|
Selenium-76
Selenium (34Se) has six natural isotopes that occur in significant quantities, along with the trace isotope 79Se, which occurs in minute quantities in uranium ores. Five of these isotopes are stable: 74Se, 76Se, 77Se, 78Se, and 80Se. The last three also occur as fission products, along with 79Se, which has a half-life of 327,000 years,The half-life of 79Se and 82Se, which has a very long half-life (~1020 years, decaying via to 82Kr) and for practical purposes can be considered to be stable. There are 23 other unstable isotope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Beta Decay
In nuclear physics, double beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which two neutrons are simultaneously transformed into two protons, or vice versa, inside an atomic nucleus. As in single beta decay, this process allows the atom to move closer to the optimal ratio of protons and neutrons. As a result of this transformation, the nucleus emits two detectable beta particles, which are electrons or positrons. The literature distinguishes between two types of double beta decay: ''ordinary'' double beta decay and ''neutrinoless'' double beta decay. In ordinary double beta decay, which has been observed in several isotopes, two electrons and two electron antineutrinos are emitted from the decaying nucleus. In neutrinoless double beta decay, a hypothesized process that has never been observed, only electrons would be emitted. History The idea of double beta decay was first proposed by M. Goeppert-Mayer in 1935. In 1937, E. Majorana demonstrated that all results of beta decay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, and also has similarities to arsenic. It seldom occurs in its elemental state or as pure ore compounds in the Earth's crust. Selenium – from Greek ( 'Moon') – was discovered in 1817 by , who noted the similarity of the new element to the previously discovered tellurium (named for the Earth). Selenium is found in metal sulfide ores, where it partially replaces the sulfur. Commercially, selenium is produced as a byproduct in the refining of these ores, most often during production. Minerals that are pure selenide or selenate compounds are known but rare. The chief commercial uses for selenium today are glassmaking and pigments. Selenium is a semiconductor and is used in photocells. Applications in electronics, once important, have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
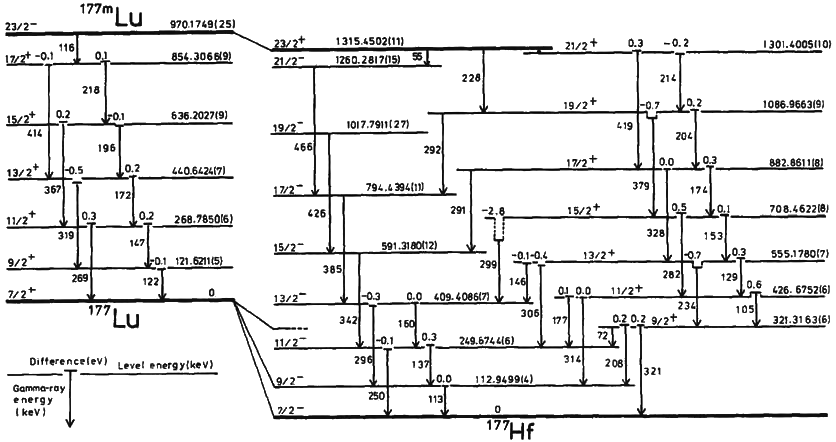
Isomeric Transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by as well as , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiopharmaceutical
Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents. The main group of these compounds are the radiotracers used to diagnose dysfunction in body tissues. While not all medical isotopes are radioactive, radiopharmaceuticals are the oldest and still most common such drugs. Drug nomenclature As with other pharmaceutical drugs, there is standardization of the drug nomenclature for radiopharmaceuticals, although various standards coexist. The International Nonproprietary Names (INNs), United States Pharmacopeia (USP) names, and IUPAC names for these agents are usually similar other than trivial style differences. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Emission
Neutron emission is a mode of radioactive decay in which one or more neutrons are ejected from a nucleus. It occurs in the most neutron-rich/proton-deficient nuclides, and also from excited states of other nuclides as in photoneutron emission and beta-delayed neutron emission. As only a neutron is lost by this process the number of protons remains unchanged, and an atom does not become an atom of a different element, but a different isotope of the same element. Neutrons are also produced in the spontaneous and induced fission of certain heavy nuclides. Spontaneous neutron emission As a consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, nuclei with an excess of protons or neutrons have a higher average energy per nucleon. Nuclei with a sufficient excess of neutrons have a greater energy than the combination of a free neutron and a nucleus with one less neutron, and therefore can decay by neutron emission. Nuclei which can decay by this process are described as lying beyond the neutron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radionuclide
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuclide the decay rate, and thus the half-life (''t''1/2) for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primordial Nuclide
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the interstellar medium from which the solar system was formed, and were formed in, or after, the Big Bang, by nucleosynthesis in stars and supernovae followed by mass ejection, by cosmic ray spallation, and potentially from other processes. They are the stable nuclides plus the long-lived fraction of radionuclides surviving in the primordial solar nebula through planet accretion until the present; 286 such nuclides are known. Stability All of the known 251 stable nuclides, plus another 35 nuclides that have half-lives long enough to have survived from the formation of the Earth, occur as primordial nuclides. These 35 primordial radionuclides represent isotopes of 28 separate elements. Cadmium, tellurium, xenon, neodymium, samarium, osmium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-lived Fission Product
Long-lived fission products (LLFPs) are radioactive materials with a long half-life (more than 200,000 years) produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium. Because of their persistent radiotoxicity it is necessary to isolate them from man and biosphere and to confine them in nuclear waste repositories for geological period of times. Evolution of radioactivity in nuclear waste Nuclear fission produces fission products, as well as actinides from nuclear fuel nuclei that capture neutrons but fail to fission, and activation products from neutron activation of reactor or environmental materials. Short-term The high short-term radioactivity of spent nuclear fuel is primarily from fission products with short half-life. The radioactivity in the fission product mixture is mostly short-lived isotopes such as 131I and 140Ba, after about four months 141Ce, 95Zr/95Nb and 89Sr take the largest share, while after about two or three years the largest share is taken by 144Ce/144Pr, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observationally Stable
Stable nuclides are nuclides that are not radioactive and so (unlike radionuclides) do not spontaneously undergo radioactive decay. When such nuclides are referred to in relation to specific elements, they are usually termed stable isotopes. The 80 elements with one or more stable isotopes comprise a total of 251 nuclides that have not been known to decay using current equipment (see list at the end of this article). Of these 80 elements, 26 have only one stable isotope; they are thus termed monoisotopic. The rest have more than one stable isotope. Tin has ten stable isotopes, the largest number of stable isotopes known for an element. Definition of stability, and naturally occurring nuclides Most naturally occurring nuclides are stable (about 251; see list at the end of this article), and about 34 more (total of 286) are known to be radioactive with sufficiently long half-lives (also known) to occur primordially. If the half-life of a nuclide is comparable to, or greater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is converted into a neutron by the emission of a positron with a neutrino in so-called ''positron emission''. Neither the beta particle nor its associated (anti-)neutrino exist within the nucleus prior to beta decay, but are created in the decay process. By this process, unstable atoms obtain a more stable ratio of protons to neutrons. The probability of a nuclide decaying due to beta and other forms of decay is determined by its nuclear binding energy. The binding energies of all existing nuclides form what is called the nuclear band or valley of stability. For either electron or positron em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. This process thereby changes a nuclear proton to a neutron and simultaneously causes the emission of an electron neutrino. : : or when written as a nuclear reaction equation, ^_e + ^_p -> ^_n + ^_ ν_e Since this single emitted neutrino carries the entire decay energy, it has this single characteristic energy. Similarly, the momentum of the neutrino emission causes the daughter atom to recoil with a single characteristic momentum. The resulting daughter nuclide, if it is in an excited state, then transitions to its ground state. Usually, a gamma ray is emitted during this transition, but nuclear de-excitation may also take place by internal conversion. Following capture of an inner electron from the atom, an outer electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |