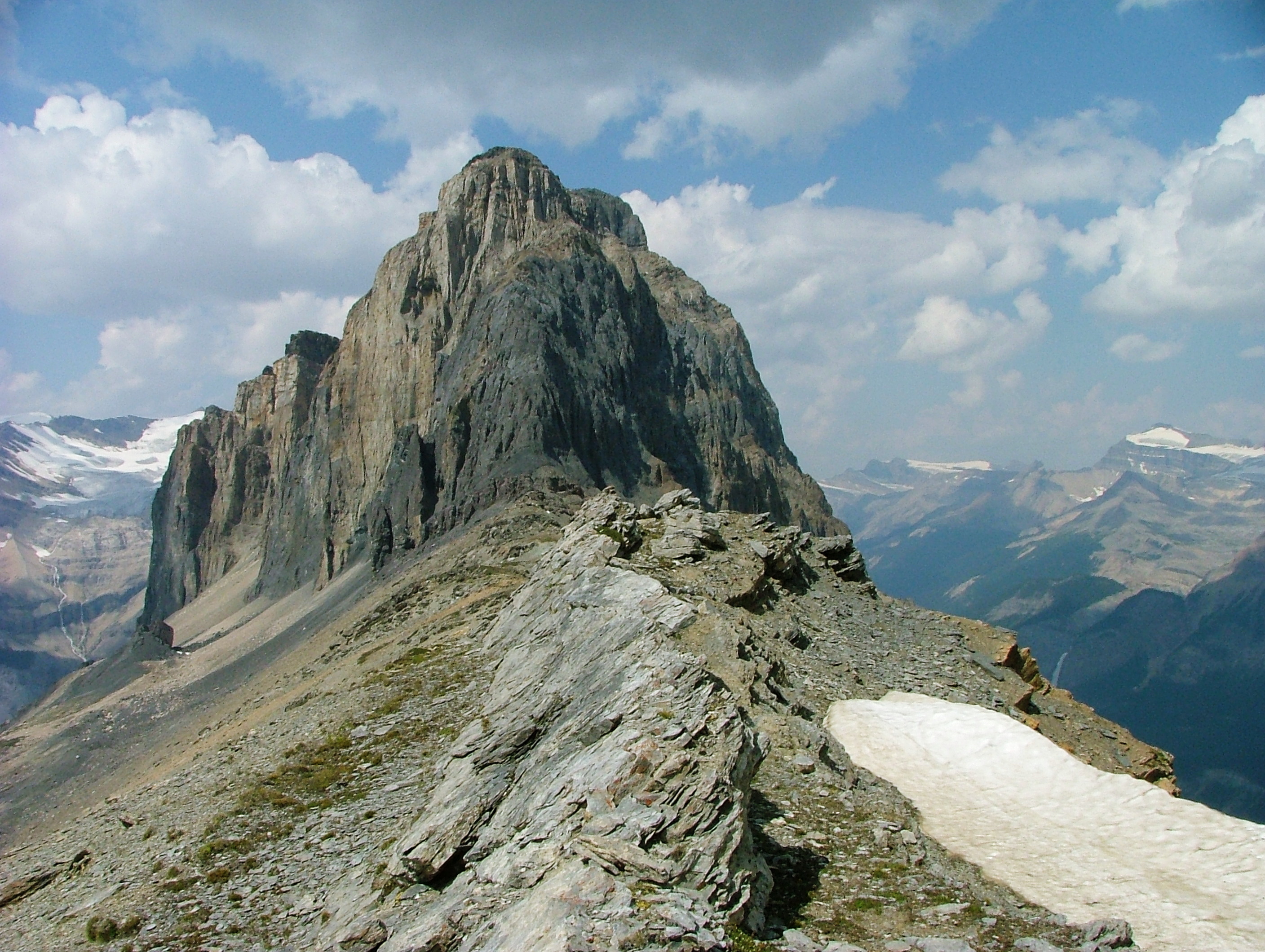
Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fossil beds containing soft-part imprints. The rock unit is a black shale and crops out at a number of localities near the town of Field in Yoho National Park Yoho National Park ( ) is a National Parks of Canada, national park of Canada. It is located within the Canadian Rockies, Rocky Mountains along the western slope of the Continental Divide of the Americas in southeastern British Columbia, bordered ... and the Kicking Horse Pass. Another outcrop is in Kootenay National Park 42 km to the south. History and significance The Burgess Shale was discovered by palaeontologist Charles Doolittle Walcott, Charles Walcott on 30 August 1909, towards the end of the season's fieldwork. He returned in 1910 with his sons, daughter, and wif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoart
Paleoart (also spelled palaeoart, paleo-art, or paleo art) is any original artistic work that attempts to depict prehistoric life according to scientific evidence. Works of paleoart may be representations of fossil remains or imagined depictions of the living creatures and their ecosystems. While paleoart is typically defined as being scientifically informed, it is often the basis of depictions of prehistoric animals in popular culture, which in turn influences public perception of and fuels interest in these animals. The word paleoart is also used in other informal sense, as a name for prehistoric art, most often cave paintings. Alternative concept of this term is the domain of archeological society. The term "paleoart"–which is a portmanteau of ''paleo'', the Ancient Greek word for "old", and "art"–was introduced in the late 1980s by Mark Hallett for art that depicts subjects related to paleontology, but is considered to have originated as a visual tradition in early 180 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priapulid
Priapulida (priapulid worms, from Gr. πριάπος, ''priāpos'' 'Priapus' + Lat. ''-ul-'', diminutive), sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertility, because their general shape and their extensible spiny introvert (eversible) proboscis may resemble the shape of a human penis. They live in the mud and in comparatively shallow waters up to deep. Some species show a remarkable tolerance for hydrogen sulfide and anoxia. They can be quite abundant in some areas. In an Alaskan bay as many as 85 adult individuals of ''Priapulus caudatus'' per square meter has been recorded, while the density of its larvae can be as high as 58,000 per square meter. Together with Echiura and Sipuncula, they were once placed in the taxon Gephyrea, but consistent morphological and molecular evidence supports their belonging to Ecdysozoa, which also includes arthropods and nematodes. Fossil findings show that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogygopsis Shale
''Ogygopsis'' is a genus of trilobite from the Cambrian of Antarctica and North America, specifically the Burgess Shale. It is the most common fossil in the Mt. Stephen fossil beds there, but rare in other Cambrian faunas. Its major characteristics are a prominent glabella with eye ridges, lack of pleural spines, a large spineless pygidium about as long as the thorax or cephalon, and its length: up to 12 cm.Coppold, Murray and Wayne Powell (2006). ''A Geoscience Guide to the Burgess Shale'', p. 56. The Burgess Shale Geoscience Foundation, Field, British Columbia. . Sources * ''Fossils'' (Smithsonian Handbooks) by David Ward (Page 64) ''Ogygopsis''in the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... External links * Corynexochida genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
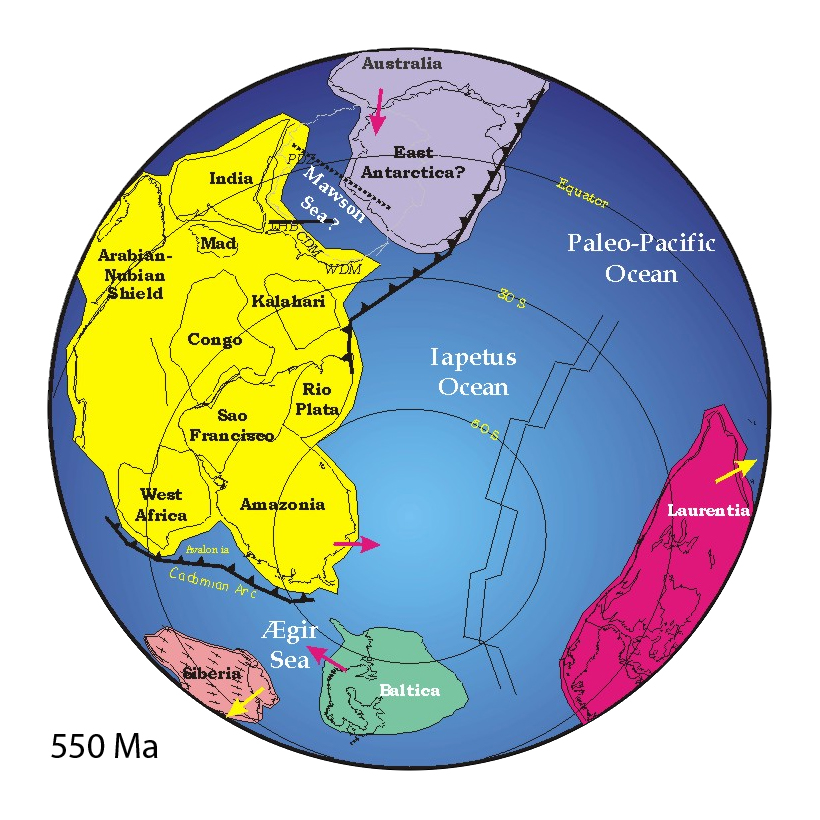
Puncoviscana Formation
Puncoviscana Formation ( es, Formación Puncoviscana) is a formation of sedimentary and metasedimentary rocks Late Ediacaran and Lower Cambrian age, estimated at between 700 and 535 Ma, that crop out in the Argentine Northwest. Most of the formation lies in Jujuy, Salta and Tucumán Province albeit some authors extend the formation further south to the Sierras Pampeanas near Córdoba. There are various tectonic interpretations on the origin and type of sedimentary basin that accumulated Puncoviscana Formations sediments. An early interpretation was that the sediments originated from a passive marginal basin of the ancient continent Gondwana. Others suggested an intra-cratonic rift or aulacogen basin between Río de la Plata-Pampia Craton and Arequipa Massif. Yet other hypotheses revolve around the idea that the Puncoviscana Formation is related to a terrane called Pampia that accreted to Gondwana causing the closure of a sea in the way. Stratigraphy, lithology and fossils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin American Journal Of Sedimentology And Basin Analysis
''Latin American Journal of Sedimentology and Basin Analysis'' (formerly ''Revista de la Asociación Argentina de Sedimentología'') is a biannual peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Asociación Argentina de Sedimentología. The journal covers the field of sedimentology and sedimentary basin Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subside ... analysis. External links * Geology journals Geology of South America Multilingual journals Open access journals Biannual journals Academic journals published by learned and professional societies of Argentina Publications established in 1994 {{geology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllopod Bed
The Phyllopod bed, designated by USNM locality number 35k, is the most famous fossil-bearing member of the Burgess Shale fossil ''Lagerstätte''. It was quarried by Charles Walcott from 1911–1917 (and later named Walcott Quarry), and was the source of 95% of the fossils he collected during this time; tens of thousands of soft-bodied fossils representing over 150 genera have been recovered from the Phyllopod bed alone. Stratigraphy and location The phyllopod bed is a 2.31 m thick layer of the 7 m thick Greater Phyllopod Bed, found in the Walcott Quarry on Fossil Ridge, between Wapta Mountain and Mount Field, at an elevation of around , around north of the railway town of Field, British Columbia, in the Canadian Rocky Mountains. It is adjacent to Mount Burgess, where Walcott first discovered the Burgess Shale formation. Walcott divided the bed into twelve units based on the rock type and fossil content. Certain fossil beds provide reference levels and can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnostid
Agnostidae is a family of Agnostida trilobites. Like all Agnostina, they were eyeless and bore only two thoracic segments. They ranged in benthic waters across the globe from 508 to 461 million years ago, containing the following genera, among others: *'' Acmarhachis'' *''Agnostus ''Agnostus'' is a genus of agnostid trilobites, belonging to the family Agnostidae, that lived during the late Middle Cambrian – early Upper Cambrian (about 506 to 492 million years ago). It is the type genus of the family Agnostidae and is sub ...'' *'' Aistagnostus'' *'' Anglagnostus'' *'' Biciragnostus'' *'' Connagnostus'' *'' Distagnostus'' *'' Eolotagnostus'' *'' Gymnagnostus'' *'' Homagnostus'' *'' Idolagnostus'' *'' Innitagnostus'' *'' Ivshinagnostus'' *'' Kymagnostus'' *'' Lotagnostus'' *'' Micragnostus'' *'' Obelagnostus'' *'' Oncagnostus'' *'' Peronopsis'' *'' Phalacroma'' *'' Phalagnostus'' *'' Quadrahomagnostus'' *'' Raragnostus'' *'' Semagnostus'' *'' Strictagnostus'' *'' Trilobagnostu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrorhytium
''Cambrorhytium'' is an enigmatic fossil genus known from the Latham Shale (California), and the Chengjiang (China) and Burgess Shale (Canadian rockies) lagerstätte. 350 specimens of ''Cambrorhytium'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.7% of the community. The fossil is conical, with iterated linear markings on its walls, parallel to its base. Its wall is thin, and it lacks the keel that is distinctive of hyoliths. It has been interpreted as a cnidarian polyp, with the interpretation suggesting that the animal lived in the tube and extended tentacles (of which no trace has been found) from the flat aperture. This is supported by similarities to Palaeoconotuba. The other possible, but probably unlikely, affinity is with the hyolith molluscs. Its name is from the Latin ''rhytium'', drinking horn. ''C. elongatum'' has been described to contain an alimentary canal in a single Chinese specimen. ''C. major'' was originally described as a member of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgess Shale Fossils
The fossils of the Burgess Shale, like the Burgess Shale itself, formed around 505 million years ago in the Mid Cambrian period. They were discovered in Canada in 1886, and Charles Doolittle Walcott collected over 65,000 specimens in a series of field trips up to the alpine site from 1909 to 1924. After a period of neglect from the 1930s to the early 1960s, new excavations and re-examinations of Walcott's collection continue to reveal new species, and statistical analysis suggests that additional discoveries will continue for the foreseeable future. Stephen Jay Gould's book '' Wonderful Life'' describes the history of discovery up to the early 1980s, although his analysis of the implications for evolution has been contested. The fossil beds are in a series of shale layers, averaging and totalling about in thickness. These layers were deposited against the face of a high undersea limestone cliff. All these features were later raised up above current sea level during the cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Protostome Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |