|
Self-healing
Self-healing refers to the process of recovery (generally from psychological disturbances, trauma, etc.), motivated by and directed by the patient, guided often only by instinct. Such a process encounters mixed fortunes due to its amateur nature, although self-motivation is a major asset. The value of self-healing lies in its ability to be tailored to the unique experience and requirements of the individual. The process can be helped and accelerated with introspection techniques such as Meditation. The different meanings of self-healing Self-healing is the ultimate phase of Gestalt Therapy. Self-healing may refer to automatic, homeostatic processes of the body that are controlled by physiological mechanisms inherent in the organism. Disorders of the spirit and the absence of faith can be self-healed. In a figurative sense, self-healing properties can be ascribed to systems or processes, which by nature or design tend to correct any disturbances brought into them. Such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Self-healing Material
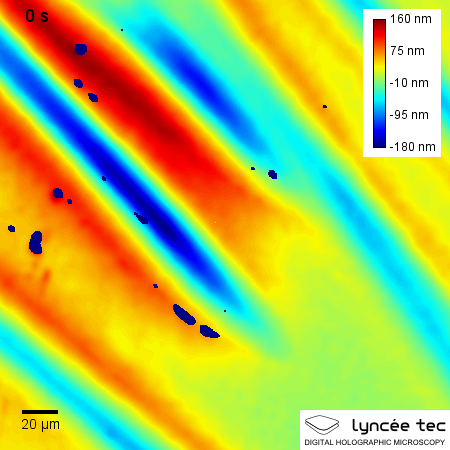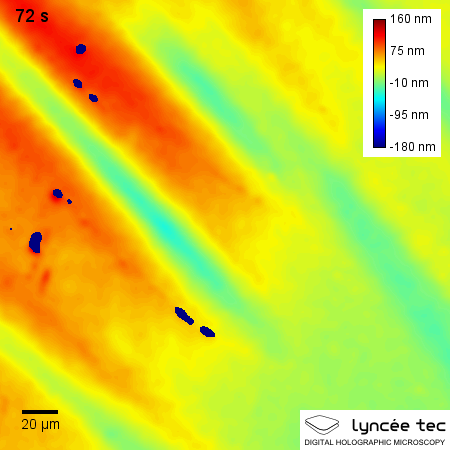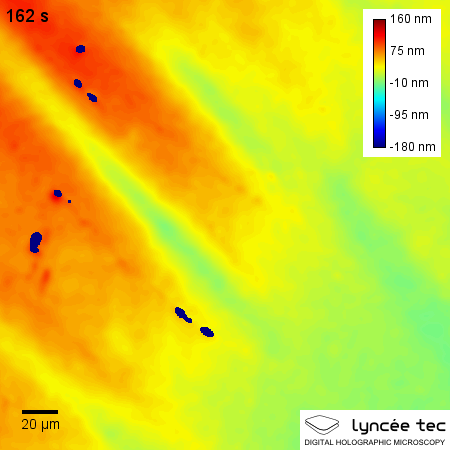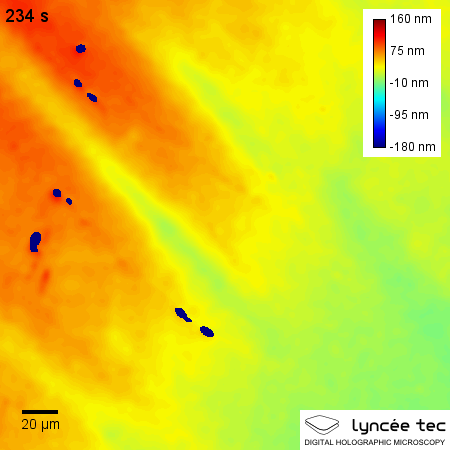
Self-healing materials are artificial or synthetically created substances that have the built-in ability to automatically repair damages to themselves without any external diagnosis of the problem or human intervention. Generally, materials will degrade over time due to fatigue, environmental conditions, or damage incurred during operation. Cracks and other types of damage on a microscopic level have been shown to change thermal, electrical, and acoustical properties of materials, and the propagation of cracks can lead to eventual failure of the material. In general, cracks are hard to detect at an early stage, and manual intervention is required for periodic inspections and repairs. In contrast, self-healing materials counter degradation through the initiation of a repair mechanism that responds to the micro-damage. Some self-healing materials are classed as smart structures, and can adapt to various environmental conditions according to their sensing and actuation properties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
T'ai Chi
Tai chi (), short for Tai chi ch'üan ( zh, s=太极拳, t=太極拳, first=t, p=Tàijíquán, labels=no), sometimes called " shadowboxing", is an internal Chinese martial art practiced for defense training, health benefits and meditation. Tai chi has practitioners worldwide from Asia to the Americas. Early practitioners such as Yang Chengfu and Sun Lutang promoted the art for its health benefits beginning in the early 20th century. Its global following may be attributed to overall benefit to personal health. Many forms are practiced, both traditional and modern. Most modern styles trace their development to the five traditional schools: Chen, Yang, Wu (Hao), Wu, and Sun. All trace their historical origins to Chen Village. Concepts ''Yin'' and ''Yang'' The concept of the ''taiji'' ("Supreme Ultimate"), in contrast with '' wuji'' ("without ultimate"), appears in both Taoist and Confucian philosophy, where it represents the fusion or mother of yin and yang into a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Self-help
Self-help or self-improvement is a self-guided improvement''APA Dictionary of Physicology'', 1st ed., Gary R. VandenBos, ed., Washington: American Psychological Association, 2007.—economically, intellectually, or emotionally—often with a substantial psychological basis. When engaged in self-help, people often use publicly available information or support groups, on the Internet as well as in person, where people in similar situations join together. From early examples in self-driven legal practiceSteve Salerno (2005) ''Sham: How the Self-Help Movement Made America Helpless'', pp. 24–25 and home-spun advice, the connotations of the word have spread and often apply particularly to education, business, psychology and psychotherapy, commonly distributed through the popular genre of self-help books. According to the ''APA Dictionary of Psychology'', potential benefits of self-help groups that professionals may not be able to provide include friendship, emotional support, experi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the natural and social sciences. Psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Fernald LD (2008)''Psychology: Six perspectives'' (pp.12–15). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. Ψ (''psi''), the first letter of the Greek word ''psyche'' from which the term psychology is derived (see below), is commonly associated with the science. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as behavioral or cognitive scientists. Some ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg) |
Psychological Stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a type of psychological pain. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the environment. Excessive amounts of stress, however, can increase the risk of strokes, heart attacks, ulcers, and mental illnesses such as depression and also aggravation of a pre-existing condition. Stress can be external and related to the environment, but may also be caused by internal perceptions that cause an individual to experience anxiety or other negative emotions surrounding a situation, such as pressure, discomfort, etc., which they then deem stressful. Hans Selye (1974) proposed four variations of stress. On one axis he locates good stress (eustress) and bad stress (distress). On the other is over-stress (hyperstress) and understress (hypostress). Selye advocates balancing these: the ultimate goal would be to balance hyperstress and hypostre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Concepts In Alternative Medicine
Concepts are defined as abstract ideas. They are understood to be the fundamental building blocks of the concept behind principles, thoughts and beliefs. They play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied by several disciplines, such as linguistics, psychology, and philosophy, and these disciplines are interested in the logical and psychological structure of concepts, and how they are put together to form thoughts and sentences. The study of concepts has served as an important flagship of an emerging interdisciplinary approach called cognitive science. In contemporary philosophy, there are at least three prevailing ways to understand what a concept is: * Concepts as mental representations, where concepts are entities that exist in the mind (mental objects) * Concepts as abilities, where concepts are abilities peculiar to cognitive agents (mental states) * Concepts as Fregean senses, where concepts are abstract objects, as opposed to mental obje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Orthopathy
Orthopathy (from the Greek ὀρθός ''orthos'' 'right' and πάθος ''pathos'' 'suffering') or natural hygiene (NH) is a set of alternative medical beliefs and practices originating from the ''Nature Cure'' movement. Proponents claim that fasting, dieting, and other lifestyle measures are all that is necessary to prevent and treat disease. Natural hygiene is an offshoot of naturopathy that advocates a philosophy of 'natural living' that was developed in the early nineteenth century. Natural hygienists oppose drugs, fluoridation, immunization, most medical treatments and endorse fasting, food combining and raw food or vegetarian diets. History and practice 19th century The orthopathy movement originated with Isaac Jennings in the 1820s, who practiced conventional medicine for many years but became discouraged with its results.Orcutt, Samuel; Beardsley, Ambrose (1880)''The History of the Old Town of Derby, Connecticut, 1642–1880. With Biographies and Genealogies'' Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Vis Medicatrix Naturae
''Vis medicatrix naturae'' (literally "the healing power of nature", and also known as ''natura medica'') is the Latin rendering of the Greek ''Νόσων φύσεις ἰητροί'' ("Nature is the physician(s) of diseases"), a phrase attributed to Hippocrates. While the phrase is not actually attested in his corpus, it nevertheless sums up one of the guiding principles of Hippocratic medicine, which is that organisms left alone can often heal themselves (''cf.'' the Hippocratic ''primum non nocere''). Hippocrates Hippocrates believed that an organism is not passive to injuries or disease, but rebalances itself to counteract them. The state of illness, therefore, is not a malady but an effort of the body to overcome a disturbed equilibrium. It is this capacity of organisms to correct imbalances that distinguishes them from non-living matter. From this follows the medical approach that “nature is the best physician” or “nature is the healer of disease”. To do this Hippocr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Twelve-step Program
Twelve-step programs are international mutual aid programs supporting recovery from substance addictions, behavioral addictions and compulsions. Developed in the 1930s, the first twelve-step program, Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), aided its membership to overcome alcoholism. Since that time dozens of other organizations have been derived from AA's approach to address problems as varied as drug addiction, compulsive gambling, sex, and overeating. All twelve-step programs utilize a version of AA's suggested twelve steps first published in the 1939 book '' Alcoholics Anonymous: The Story of How More Than One Hundred Men Have Recovered from Alcoholism.'' As summarized by the American Psychological Association (APA), the process involves the following: * admitting that one cannot control one's alcoholism, addiction, or compulsion; * coming to believe in a Higher Power that can give strength; * examining past errors with the help of a sponsor (experienced member); * making amends f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
New York (magazine)
''New York'' is an American biweekly magazine concerned with life, culture, politics, and style generally, and with a particular emphasis on New York City. Founded by Milton Glaser and Clay Felker in 1968 as a competitor to ''The New Yorker'', it was brasher and less polite, and established itself as a cradle of New Journalism. Over time, it became more national in scope, publishing many noteworthy articles on American culture by writers such as Tom Wolfe, Jimmy Breslin, Nora Ephron, John Heilemann, Frank Rich, and Rebecca Traister. In its 21st-century incarnation under editor-in-chief Adam Moss, "The nation's best and most-imitated city magazine is often not about the city—at least not in the overcrowded, traffic-clogged, five-boroughs sense", wrote then-'' Washington Post'' media critic Howard Kurtz, as the magazine increasingly published political and cultural stories of national significance. Since its redesign and relaunch in 2004, the magazine has won more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Kathryn Schulz
Kathryn Schulz is an American journalist and author. She is a staff writer at ''The New Yorker''. In 2016, she won the Pulitzer Prize for Feature Writing for her article on the risk of a major earthquake and tsunami in the Pacific Northwest. Biography Schulz was born in Shaker Heights, Ohio, to teacher Margot Schulz and lawyer Isaac Schulz. Her sister is the MIT cognitive scientist Laura Schulz. Schulz has described her family as "a fiercely intellectual family that is very interested in ideas." Schulz graduated from Shaker Heights High School in 1992. She matriculated at Brown University, graduating with a Bachelor of Arts in history in 1996. After graduation Schulz planned to take a year off before pursuing a Ph.D.; she lived in Portland, Oregon briefly before moving to Costa Rica with her sister's family. Seeking to remain in Latin America and use her Spanish, Schulz became an editor and reporter at '' The Santiago Times.'' Through the experience she "realized that erat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |